Coming soon: a nation in space for humans.


As America has turned away from searching for extraterrestrial intelligence, China has built the world’s largest radio dish for precisely that purpose.
Last January, the Chinese Academy of Sciences invited Liu Cixin, China’s preeminent science-fiction writer, to visit its new state-of-the-art radio dish in the country’s southwest. Almost twice as wide as the dish at America’s Arecibo Observatory, in the Puerto Rican jungle, the new Chinese dish is the largest in the world, if not the universe. Though it is sensitive enough to detect spy satellites even when they’re not broadcasting, its main uses will be scientific, including an unusual one: The dish is Earth’s first flagship observatory custom-built to listen for a message from an extraterrestrial intelligence. If such a sign comes down from the heavens during the next decade, China may well hear it first.

NASA’s OCO-2 satellite has detected a dramatic spike in global atmospheric carbon dioxide, and overheated tropical forests are partly to blame.

Sending satellites into space is going to continue to get cheaper since SpaceX proved it could reliably launch refurbished rockets. This is going to open up space exploration to more entities allowing for the continued democratization of space. Other technological advances could make a global space centered sharing economy a real possibility.
The rise of the internet and the ubiquity of mobile computing devices have changed everything from travel and shopping to politics – think Uber, Amazon, and Twitter.
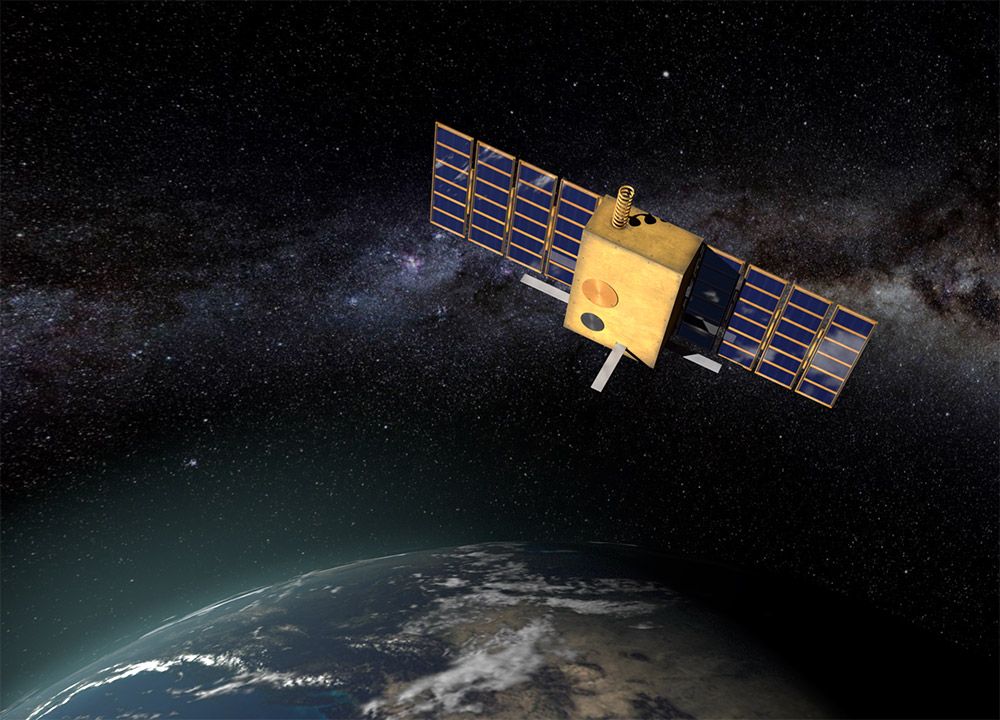

WASHINGTON — General Atomics is better known for building Predator combat drones and mining uranium than building spacecraft, but that could change as the company develops an interest in building defense-focused cubesats.
Also in the realm of possibility: using expertise from building railguns to design a large, electromagnetic cannon as a means to orbit small satellites.
Nick Bucci, vice president of missile defense and space systems for General Atomic’s Electromagnetic Systems Group, said the company has built 11 cubesats for the U.S. Army over the past seven years, and is gradually becoming more and more invested in space.

RT has released the first-ever 360-degree footage shot by man in outer space, putting viewers in the shoes of two Russian cosmonauts launching nanosatellites from outside the International Space Station (ISS).
The video, which shows out-of-this-world views of Planet Earth, is the first time that the so-called extravehicular activity (EVA) has been filmed in 360. The immersive new format previously helped viewers explore the ISS modules as part of the Space 360 project.
Cosmonauts Sergey Ryazansky and Fedor Yurchikhin captured the breathtaking scenery while doing their 7.5-hour spacewalk in August, which included maintenance tasks and the launch of five miniature satellites.
Washington (AP) — Seated before the grounded space shuttle Discovery, a constellation of Trump administration officials used soaring rhetoric to vow to send Americans back to the moon and then on to Mars.
After voicing celestial aspirations, top officials moved to what National Intelligence Director Dan Coats called “a dark side” to space policy. Coats, Vice President Mike Pence, other top officials and outside space experts said the United States has to counter and perhaps match potential enemies’ ability to target U.S. satellites.
Pence, several cabinet secretaries and White House advisers gathered in the shadow of the shuttle at the Smithsonian Institution’s Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center to chart a new path in space — government, commercial and military — for the country. It was the first meeting of the National Space Council, revived after it was disbanded in 1993.