Autonomous delivery robots join the fight against the #coronavirus epidemic in Wuhan, China.
Category: robotics/AI – Page 2,248
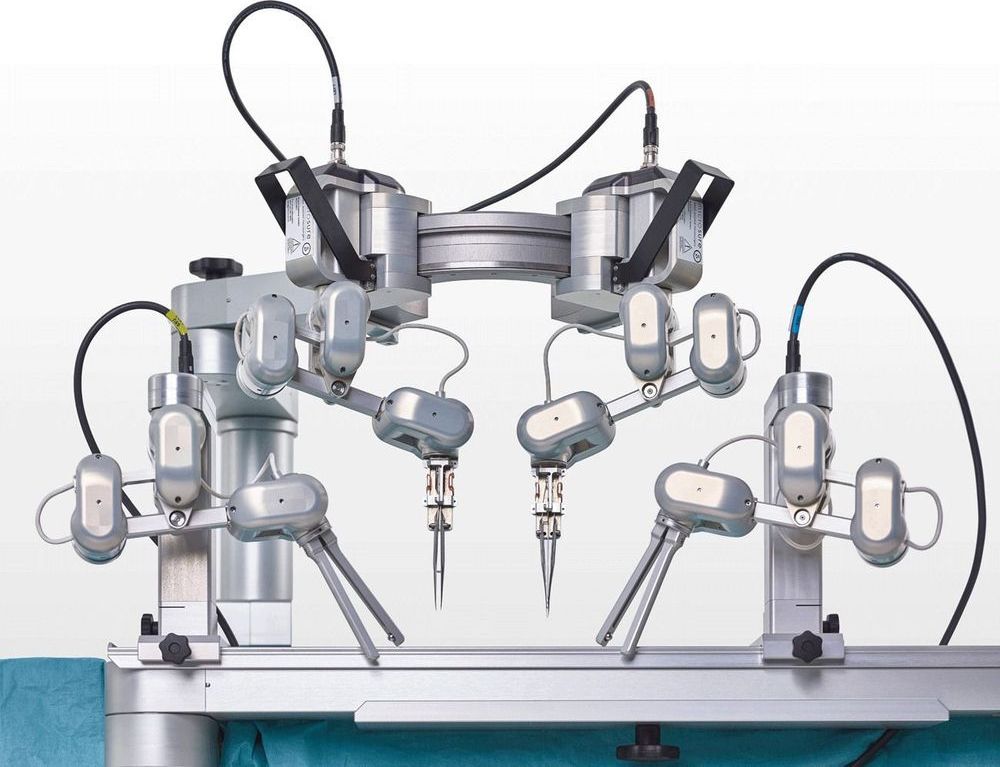


Robot completes first round of “supermicrosurgeries” on human patients
A highly precise form of reconstructive surgery, known as supermicrosurgery, seeks to connect ultra-thin blood and lymph vessels as a way of restoring them to healthy function. This requires a high level of expertise on part of the surgeons, but they may soon have a new robotic tool at their disposal called Musa, which has performed its first round of procedures with great success.
Supermicrosurgery is a relatively new medical technique that focuses on reconnecting vessels with diameters ranging from 0.3 mm to 0.8 mm. One of its primary applications is tackling lymphedema, which commonly occurs following breast cancer treatment and leads to swelling and localized fluid retention. Given the delicate nature of the process, only a small number of surgeons are currently capable of performing these operations.
Microsure is a Dutch startup spun out of Eindhoven University of Technology and Maastricht University Medical Centre, where researchers have been developing a robot to take on the task of supermicrosurgery. Called Musa, the robot is controlled by a surgeon, but translates their hand movements into more precise actions for a set of robotic hands.
Watch Drone Dome laser take down DJI Phantoms [video]
Take a look at this latest Israeli-developed counter-drone technology and watch the Drone Dome laser, dubbed Light Blade, take down a number of DJI Phantoms. The video that was uploaded to YouTube today shows a truck-mounted version of Drone Dome, a Counter-Unmanned Aerial System (C-UAS) weapon. The setup includes a search radar, drone-radio command detector, an electro-optical sensor, and a command-and-control system.
AI Predicts Coronavirus Vulnerable to HIV’s Atazanavir
An international collaboration between researchers at Deargen and Dankook University in the Republic of Korea, and Emory University in the United States, have published a prediction model for antiviral drugs that may be effective on 2019-nCoV.
The work is published in the article “Predicting commercially available antiviral drugs that may act on the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), Wuhan, China, through a drug-target interaction deep learning model” posted on the bioRxiv preprint server.
When an international team used an AI model to suggest available drugs that could be used against 2019-nCoV, the top candidates targeted viral proteinases.
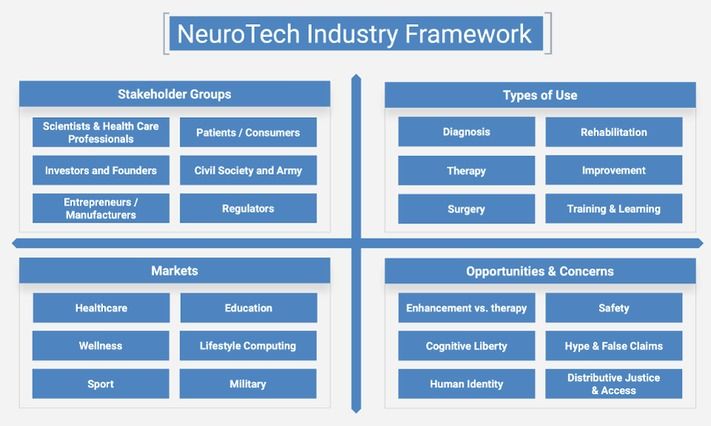
How AI Is Advancing NeuroTech
The idea is to use AI to develop a platform for detecting biomarkers from neural data. Then long-life neural interfaces (connections that allow computers to read and write neural data directly to and from the body) could be combined with a deep intelligence system trained to assess biomarkers directly from neural data.
If the AI platform is able to understand the “language” of the nervous system it could be used in closed-loop experiments to test neuromodulation therapy on new targets. This could accelerate the development of treatments for a number of chronic conditions and would also be a big step closer to real-world clinical applications of AI within the body. This progress could create a new way to investigate medical conditions, accelerate the detection of neural biomarkers, and open the door to a new generation of AI-based neural medical procedures.
NeuroTech is one of the most promising areas of BioTech. In the last 20 years private capital funds invested more than $19 billion in the sector, and annual growth of investment in the sector is 31%. Some NeuroTech subsectors are already well-established with practical implementations and products on the market. Over the next several years, many early-stage startups will evolve into mature companies and bring new NeuroTech products to market. Advances in AI and increased integration of computers and biology could lead to improved brain health for people all over the world.

FIFA experiments with AI for more accurate offside calls
FIFA, football’s governing body, is experimenting with artificial intelligence in hope of making better offside calls with the Video Assistant Referee (VAR) system.
A report by Forbes notes FIFA tested the new system during last year’s Club World Cup, but kept it separate from on-ground refereeing decisions.
Boston Dynamics Robot Dog Goes on Patrol at Norwegian Oil Rig
Meet Spot, the first robot to get its own employee number at Norwegian oil producer Aker BP ASA.

