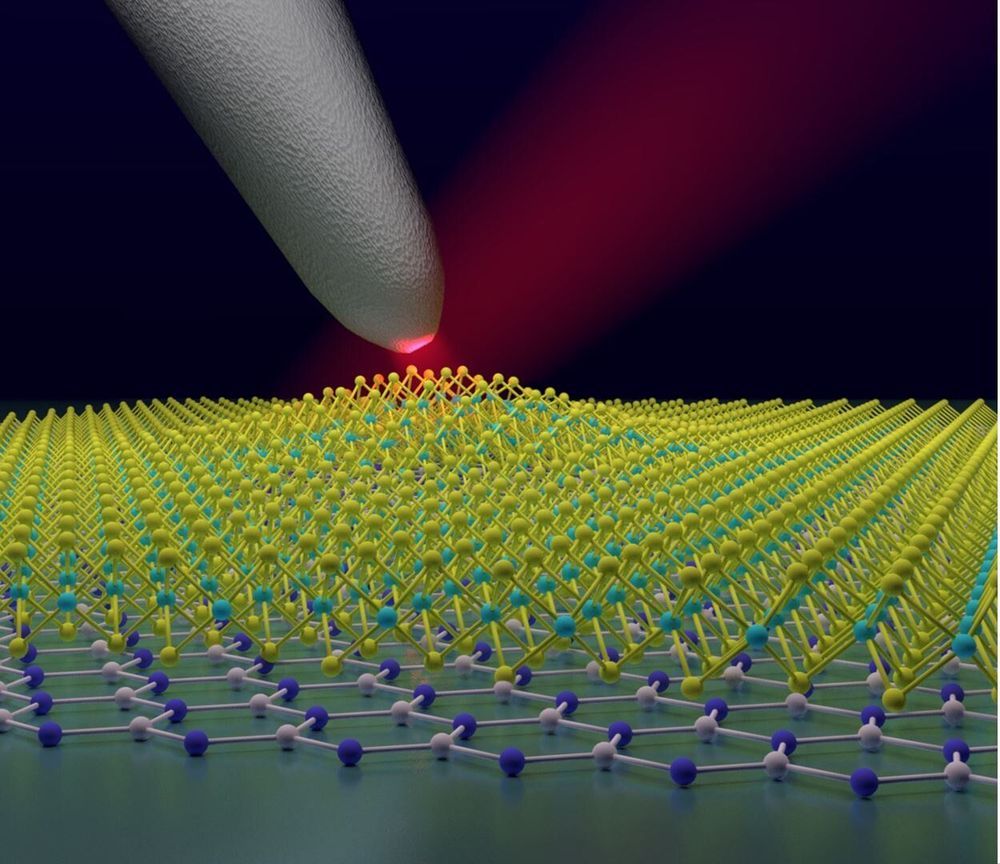
Evidence has emerged for long-proposed, but previously unconfirmed quasiparticles called anyons. The concept of anyons goes back 43 years, and physicists have found evidence collections of particles are behaving as anyons for some time, but have lacked confirmation. Now, within months of each other, two teams have found different methods to verify that this is what they are dealing with that look much more conclusive.
The universe’s particles are divided into two sorts; fermions and bosons. Fermions, including the components of atoms, cannot occupy the same quantum state as each other while bosons, which include photons of light, have no such problem.
Anyone who has spent much time around physicists will not be surprised to learn that many have wondered if there could be something else. For some, the so-called “particle zoo” is never sufficiently weird and wonderful. This led to the proposal of anyons, which can only exist in two-dimensional space.