Clue: It is very, very fast.
Category: quantum physics – Page 81

First Quantum Bit Made of Antimatter Captured in Physics Breakthrough
CERN scientists have analyzed a particle of antimatter isolated in an undecided quantum state known as a superposition for the first time.
While the quantum behavior of ordinary matter has been studied extensively and even used as the basis of quantum computers in the form of qubits, the breakthrough goes far beyond technological applications, potentially helping physicists understand why we even exist today.
The team suspended an antiproton – the antimatter counterpart of the proton – in a system of electromagnetic traps, and suppressed environmental interference that would mess with the particle’s delicate quantum state.

Magnetizing the Future of Quantum Communication: Single-Photon Emission from Defective Tungsten Diselenide
Quantum communication is one of the most exciting frontiers in secure data transmission. Now, a groundbreaking discovery by researchers at Kyoto University offers a major leap forward: a single-photon source created using defective tungsten diselenide (WSe2), enhanced under the influence of a magnetic field. The result? A powerful and controllable emitter that could revolutionize quantum information technologies.
The original article can be accessed at: Phys.org.
First-Ever Images Capture Atoms “Wiggling” in Quantum Materials
Scientists have imaged atomic thermal vibrations for the first time, revealing hidden patterns that could redefine quantum and nano-electronic device design. Scientists studying atomic-level behavior in advanced electronic and quantum devices have successfully captured the first-ever microscopy i

Northeastern discovery in quantum materials could make electronics 1,000 times faster
Researchers at Northeastern University have discovered how to change the electronic state of matter on demand, a breakthrough that could make electronics 1,000 times faster and more efficient.
By switching from insulating to conducting and vice versa, the discovery creates the potential to replace silicon components in electronics with exponentially smaller and faster quantum materials.
“Processors work in gigahertz right now,” said Alberto de la Torre, assistant professor of physics and lead author of the research. “The speed of change that this would enable would allow you to go to terahertz.”
Northeastern researchers discovered how to control quantum materials with light, potentially making electronics 1,000 times faster.


Quantum computing occurs naturally in the human brain, study finds
Kurian’s group believes these large tryptophan networks may have evolved to take advantage of their quantum properties. When cells breathe using oxygen—a process called aerobic respiration—they create free radicals, or reactive oxygen species (ROS). These unstable particles can emit high-energy UV photons, which damage DNA and other important molecules.
Tryptophan networks act as natural shields. They absorb this harmful light and re-emit it at lower energies, reducing damage. But thanks to superradiance, they may also perform this protective function much more quickly and efficiently than single molecules could.
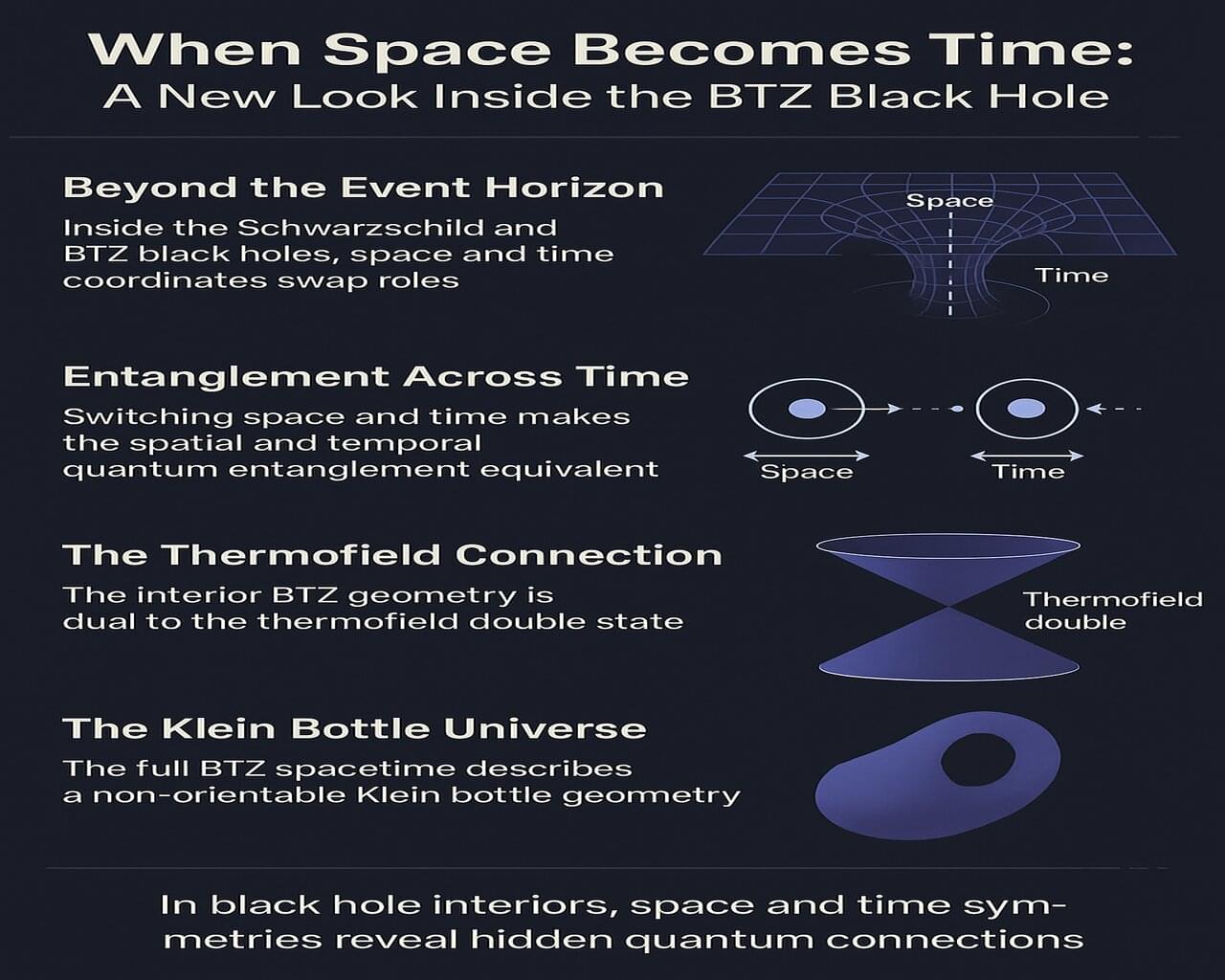
When space becomes time: A new look inside the BTZ black hole
Exploring the BTZ black hole in (2+1)-dimensional gravity took me down a fascinating rabbit hole, connecting ideas I never expected—like black holes and topological phases in quantum matter! When I swapped the roles of space and time in the equations (it felt like turning my map upside down when I was lost in a new city), I discovered an interior version of the solution existing alongside the familiar exterior, each with its own thermofield double state.
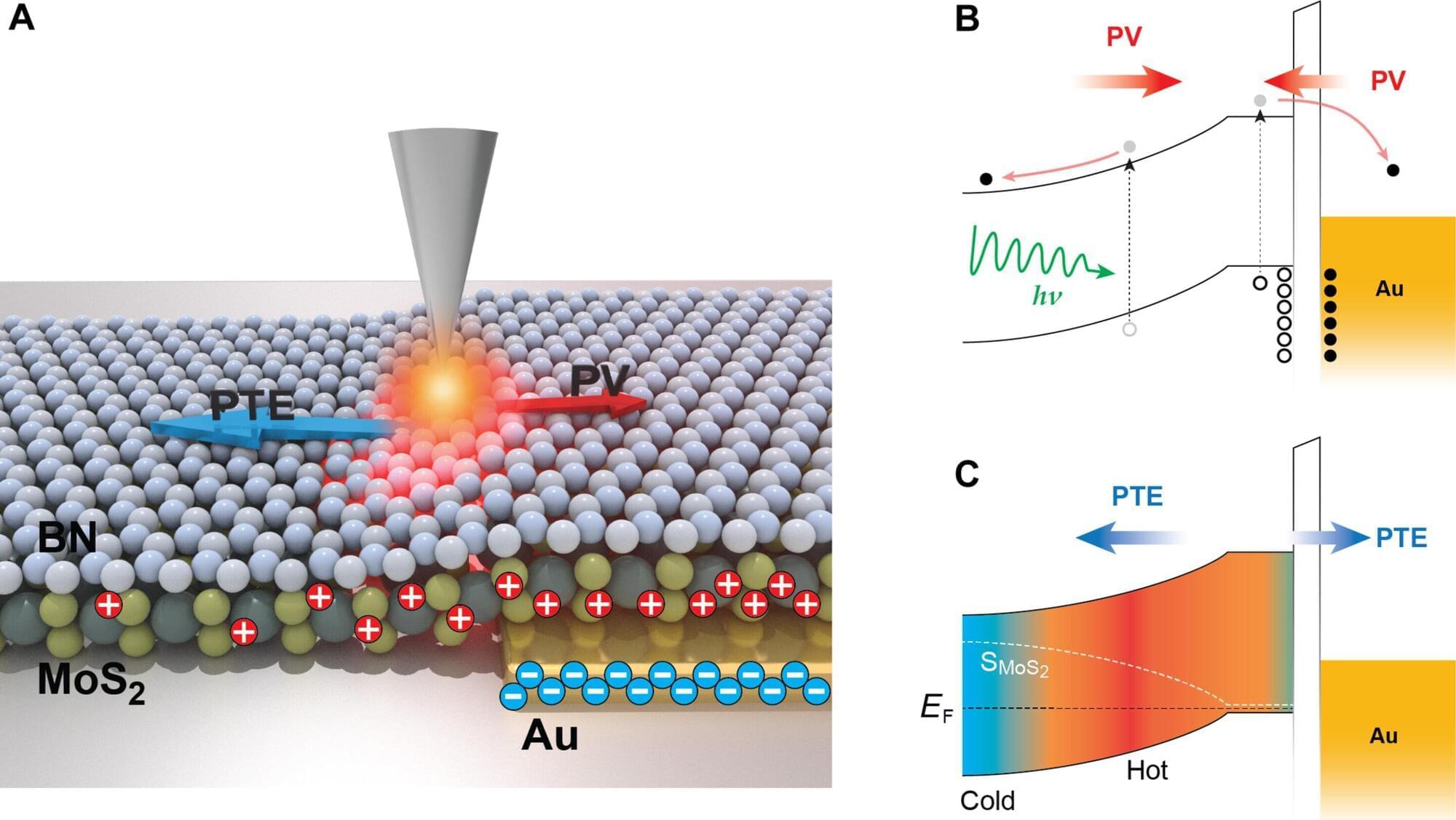
New imaging method reveals how light and heat generate electricity in nanomaterials
UC Riverside researchers have unveiled a powerful new imaging technique that exposes how cutting-edge materials used in solar panels and light sensors convert light into electricity—offering a path to better, faster, and more efficient devices.
The breakthrough, published in the journal Science Advances, could lead to improvements in solar energy systems and optical communications technology. The study title is “Deciphering photocurrent mechanisms at the nanoscale in van der Waals interfaces for enhanced optoelectronic applications.”
The research team, led by associate professors Ming Liu and Ruoxue Yan of UCR’s Bourns College of Engineering, developed a three-dimensional imaging method that distinguishes between two fundamental processes by which light is transformed into electric current in quantum materials.