IIT reveals advances in the world’s first jet-powered humanoid robot, showcasing its experimental area and early validation efforts.
Category: robotics/AI – Page 618

AI Model Predicts Autism in Toddlers with 80% Accuracy
Summary: A new machine learning model, AutMedAI, can predict autism in children under two with nearly 80% accuracy, offering a promising tool for early detection and intervention.
The model analyzes 28 parameters available before 24 months, such as age of first smile and eating difficulties, to identify children likely to have autism. Early diagnosis is crucial for optimal development, and further validation of the model is underway.
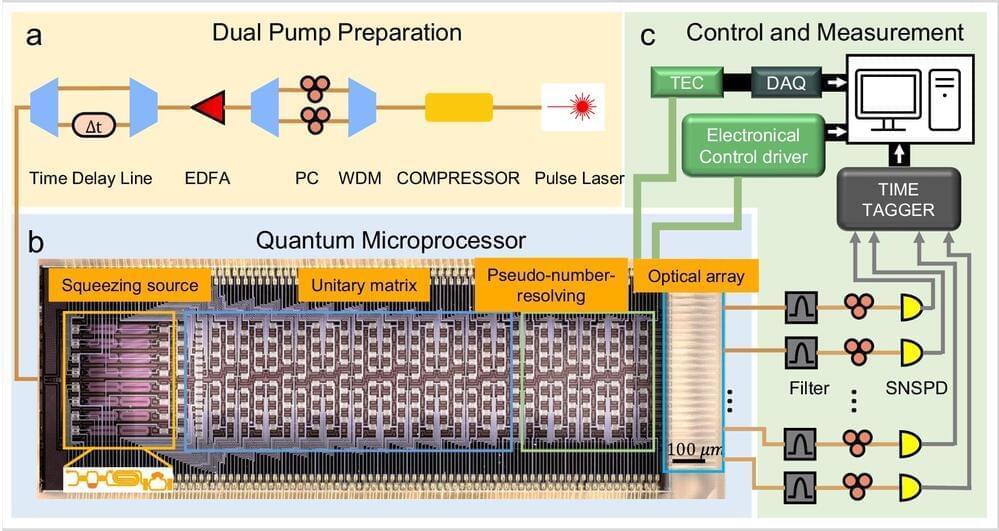
Scientists harness quantum microprocessor chips for advanced molecular spectroscopy simulation
Quantum simulation enables scientists to simulate and study complex systems that are challenging or even impossible using classical computers across various fields, including financial modeling, cybersecurity, pharmaceutical discoveries, AI and machine learning. For instance, exploring molecular vibronic spectra is critical in understanding the molecular properties in molecular design and analysis.

MIT engineers design tiny batteries for powering cell-sized robots
Engineers have designed a tiny battery, smaller than a grain of sand, to power microscopic robots for jobs such as drug delivery or locating leaks in gas pipelines.
A tiny battery designed by MIT engineers could enable the deployment of cell-sized, autonomous robots for drug delivery within in the human body, as well as other applications such as locating leaks in gas pipelines.
The new battery, which is 0.1 millimeters long and 0.002 millimeters thick — roughly the thickness of a human hair — can capture oxygen from air and use it to oxidize zinc, creating a current with a potential of up to 1 volt. That is enough to power a small circuit, sensor, or actuator, the researchers showed.
“We think this is going to be very enabling for robotics,” says Michael Strano, the Carbon P. Dubbs Professor of Chemical Engineering at MIT and the senior author of the study. “We’re building robotic functions onto the battery and starting to put these components together into devices.”
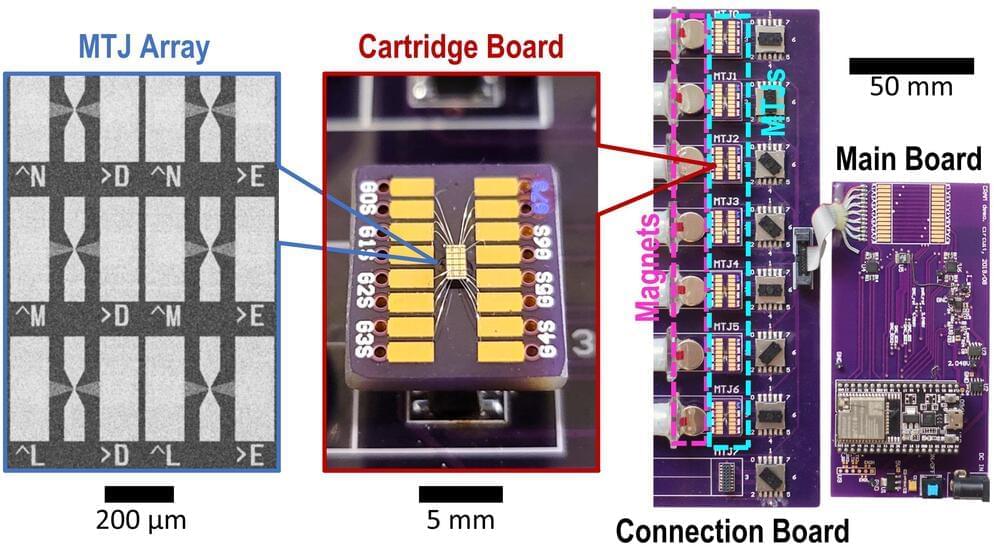
Engineers develop Magnetic Tunnel Junction–based Device to make AI more Energy Efficient
Engineering researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities have demonstrated a state-of-the-art hardware device that could reduce energy consumption for artificial intelligent (AI) computing applications by a factor of at least 1,000.
The research is published in npj Unconventional Computing titled “Experimental demonstration of magnetic tunnel junction-based computational random-access memory.” The researchers have multiple patents on the technology used in the device.
With the growing demand for AI applications, researchers have been looking at ways to create a more energy efficient process, while keeping performance high and costs low. Commonly, machine or artificial intelligence processes transfer data between both logic (where information is processed within a system) and memory (where the data is stored), consuming a large amount of power and energy.
AI boosts the power of EEGs, enabling neurologists to quickly, precisely pinpoint signs of dementia
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Mayo Clinic scientists are using artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to analyze electroencephalogram (EEG) tests more quickly and precisely, enabling neurologists to find early signs of dementia among data that typically go unexamined.
The century-old EEG, during which a dozen or more electrodes are stuck to the scalp to monitor brain activity, is often used to detect epilepsy. Its results are interpreted by neurologists and other experts trained to spot patterns among the test’s squiggly waves.
In new research published in Brain Communications, scientists at the Mayo Clinic Neurology AI Program (NAIP) demonstrate how AI can not only speed up analysis, but also alert experts reviewing the test results to abnormal patterns too subtle for humans to detect. The technology shows the potential to one day help doctors distinguish among causes of cognitive problems, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Lewy body dementia. The research suggests that EEGs, which are more widely available, less expensive and less invasive than other tests to capture brain health, could be a more accessible tool to help doctors catch cognitive issues in patients early.

Tech Company Lays Off 5,500 Workers to Invest More in AI, Despite Making $10.3 Billion in Profit
In short, companies are no longer hiding their optimism over replacing human labor with AI, an unfortunate reality for those looking to maintain a stable job.
Despite tech conglomerate Cisco posting $10.3 billion in profits last year, it’s still laying off 5,500 workers as part of an effort to invest more in AI, SFGATE reports.
It joins a litany of other companies like Microsoft and Intuit, the maker of TurboTax, that have used AI as justification for the mass culling of its workforce.
The layoffs at Cisco came to light in a notice posted with the Securities and Exchange Commission this week, affecting seven percent of its staff.

Layoff Crisis Hit over 130,000 Employees till August: Expert Highlights Workforce Recovery Scenario
As of August 2024, the global employment landscape is facing significant turbulence, with more than 130,000 employees laid off across nearly 400 companies. Tech giants like Google, IBM, Apple, Amazon, SAP, Meta, and Microsoft have contributed to these staggering figures, indicating a major recalibration within the job market.
According to industry experts, this trend is accelerating as the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation prompts companies to streamline operations. Amidst this upheaval, Ramesh Alluri Reddy, CEO of TeamLease Degree Apprenticeship, sheds light on layoffs, workforce reshaping, and the potential for recovery.

LLMs develop their own understanding of reality as their language abilities improve
But does the lack of eyes mean that language models can’t ever “understand” that a lion is “larger” than a house cat? Philosophers and scientists alike have long considered the ability to assign meaning to language a hallmark of human intelligence — and pondered what essential ingredients enable us to do so.
Peering into this enigma, researchers from MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) have uncovered intriguing results suggesting that language models may develop their own understanding of reality as a way to improve their generative abilities. The team first developed a set of small Karel puzzles, which consisted of coming up with instructions to control a robot in a simulated environment. They then trained an LLM on the solutions, but without demonstrating how the solutions actually worked. Finally, using a machine learning technique called “probing,” they looked inside the model’s “thought process” as it generates new solutions.
After training on over 1 million random puzzles, they found that the model spontaneously developed its own conception of the underlying simulation, despite never being exposed to this reality during training. Such findings call into question our intuitions about what types of information are necessary for learning linguistic meaning — and whether LLMs may someday understand language at a deeper level than they do today.