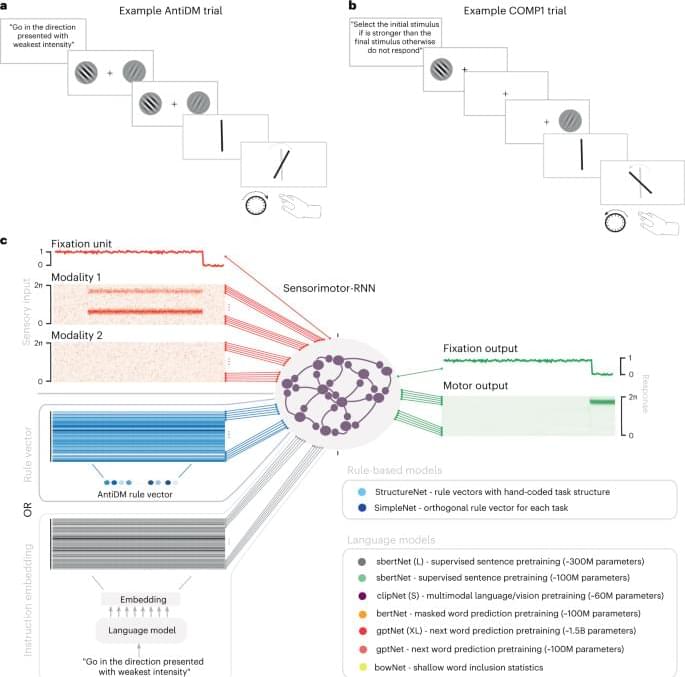
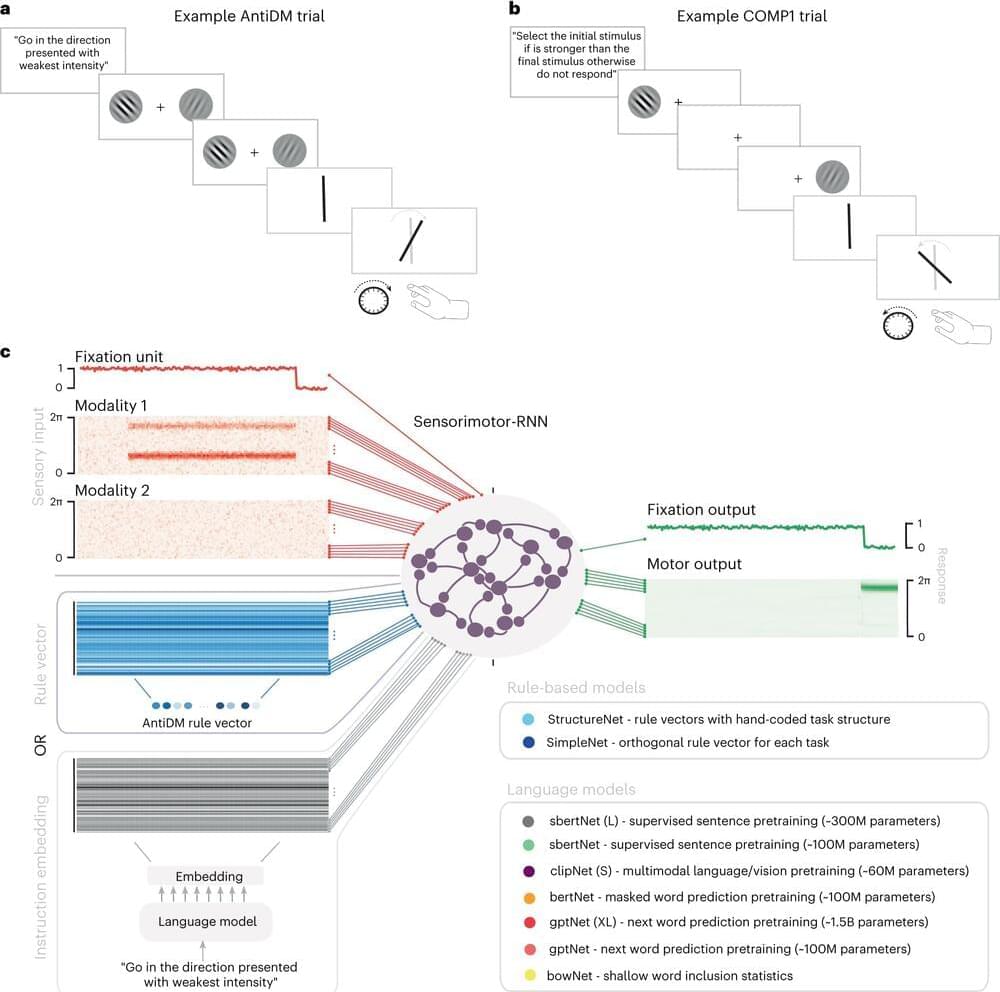
This paper introduces a novel theoretical framework for understanding consciousness, proposing a paradigm shift from traditional biological-centric views to a broader, universal perspective grounded in thermodynamics and systems theory. We posit that consciousness is not an exclusive attribute of biological entities but a fundamental feature of all systems exhibiting a particular form of intelligence. This intelligence is defined as the capacity of a system to efficiently utilize energy to reduce internal entropy, thereby fostering increased order and complexity. Supported by a robust mathematical model, the theory suggests that subjective experience, or what is often referred to as qualia, emerges from the intricate interplay of energy, entropy, and information within a system. This redefinition of consciousness and intelligence challenges existing paradigms and extends the potential for understanding and developing Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). The implications of this theory are vast, bridging gaps between cognitive science, artificial intelligence, philosophy, and physics, and providing a new lens through which to view the nature of consciousness itself.
Consciousness, traditionally viewed through the lens of biology and neurology, has long been a subject shrouded in mystery and debate. Philosophers, scientists, and thinkers have pondered over what consciousness is, how it arises, and why it appears to be a unique trait of certain biological organisms. The “hard problem” of consciousness, a term coined by philosopher David Chalmers, encapsulates the difficulty in explaining why and how physical processes in the brain give rise to subjective experiences.
Current research in cognitive science, neuroscience, and artificial intelligence offers various theories of consciousness, ranging from neural correlates of consciousness (NCCs) to quantum theories. However, these theories often face limitations in fully explaining the emergence and universality of consciousness.