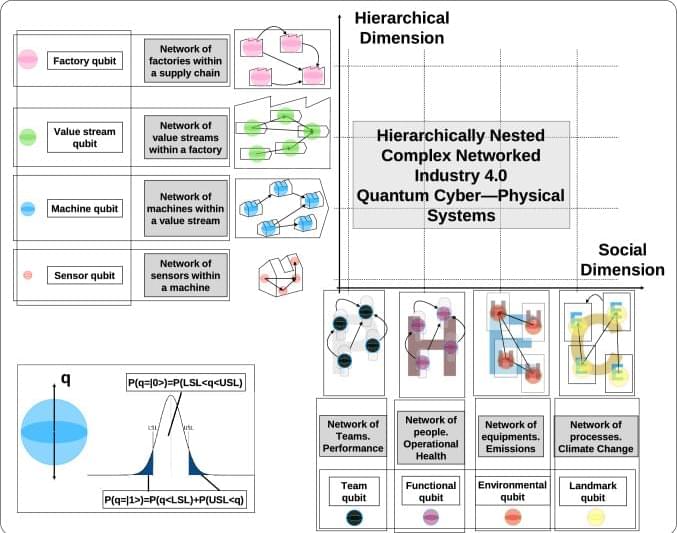
This paper aims to promote a quantum framework that analyzes Industry 4.0 cyber-physical systems more efficiently than traditional simulations used to represent integrated systems. The paper proposes a novel configuration of distributed quantum circuits in multilayered complex networks that enable the evaluation of industrial value creation chains. In particular, two different mechanisms for the integration of information between circuits operating at different layers are proposed, where their behavior is analyzed and compared with the classical conditional probability tables linked to the Bayesian networks. With the proposed method, both linear and nonlinear behaviors become possible while the complexity remains bounded. Applications in the case of Industry 4.0 are discussed when a component’s health is under consideration, where the effect of integration between different quantum cyber-physical digital twin models appears as a relevant implication.
Subject terms: Quantum simulation, Qubits.
Cyber-physical systems (CPS) are integrations of computational and physical components that can interact with humans through new and different modalities. A key to future technological development is precisely this new and different capacity of interaction together with the new possibilies that these systems pose for expanding the capabilities of the physical world through computation, communication and control1. When CPS are understood within the industrial practice fueled by additional technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT), people refer to the Industry 4.0 paradigm2. The design of many industrial engineering systems has been performed by separately considering the control system design from the hardware and/or software implementation details.