How can gravity and the quantum world be unified? What are the different string theories? And what is \.
Category: quantum physics – Page 8
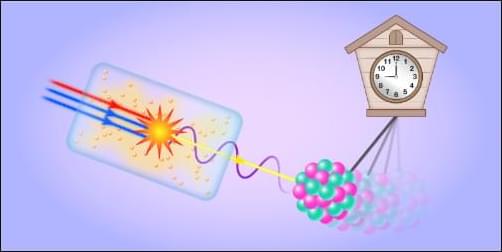
A Laser Built for Nuclear Timekeeping
Researchers have designed and demonstrated an ultraviolet laser that removes a major bottleneck in the development of a nuclear clock.
Whereas ordinary atomic clocks keep time using transitions of electrons in atoms, a prospective nuclear clock would harness a transition between states of the nucleus. Compared with electronic transitions, nuclear ones are much less sensitive to environmental disturbances, which would potentially give nuclear clocks unprecedented precision and stability. Such devices could improve GPS systems and enable more sensitive probes of fundamental physics. The main hurdle has been that nuclear transitions are extremely difficult to drive controllably using existing laser technology. Now Qi Xiao at Tsinghua University in China and colleagues have proposed and realized an intense single-frequency ultraviolet laser that can achieve such driving for thorium-229 nuclei [1, 2]. Beyond timekeeping, the team’s laser platform could find uses across quantum information science, condensed-matter physics, and high-resolution spectroscopy.
For most nuclear transitions, the energy difference between the two states lies in the kilo-electron-volt to mega-electron-volt range. Consequently, such transitions are inaccessible to today’s high-precision lasers, which can deliver photons of typically a few electron volts in energy. A long-known exception is the transition between the ground state and first excited state of thorium-229 nuclei. Indirect measurements over the past 50 years have gradually pinned down that transition’s energy difference to only about 8.4 eV. As a result, this transition is being actively investigated as a candidate for developing a nuclear clock.
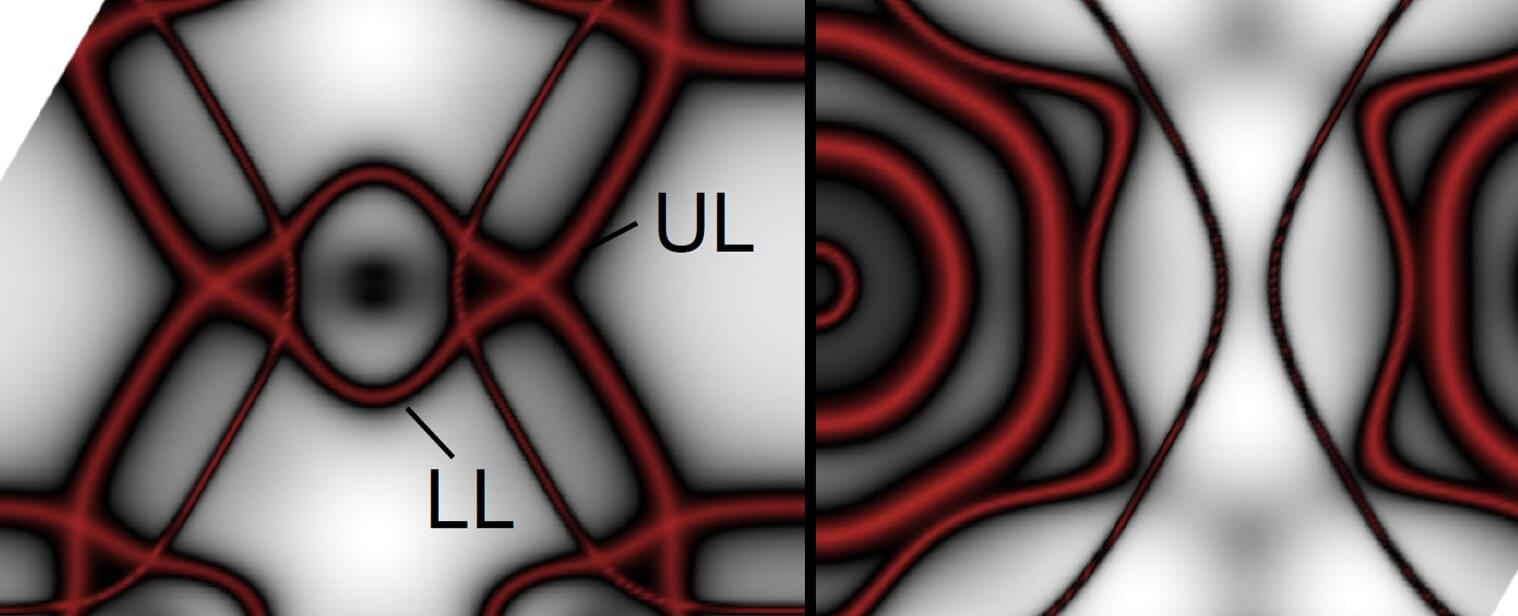
A familiar magnet gets stranger: Why cobalt’s topological states could matter for spintronics
The element cobalt is considered a typical ferromagnet with no further secrets. However, an international team led by HZB researcher Dr. Jaime Sánchez-Barriga has now uncovered complex topological features in its electronic structure. Spin-resolved measurements of the band structure (spin-ARPES) at BESSY II revealed entangled energy bands that cross each other along extended paths in specific crystallographic directions, even at room temperature. As a result, cobalt can be considered as a highly tunable and unexpectedly rich topological platform, opening new perspectives for exploiting magnetic topological states in future information technologies.
The findings are published in the journal Communications Materials.
Cobalt is an elementary ferromagnet, and its properties and crystal structure have long been known. However, an international team has now discovered that cobalt hosts an unexpectedly rich topological electronic structure that remains robust at room temperature, revealing a surprising new level of quantum complexity in this material.
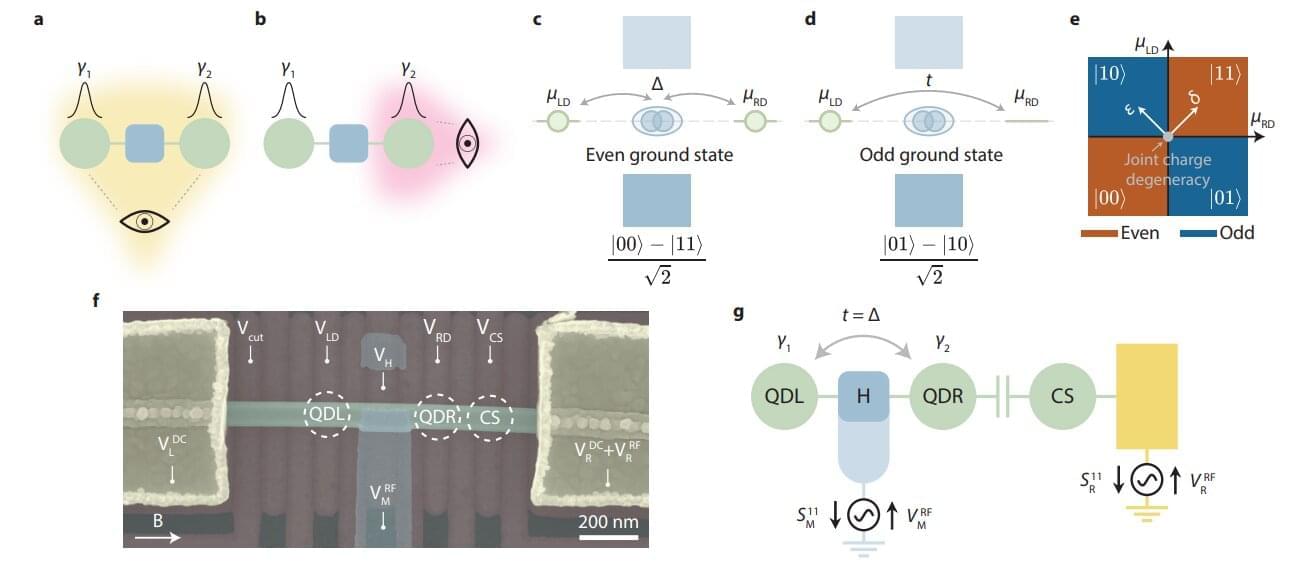
Majorana qubits become readable as quantum capacitance detects even-odd states
The race to build reliable quantum computers is fraught with obstacles, and one of the most difficult to overcome is related to the promising but elusive Majorana qubits. Now, an international team has read the information stored in these quantum bits. The findings are published in the journal Nature.
“This is a crucial advance,” explains Ramón Aguado, a Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) researcher at the Madrid Institute of Materials Science (ICMM) and one of the study’s authors.
“Our work is pioneering because we demonstrate that we can access the information stored in Majorana qubits using a new technique called quantum capacitance,” continues the scientist, who explains that this technique “acts as a global probe sensitive to the overall state of the system.”


Quantum Computing Breakthrough: Scientists Finally Unlock the Secret of Majorana Qubits
Scientists have finally figured out how to read ultra-secure Majorana qubits—bringing robust quantum computing a big step closer.
“This is a crucial advance,” says Ramón Aguado, a CSIC researcher at the Madrid Institute of Materials Science (ICMM) and co author of the study. He explains that the team has shown it is possible to retrieve information stored in Majorana qubits using a technique known as quantum capacitance. According to Aguado, this method works as “a global probe sensitive to the overall state of the system,” allowing researchers to detect properties that were previously out of reach.
Why topological qubits are so hard to measure.


Chinese Researchers Clear Hurdles For Long-Distance Quantum Networks
A Chinese research team has reported a pair of advances that could remove two of the biggest technical barriers to building large-scale quantum communication networks, including the generation of ultra-secure encryption keys over 11 kilometers of optical fiber and the validation of the approach at distances up to 100 kilometers, according to China Daily, a state-associated news service.
Researchers from the University of Science and Technology of China said they have demonstrated, for the first time, a scalable core component of a quantum repeater — a long-sought technology needed to extend quantum communication across long distances — while also setting new records for ultra-secure quantum key distribution over fiber networks.
The findings were published in Nature and Science, underscoring their significance within the international research community. Noted Chinese physicist Pan Jianwei led the work.

Time crystals could be used to build accurate quantum clocks
Once considered an oddity of quantum physics, time crystals could be a good building block for accurate clocks and sensors, according to new calculations.