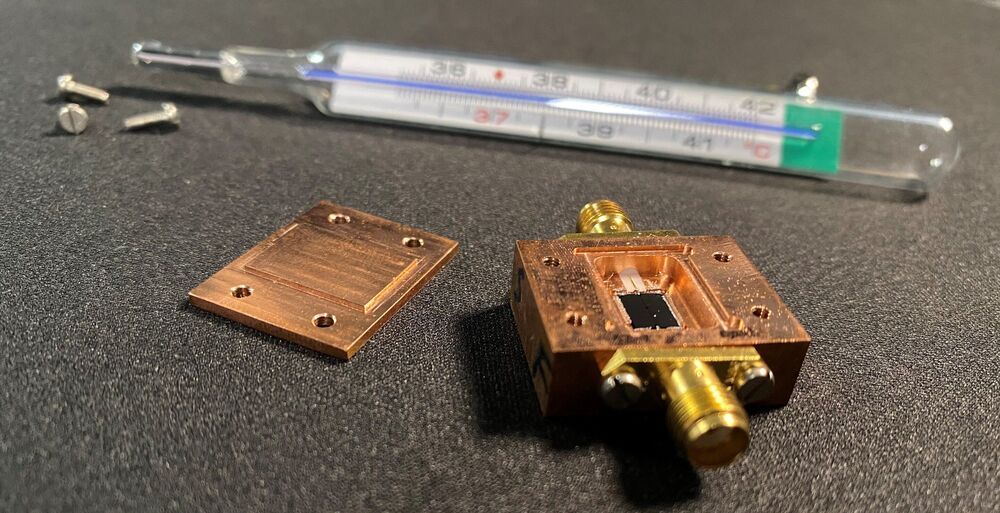
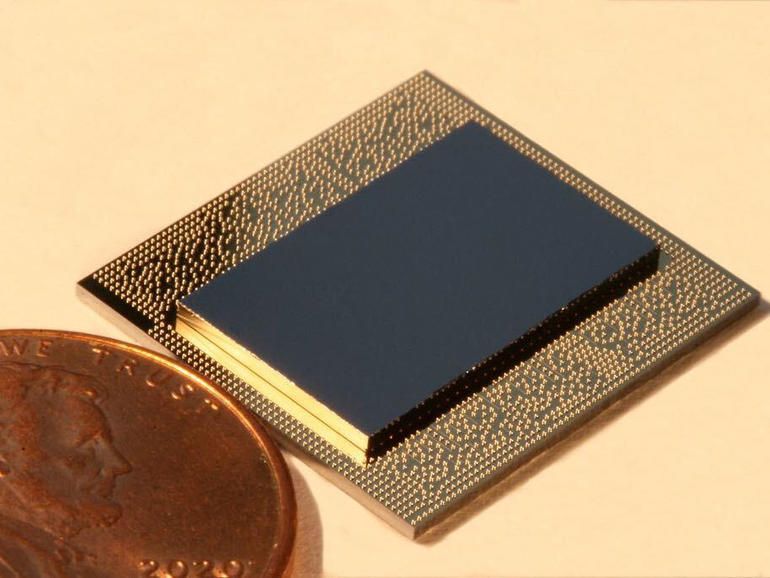
“Previously reported detection of plant biomagnetism, which established the existence of measurable magnetic activity in the plant kingdom, was carried out using superconducting-quantum-interference-device (SQUID) magnetometers1, 5, 16. Atomic magnetometers are arguably more attractive for biological applications, since, unlike SQUIDs34, 35, they are non-cryogenic and can be miniaturized to optimize spatial resolution of measured biological features14, 15, 36. In the future, the SNR of magnetic measurements in plants will benefit from optimizing the low-frequency stability and sensitivity of atomic magnetometers. Just as noninvasive magnetic techniques have become essential tools for medical diagnostics of the human brain and body, this noninvasive technique could also be useful in the future for crop-plant diagnostics—by measuring the electromagnetic response of plants facing such challenges as sudden temperature change, herbivore attack, and chemical exposure.”
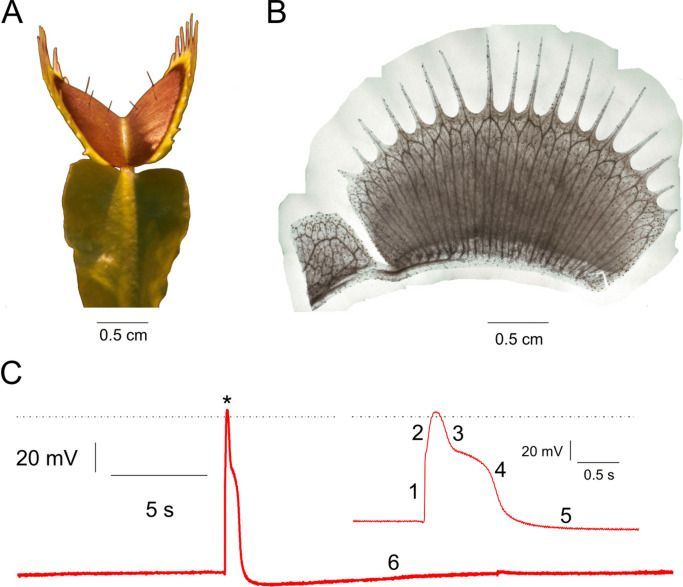
Upon stimulation, plants elicit electrical signals that can travel within a cellular network analogous to the animal nervous system. It is well-known that in the human brain, voltage changes in certain regions result from concerted electrical activity which, in the form of action potentials (APs), travels within nerve-cell arrays. Electro-and magnetophysiological techniques like electroencephalography, magnetoencephalography, and magnetic resonance imaging are used to record this activity and to diagnose disorders. Here we demonstrate that APs in a multicellular plant system produce measurable magnetic fields. Using atomic optically pumped magnetometers, biomagnetism associated with electrical activity in the carnivorous Venus flytrap, Dionaea muscipula, was recorded. Action potentials were induced by heat stimulation and detected both electrically and magnetically.