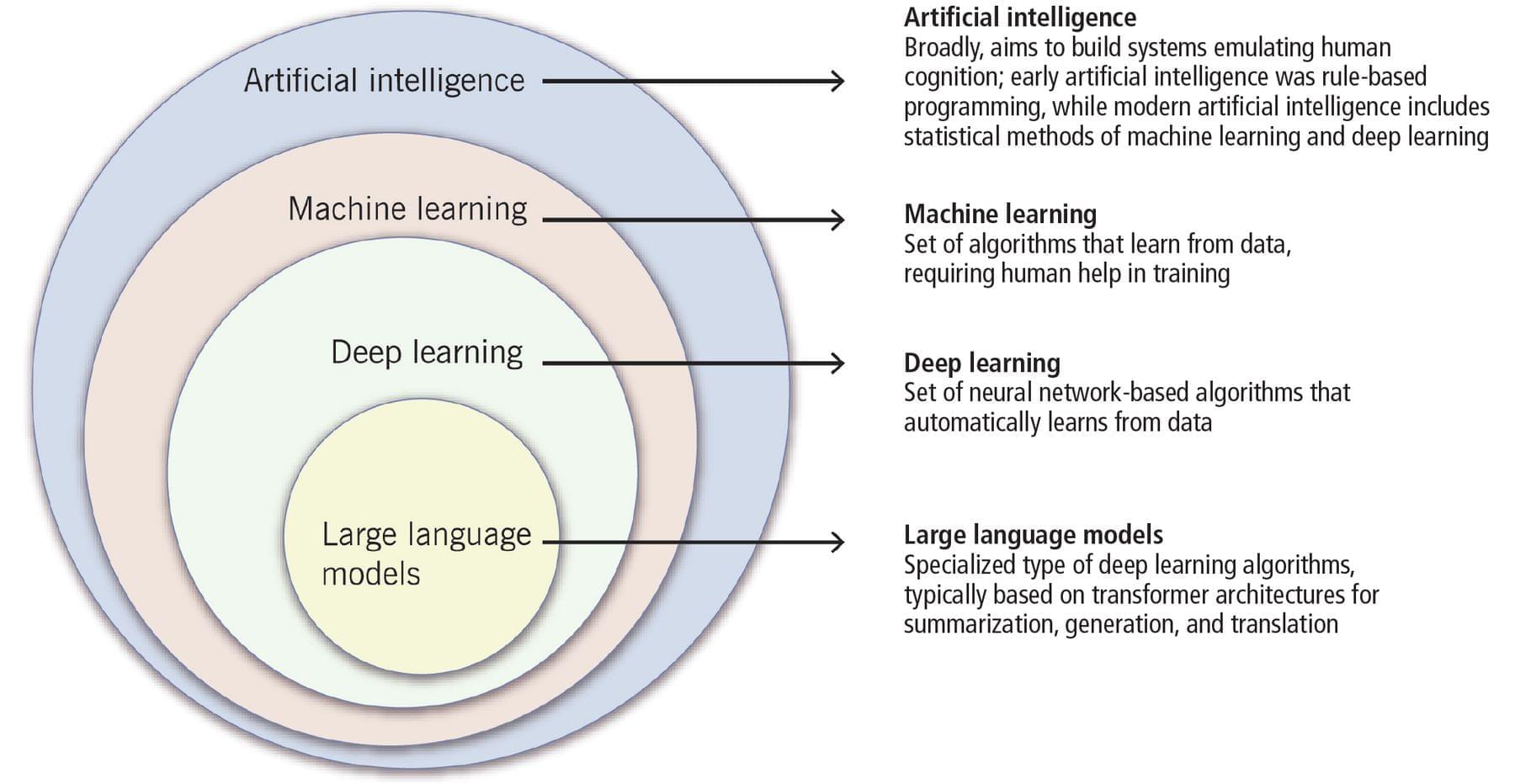
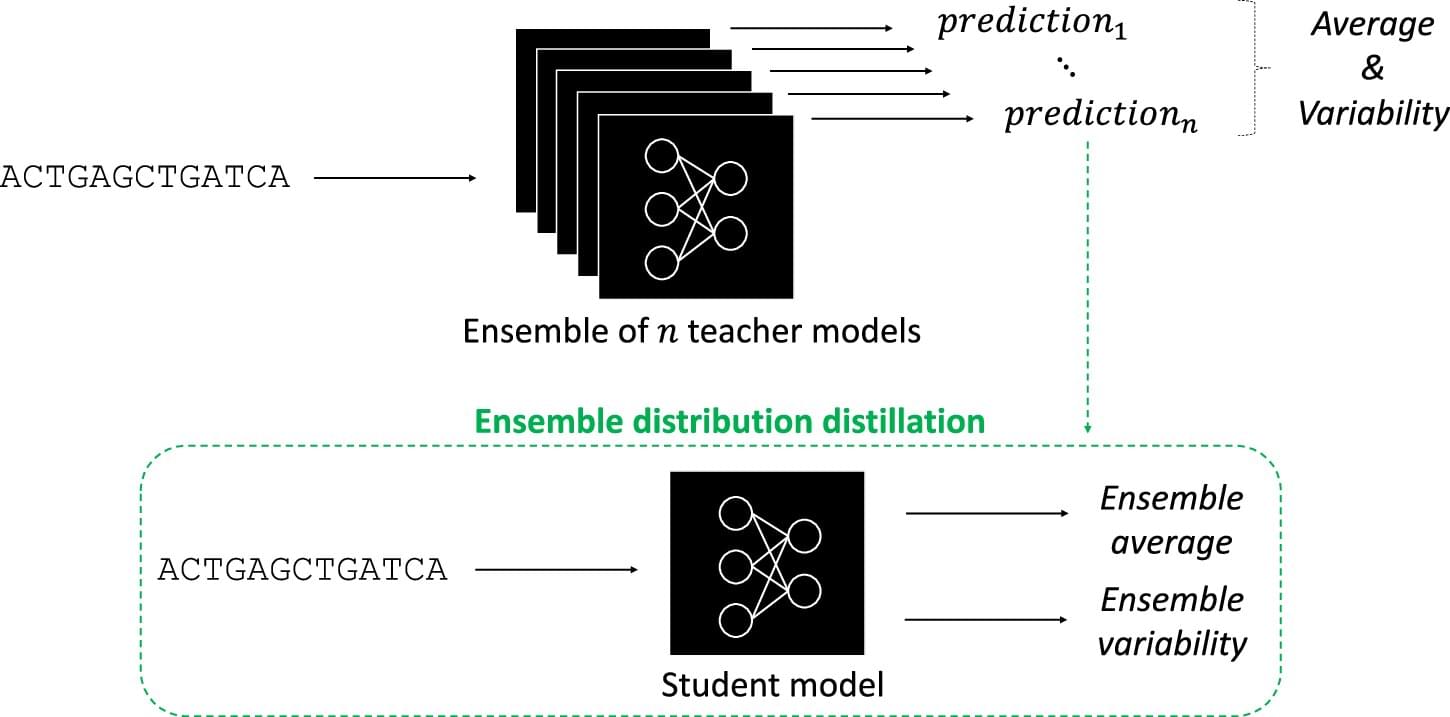
Artificial intelligence has taken the world by storm. In biology, AI tools called deep neural networks (DNNs) have proven invaluable for predicting the results of genomic experiments. Their usefulness has these tools poised to set the stage for efficient, AI-guided research and potentially lifesaving discoveries—if scientists can work out the kinks. The findings are published in the journal npj Artificial Intelligence.
“Right now, there are a lot of different AI tools where you’ll give an input, and they’ll give an output, but we don’t have a good way of assessing the certainty, or how confident they are, in their answers,” explains Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Associate Professor Peter Koo. “They all come out in the same format, whether you’re using a large language model or DNNs used in genomics and other fields of biology.”
It’s one of the greatest challenges today’s researchers face. Now, Koo, former CSHL postdoc Jessica Zhou, and graduate student Kaeli Rizzo have devised a potential solution—DEGU (Distilling Ensembles for Genomic Uncertainty-aware models). DNNs trained using DEGU are more efficient and more accurate in their predictions than those learning via standard methods.