“A common challenge to the ideas presented in this book is that these exponential trends must reach a limit, as exponential trends commonly do.” –Ray Kurzweil, The Singularity Is Near
Much of the future we envision today depends on the exponential progress of information technology, most popularly illustrated by Moore’s Law. Thanks to shrinking processors, computers have gone from plodding, room-sized monoliths to the quick devices in our pockets or on our wrists. Looking back, this accelerating progress is hard to miss—it’s been amazingly consistent for over five decades.
But how long will it continue?
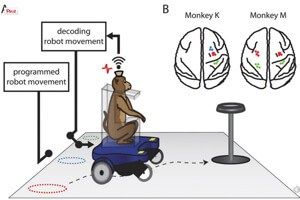 To start, the monkeys sat in wheelchairs that were moved along various paths toward a bowl of grapes across the room. Their brain activity was read and decoded by a computer program and then associated with wheelchair commands.
To start, the monkeys sat in wheelchairs that were moved along various paths toward a bowl of grapes across the room. Their brain activity was read and decoded by a computer program and then associated with wheelchair commands. Dear readers,
Dear readers,