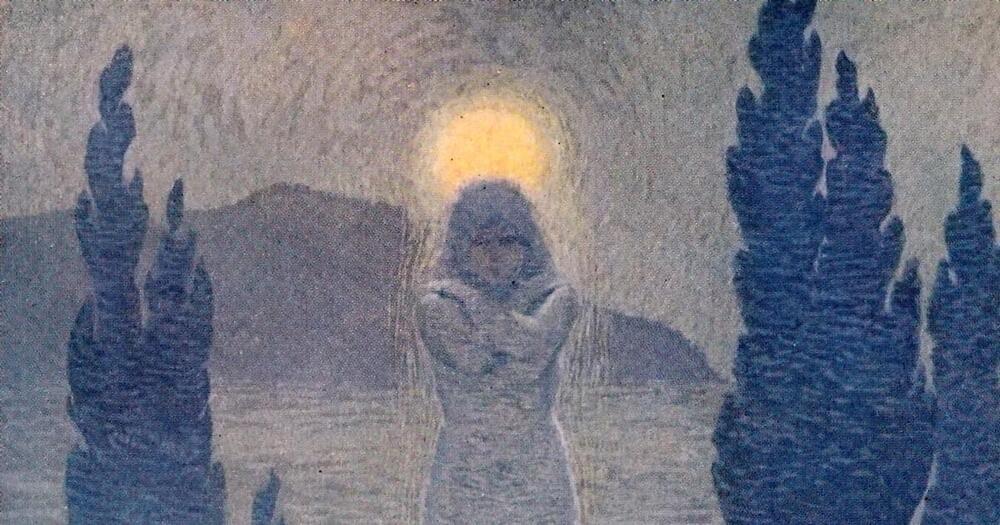
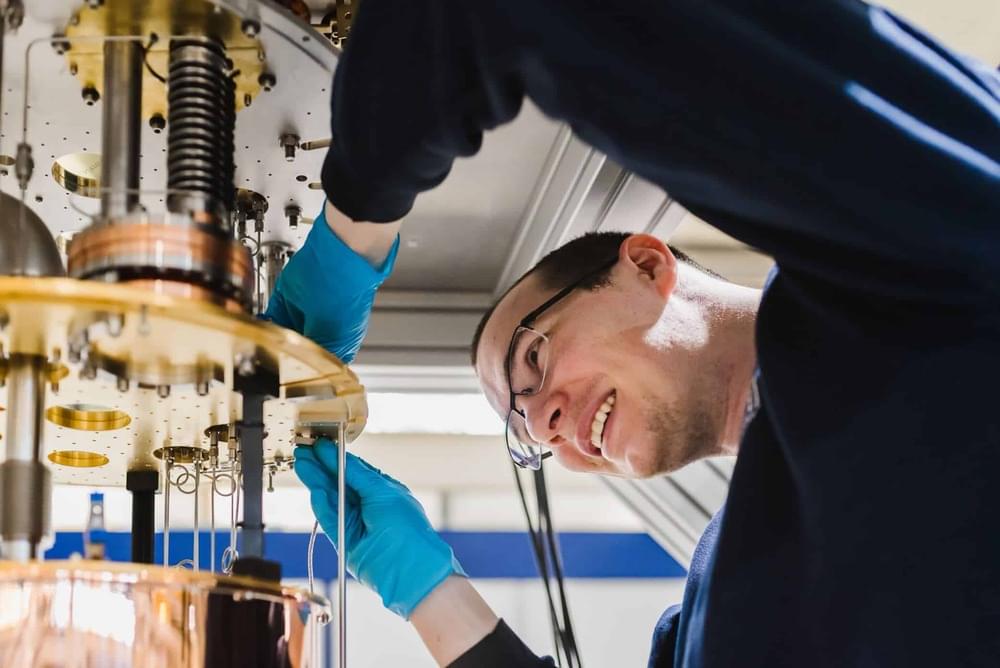
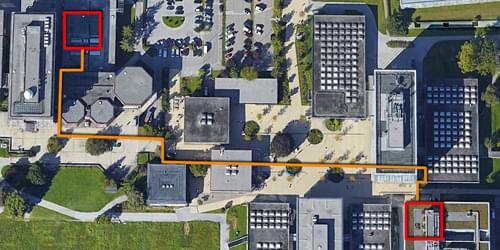
Researchers have achieved long-distance entanglement between two calcium ions, each of which lies in a different building, showing that trapped ions could be used to create quantum networks.
Among the many candidate platforms for quantum-information applications, trapped-ion qubits are promising because of their long coherence times and their potential for multiqubit operations (see Viewpoint: Trapped Ions Make Impeccable Qubits). Alone, those properties are insufficient for some quantum applications, however: to build quantum communication networks, for example, requires the qubits’ delicate quantum states be shared over long distances. Demonstrations of this ability have been lacking for trapped-ion systems. Now a team led by Benjamin Lanyon at the Institute for Quantum Optics and Quantum Information, Austria, and Tracy Northup at the University of Innsbruck, Austria, have addressed this shortfall by entangling two trapped-ion qubits residing in different buildings [1].
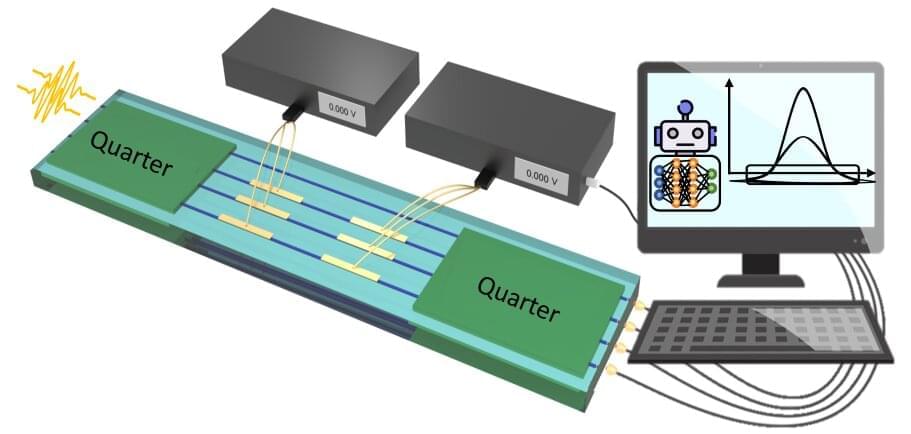
Lanyon, Northup, and colleagues used trapped-ion qubits inside optical cavities. For each qubit, they excited the ion using a dual-wavelength laser, prompting the ion to emit a single photon. The photon’s polarization depended on which of the two laser wavelengths the ion absorbed, entangling the photon with the ion’s final state. To entangle the two ions, the team then transmitted the photon from one ion through 510 m of optical fiber to a beam splitter near the other ion, where the two photons interacted. The researchers claimed successful entanglement when they subsequently detected a pair of photons with specific individual polarizations.