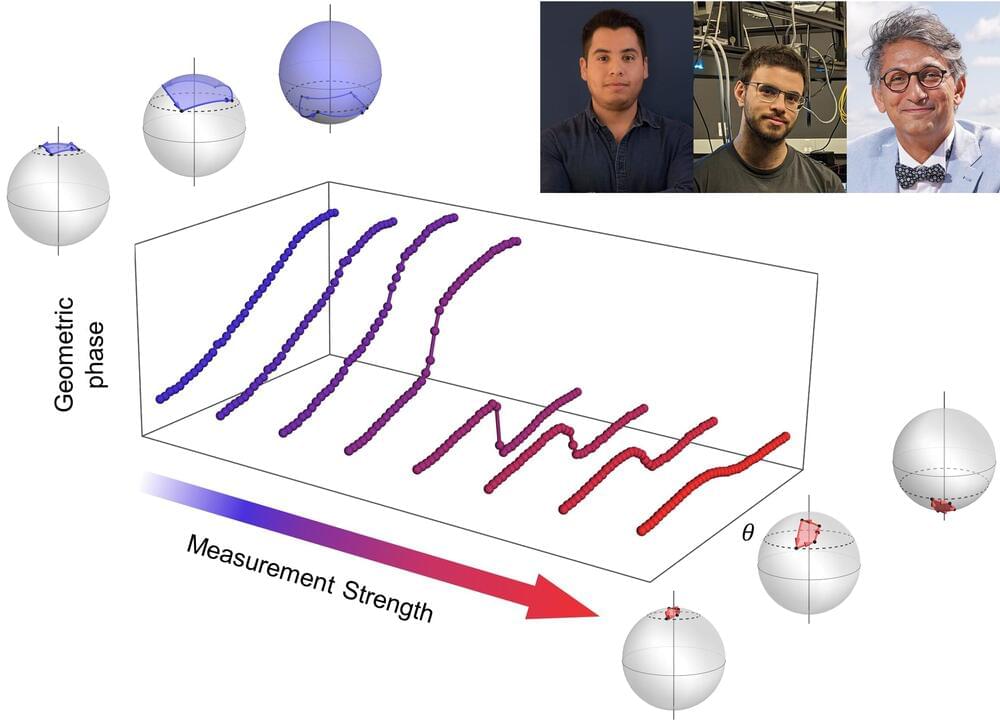
Researchers from the University of Ottawa (uOttawa), in collaboration with the Weizmann Institute of Science and Lancaster University, have observed a hidden quantum transition that can only be seen depending on how observers perform measurements.
The study “Topological Transitions of the generalized Pancharatnam-Berry phase” was published in Science Advances on 24 November 2023.
An essential part of the scientific method relies on the ability to measure the output of an experiment accurately and to juxtapose these findings with previous results. Scientists develop measurement devices, or meters, which enable them to precisely quantify the magnitude of physical properties. However, the “measurement process” raises a critical and intriguing question: does the process of measuring a parameter alter the system being measured?