CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. (Reuters) — SpaceX said all systems and weather were “go” for blast-off on Wednesday of its first high-priority science mission for NASA, a planet-hunting space telescope whose launch was delayed for two days by a rocket-guidance glitch.
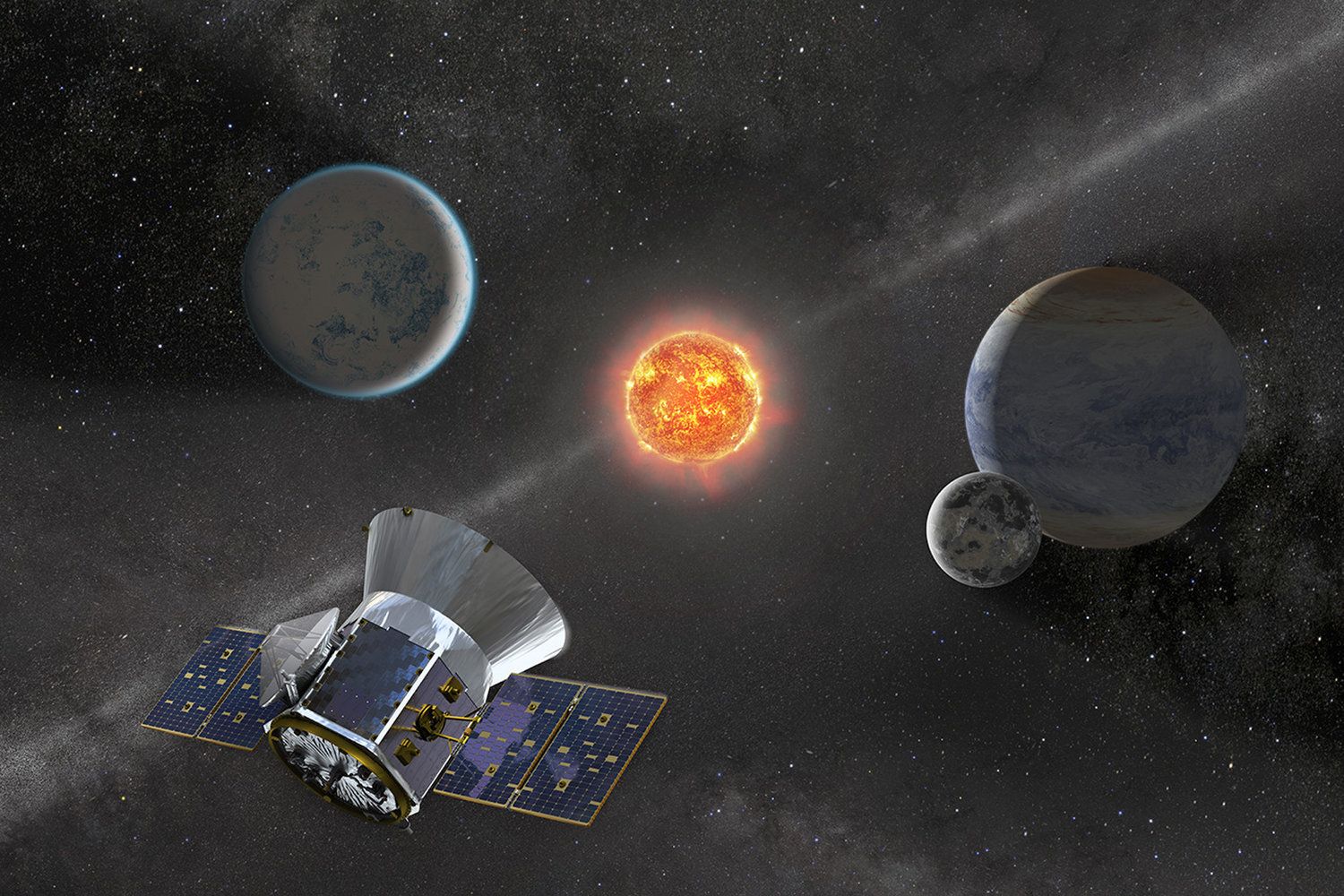
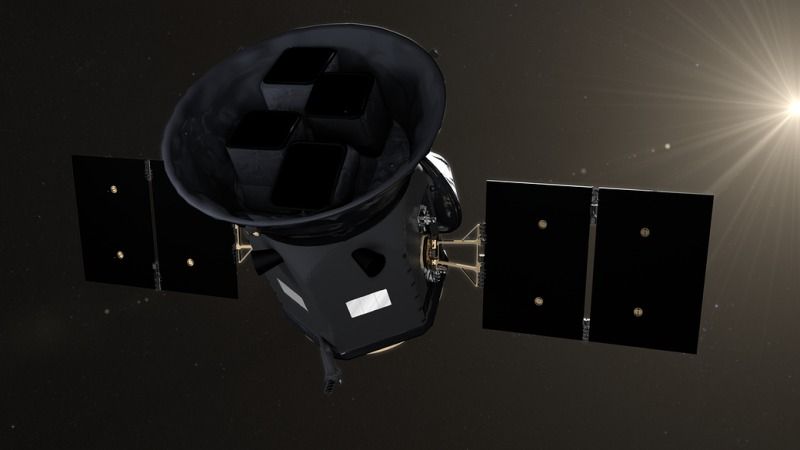
FILE PHOTO: NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite, scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, U.S., is shown in this artist’s rendering image obtained on April 9, 2018. Courtesy Chris Meaney/Goddard Space Flight Center/NASA/Handout via REUTERS.