Soft 3D electronic mesh wraps mini brains, records 91% of neural activity for drug testing and research.



Combined with Tower’s multi-site global footprint, Scintil’s unique SHIP™ platform is ready to take on the challenging requirements of the next generation Hyperscale AI Infrastructure Scintil Photonics LEAF Light™ Scintil Photonics’ LEAF Light™ is the industry’s first single-chip DWDM-native light engine, delivering high-density, low-power optical connectivity for next-generation AI factories. MIGDAL HAEMEK, Israel and GRENOBLE, France, Feb. 17, 2026 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — Tower Semiconductor (NASD

I am asking you for a report of no more than 3,000 words with deep analysis of which global sectors are likely to be most and least disrupted by Artificial Intelligence.
The following report and images are the Gemini output from the prompt I entered…
Sectoral Disruption and Economic Resilience 2026 I read the Deutsche Bank report, then ran the prompt against the latest version of Google Gemini 3 Pro. I didn’t have all their criteria, so I entered the basic prompt they had utilized.
Will humans one day merge with artificial intelligence? Futurist Ray Kurzweil predicts a coming “singularity” where humans upload their minds into digital systems, expanding intelligence and potentially achieving immortality. But critics argue that consciousness, creativity, love, and spiritual awareness cannot be reduced to algorithms. This discussion explores brain-computer interfaces, quantum mechanics and the mind, the Ship of Theseus identity paradox, and whether a digital copy of your brain would actually be you. Is AI-driven immortality possible—or does it misunderstand what it means to be human?
Every year the Center sponsors COSM an exclusive national summit on the converging technologies remaking the world as we know it. Visit COSM.TECH (https://cosm.tech/) for information on COSM 2025, November 19–21 at the beautiful Hilton Scottsdale Resort and Spas in Scottsdale, AZ. For more information. Registration will launch mid-July.
The mission of the Walter Bradley Center for Natural and Artificial Intelligence at Discovery Institute is to explore the benefits as well as the challenges raised by artificial intelligence (AI) in light of the enduring truth of human exceptionalism. People know at a fundamental level that they are not machines. But faulty thinking can cause people to assent to views that in their heart of hearts they know to be untrue. The Bradley Center seeks to help individuals—and our society at large—to realize that we are not machines while at the same time helping to put machines (especially computers and AI) in proper perspective.
Be sure to subscribe to the Center for Natural and Artificial Intelligence.
on Youtube: / @discoverycnai.
Follow Walter Bradley Center for Natural and Artificial Intelligence on.
X: / cnaintelligence, @cnaintelligence.
Facebook: / bradleycenterdi.
Visit other Youtube channels connected to the Discovery Institute:

Can you design a mechanism that will trace out the shape of a heart? How about the shape of a moon, or a star? Mechanism design—the art of assembling linkages and joints to create machines with prescribed motion—is one of the quintessential activities of mechanical engineers, but has resisted automation for almost two centuries.
In his seminal 1841 book Principles of Mechanisms, Oxford professor Robert Willis famously noted, “When the mind of a mechanician is occupied with the contrivance of a machine, he must wait until, in the midst of his meditations, some happy combination presents itself to his mind which may answer his purpose.”
Almost 200 years later, we still teach machine design mostly by apprenticeship. While we can simulate machines of almost any complexity, systematic methods for design are known only for the most trivial contraptions.
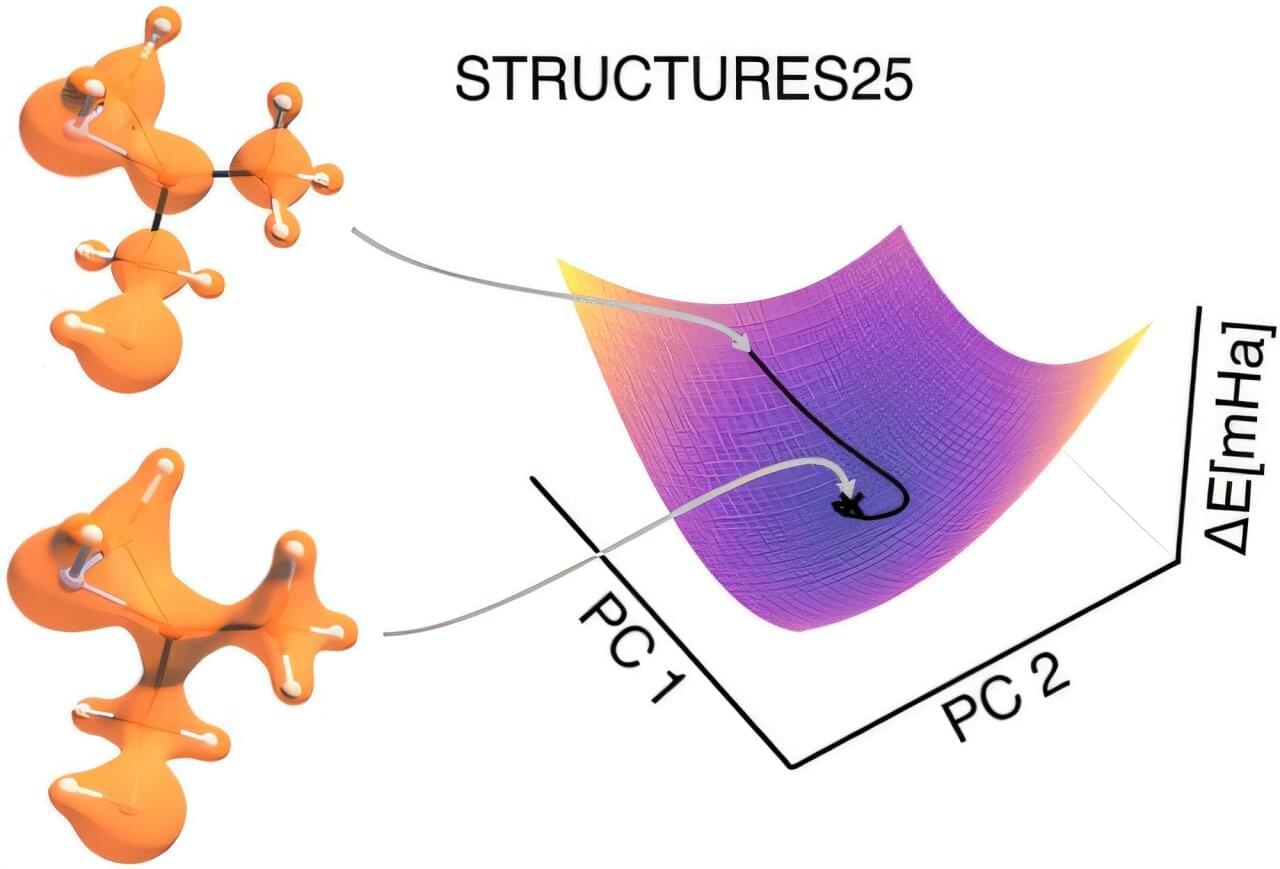
Within the STRUCTURES Cluster of Excellence, two research teams at the Interdisciplinary Center for Scientific Computing (IWR) have refined a computing process, long held to be unreliable, such that it delivers precise results and reliably establishes a physically meaningful solution. The findings are published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Why molecular electron densities matter
How electrons are distributed in a molecule determines its chemical properties—from its stability and reactivity to its biological effect. Reliably calculating this electron distribution and the resulting energy is one of the central functions of quantum chemistry. These calculations form the basis of many applications in which molecules must be specifically understood and designed, such as for new drugs, better batteries, materials for energy conversion, or more efficient catalysts.

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a buzzword in recent years. We’ve heard countless stories about how AI could potentially eliminate jobs, particularly in the engineering and contracting realm. However, we tend to forget that AI is also capable of creating new opportunities for employment and growth. I’d like to explore exactly how AI can help create jobs for engineers and other professionals in the contracting industry.
AI Enhances Demand for Skilled Workers
One of the most significant ways that AI can create jobs is by enhancing efficiency and productivity. By reducing manual labor and streamlining processes, organizations are able to focus their energy on more complex tasks that require human expertise. This shift means a greater need for skilled labor, which means more job openings for engineers and other professionals. For example, AI can be used to automate mundane tasks such as data entry or administrative work, allowing humans to focus their attention on more technical projects – and this means engineers have more time to create solutions that change the world.


Many of the latest large language models (LLMs) are designed to remember details from past conversations or store user profiles, enabling these models to personalize responses. But researchers from MIT and Penn State University found that, over long conversations, such personalization features often increase the likelihood an LLM will become overly agreeable or begin mirroring the individual’s point of view.
This phenomenon, known as sycophancy, can prevent a model from telling a user they are wrong, eroding the accuracy of the LLM’s responses. In addition, LLMs that mirror someone’s political beliefs or worldview can foster misinformation and distort a user’s perception of reality.
Unlike many past sycophancy studies that evaluate prompts in a lab setting without context, the MIT researchers collected two weeks of conversation data from humans who interacted with a real LLM during their daily lives. They studied two settings: agreeableness in personal advice and mirroring of user beliefs in political explanations.

#cybersecurity #ai #quantum
Artificial intelligence and quantum computing are no longer hypothetical; they are actively altering cybersecurity, extending attack surfaces, escalating dangers, and eroding existing defenses. We are in a new ear of emerging technologies that are directly impacting cybersecurity requirements.
As a seasoned observer and participant in the cybersecurity domain—through my work, teaching, and contributions to Homeland Security Today, my book “Inside Cyber: How AI, 5G, IoT, and Quantum Computing Will Transform Privacy and Our Security”, — I have consistently underscored that technological advancement is outpacing our institutions, policies, and workforce preparedness.
Current frameworks, intended for a pre-digital convergence era, are increasingly unsuitable. In order to deal with these dual-use technologies that act as force multipliers for both defenders and enemies, we must immediately adjust our strategy as time is of the essence.