Researchers at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory’s Advanced Quantum Testbed (AQT) demonstrated that an experimental method known as randomized compiling (RC) can dramatically reduce error rates in quantum algorithms and lead to more accurate and stable quantum computations. No longer just a theoretical concept for quantum computing, the multidisciplinary team’s breakthrough experimental results are published in Physical Review X.
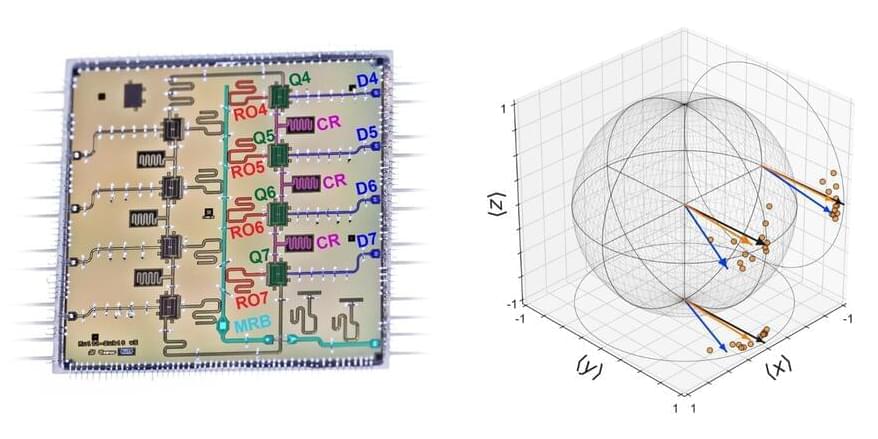
The experiments at AQT were performed on a four-qubit superconducting quantum processor. The researchers demonstrated that RC can suppress one of the most severe types of errors in quantum computers: coherent errors.
Akel Hashim, AQT researcher, involved in the experimental breakthrough and a graduate student at the University of California, Berkeley explained: “We can perform quantum computations in this era of noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) computing, but these are very noisy, prone to errors from many different sources, and don’t last very long due to the decoherence—that is, information loss—of our qubits.”