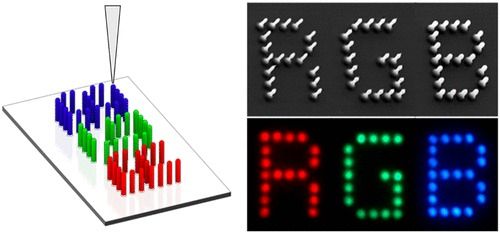
For the first time, researchers have designed a fully connected 32-qubit trapped-ion quantum computer register operating at cryogenic temperatures. The new system represents an important step toward developing practical quantum computers.
Junki Kim from Duke University will present the new hardware design at the inaugural OSA Quantum 2.0 conference to be co-located as an all-virtual event with OSA Frontiers in Optics and Laser Science APS/DLS (FiO + LS) conference 14—17 September.
Instead of using traditional computer bits that can only be a zero or a one, quantum computers use qubits that can be in a superposition of computational states. This allows quantum computers to solve problems that are too complex for traditional computers.