Experiment with two superconducting cavities could lead to better quantum computers.
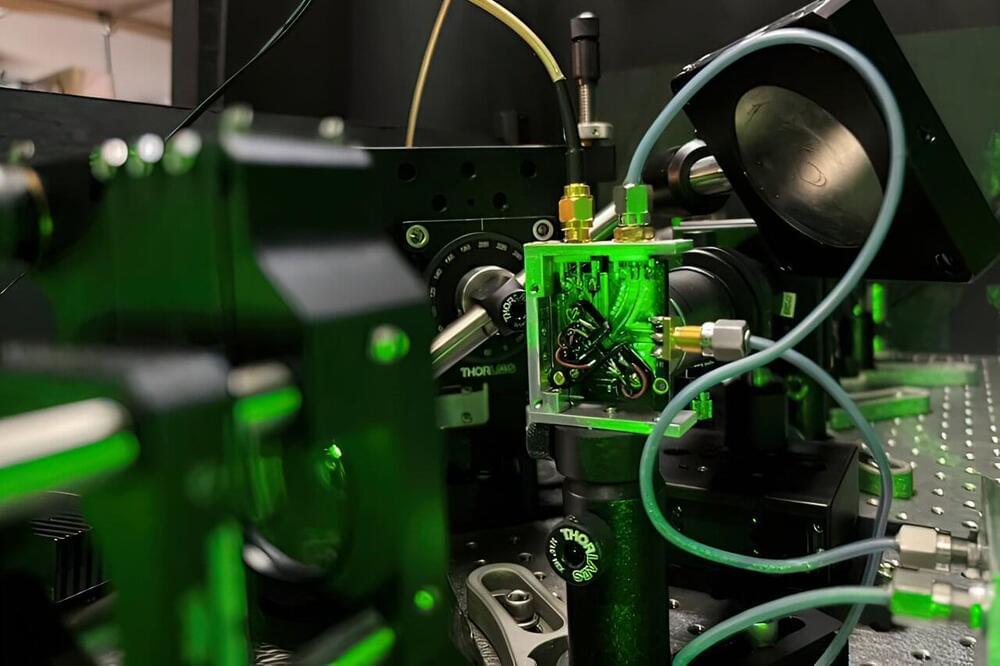
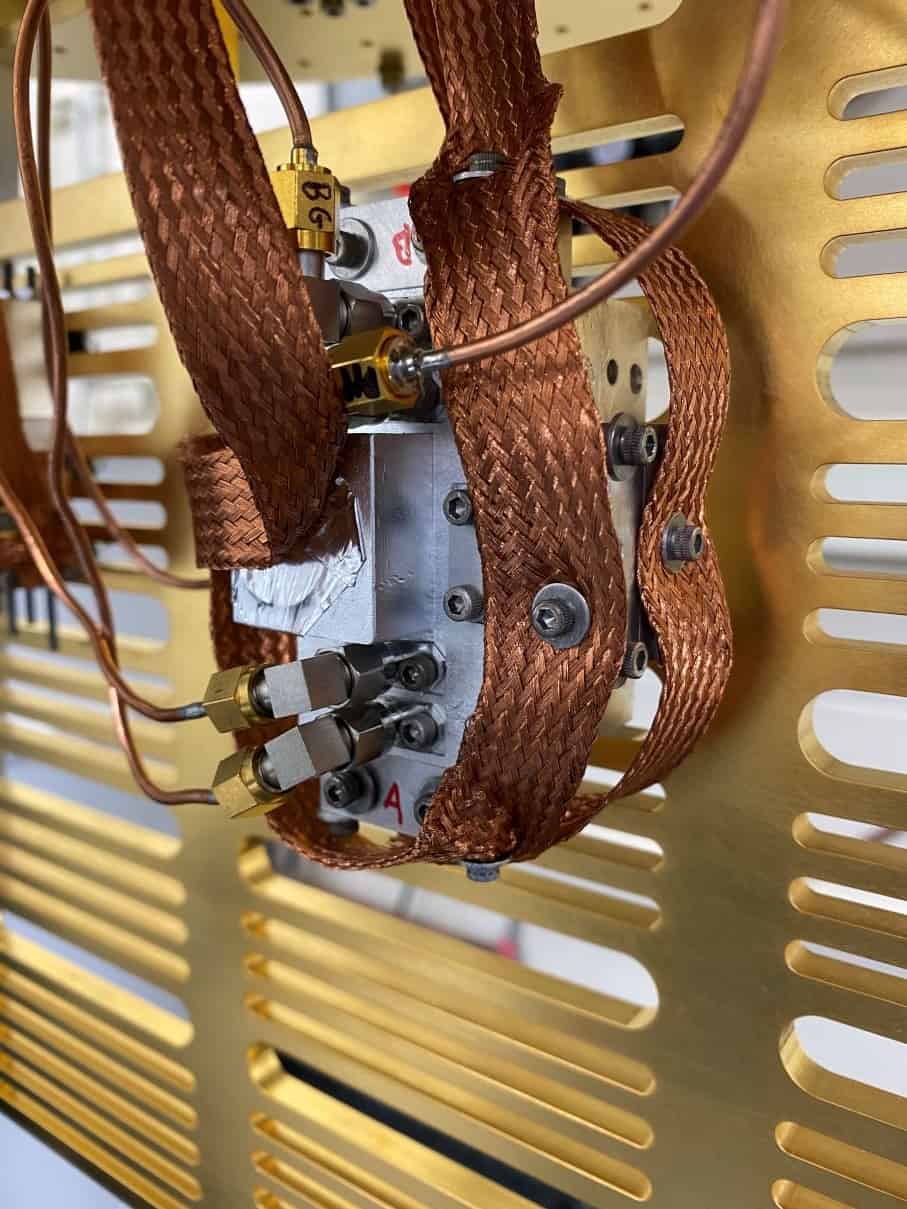


For years, researchers have tried various ways to coax quantum bits—or qubits, the basic building blocks of quantum computers—to remain in their quantum state for ever-longer times, a key step in creating devices like quantum sensors, gyroscopes, and memories.
A team of physicists from MIT have taken an important step forward in that quest, and to do it, they borrowed a concept from an unlikely source—noise-cancelling headphones.
Led by Ju Li, the Battelle Energy Alliance Professor in Nuclear Engineering and professor of materials science and engineering, and Paola Cappellaro, the Ford Professor of Engineering in the Department of Nuclear Science and Engineering and Research Laboratory of Electronics, and a professor of physics, the team described a method to achieve a 20-fold increase in the coherence times for nuclear-spin qubits.
Tiny dents on thin material produce photon-polarizing magnetic fields.
Researchers at Los Alamos National Laboratory have developed a technique that can produce polarized photons more easily and cheaply than existing methods. The technique.
Quantum communication uses photons to carry information, much as classical communication uses electrons. But while classical computers encode information by turning current… More.
Researchers at UC San Francisco and UC Berkeley have developed a brain-computer interface (BCI) that has enabled a woman with severe paralysis from a brainstem stroke to speak through a digital avatar.
It is the first time that either speech or facial expressions have been synthesized from brain signals. The system can also decode these signals into text at nearly 80 words per minute, a vast improvement over commercially available technology.
Dias didn’t disappoint. He and his colleagues had created a material — lutetium mixed with nitrogen and hydrogen, or LuNH — that was a superconductor at room temperature, he announced.
That claim, which the scientists published in Nature the next day1, would have been historic — if true. Superconductors conduct electricity with zero resistance, meaning that no energy is lost as heat. But they usually work only at very low temperatures, well below −100 °C, so need expensive refrigeration. This limits their use to niche applications, such as magnetic resonance imaging scans and quantum computing. A superconducting material that needs no cooling could potentially transform electricity generation and transmission, transportation and a slew of other applications.
Dias’s claim was remarkable not only for the material’s balmy operating temperature of 21 °C (294 K), but also because it required comparatively modest pressures. Other teams working with hydrogen compounds, called hydrides, have observed superconductivity at high temperatures, but had to squeeze their samples to hundreds of gigapascals (GPa) — millions of times more than atmospheric pressure. Dias, by contrast, said that his hydride needed just 1 GPa (10,000 times atmospheric pressure): still impractical for real-world applications, but a striking advance. A patent application for LuNH, released in April, goes further, claiming superconductivity at room temperature and pressure.
Scientists with the University of Chicago have demonstrated a way to create infrared light using colloidal quantum dots. The researchers said the method demonstrates great promise; the dots are already as efficient as existing conventional methods, even though the experiments are still in early stages.
The dots could someday form the basis of infrared lasers as well as small and cost-effective sensors, such as those used in exhaust emissions tests or breathalyzers.
“Right now the performance for these dots is close to existing commercial infrared light sources, and we have reason to believe we could significantly improve that,” said Philippe Guyot-Sionnest, a professor of physics and chemistry at the University of Chicago, member of the James Frank Institute, and one of three authors on the paper published in Nature Photonics. “We’re very excited for the possibilities.”
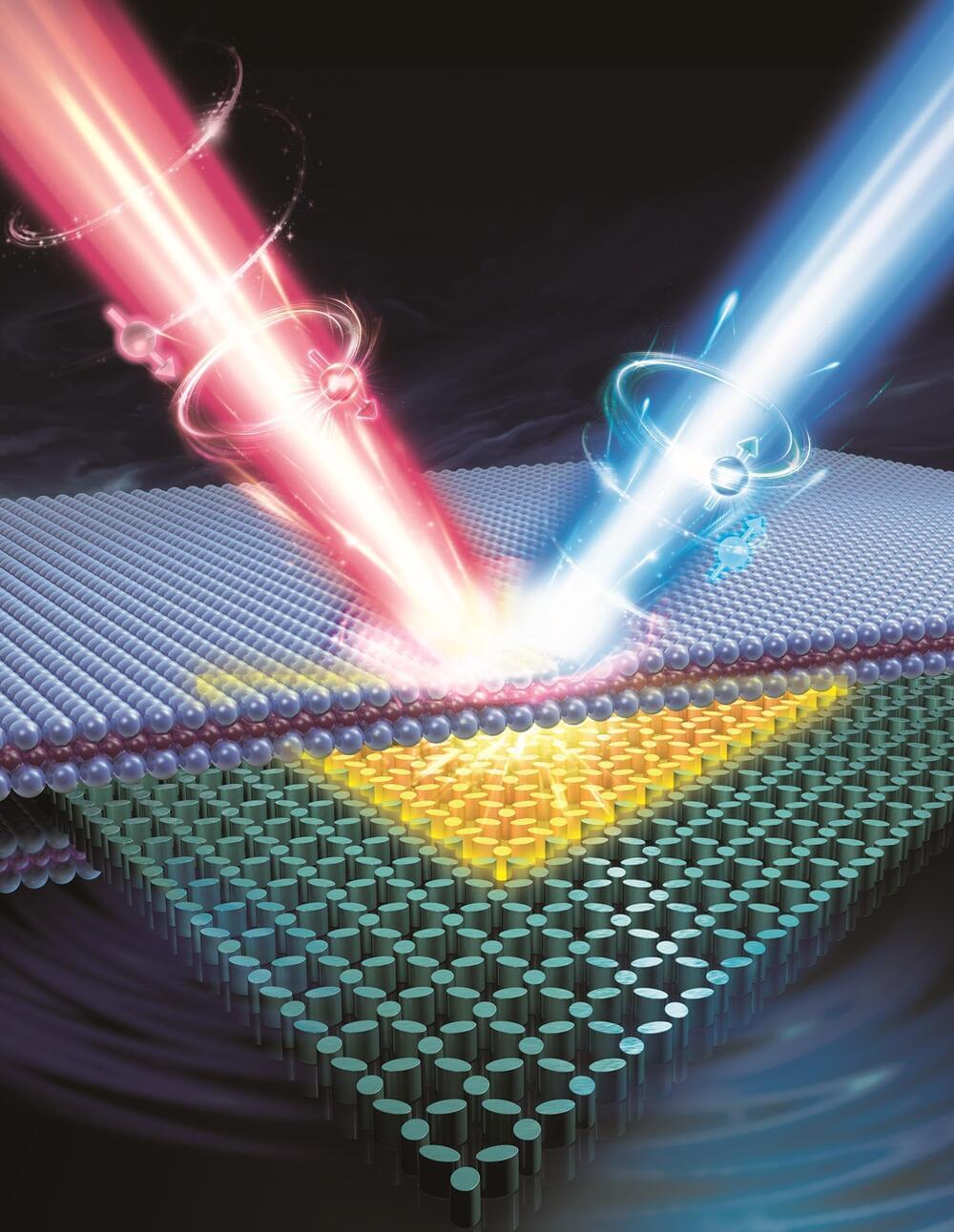
Researchers at the Technion—Israel Institute of Technology have developed a coherent and controllable spin-optical laser based on a single atomic layer. This discovery is enabled by coherent spin-dependent interactions between a single atomic layer and a laterally confined photonic spin lattice, the latter of which supports high-Q spin-valley states through the photonic Rashba-type spin splitting of a bound state in the continuum.
Published in Nature Materials and also featured in the journal’s Research Briefing, the achievement paves the way to study coherent spin-dependent phenomena in both classical and quantum regimes, opening new horizons in fundamental research and optoelectronic devices exploiting both electron and photon spins.
Can we lift the spin degeneracy of light sources in the absence of magnetic fields at room temperature? According to Dr. Rong, “Spin-optical light sources combine photonic modes and electronic transitions and therefore provide a way to study the exchange of spin information between electrons and photons and to develop advanced optoelectronic devices.”

Quantum computers, technologies that perform computations leveraging quantum mechanical phenomena, could eventually outperform classical computers on many complex computational and optimization problems. While some quantum computers have attained remarkable results on some tasks, their advantage over classical computers is yet to be conclusively and consistently demonstrated.
Ramis Movassagh, a researcher at Google Quantum AI, who was formerly at IBM Quantum, recently carried out a theoretical study aimed at mathematically demonstrating the notable advantages of quantum computers. His paper, published in Nature Physics, mathematically shows that simulating random quantum circuits and estimating their outputs is so-called #P-hard for classical computers (i.e., meaning that is highly difficult).
“A key question in the field of quantum computation is: Are quantum computers exponentially more powerful than classical ones?” Ramis Movassagh, who carried out the study, told Phys.org. “Quantum supremacy conjecture (which we renamed to Quantum Primacy conjecture) says yes. However, mathematically it’s been a major open problem to establish rigorously.”

Perovskite light-emitting diode is used as the light source for a quantum random number generator used in encryption.
Encryption plays an important role in protecting information in this digital era, and a random number generator plays a vital part in this by providing keys that are used to both encrypt and unlock the information at the receiving end.
Now, a team of researchers has made use of light-emitting diodes made from the crystal-like material perovskite to devise a new type of Quantum Random Number Generator (QRNG) that can be used for encryption but also for betting and computer simulations.
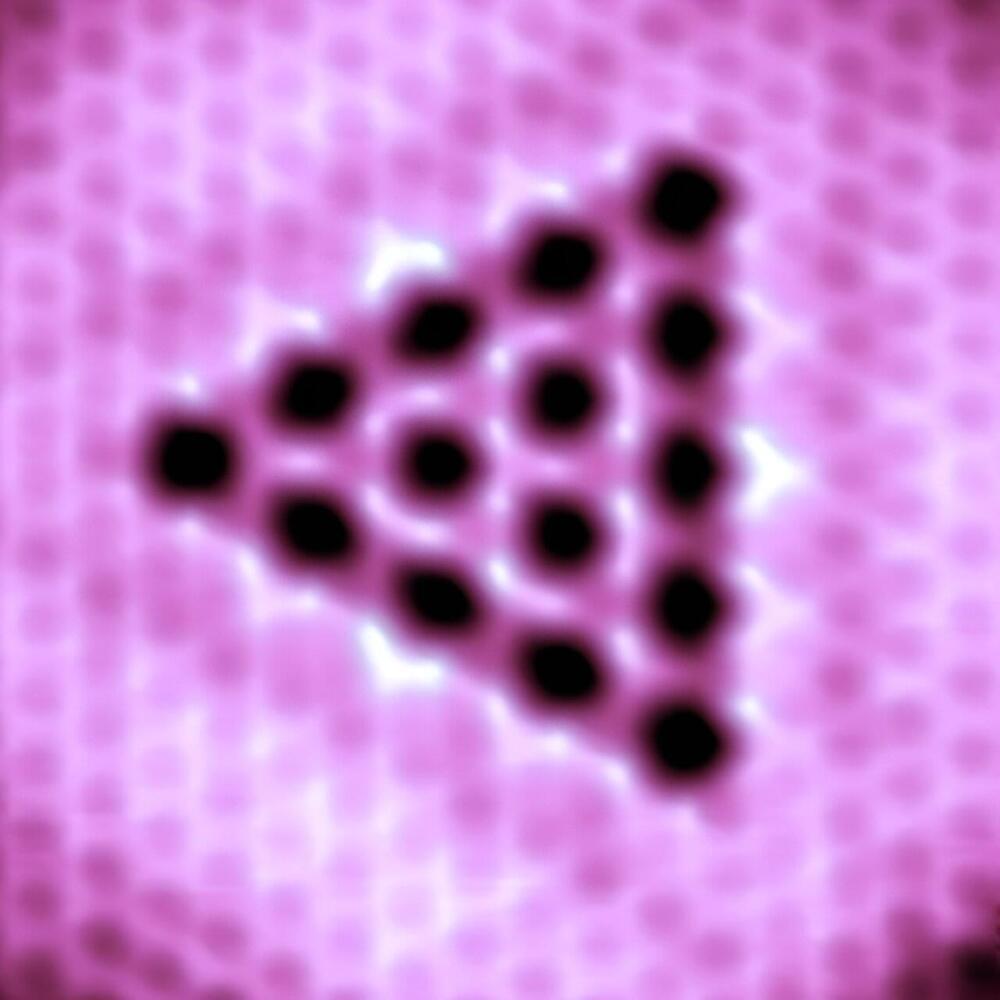
National University of Singapore (NUS) scientists demonstrated a conceptual breakthrough by fabricating atomically precise quantum antidots (QAD) using self-assembled single vacancies (SVs) in a two-dimensional (2D) transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD).
Quantum dots confine electrons on a nanoscale level. In contrast, an antidot refers to a region characterized by a potential hill that repels electrons. By strategically introducing antidot patterns (“voids”) into carefully designed antidot lattices, intriguing artificial structures emerge.
These structures exhibit periodic potential modulation to change 2D electron behavior, leading to novel transport properties and unique quantum phenomena. As the trend towards miniaturized devices continue, it is important to accurately control the size and spacing of each antidot at the atomic level. This control together with resilience to environmental perturbations is crucial to address technological challenges in nanoelectronics.