An international team of astronomers using NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) has detected a rocky planet, about half the mass of Earth, in an extraordinarily short 7.7-hour orbit around its parent star.
It’s a reminder that the science of extrasolar planet hunting seems to enter bizarro land with each new discovery. Planetary scientists still haven’t figured out how our own tiny Mercury — which orbits our Sun once every 88 days — actually formed and evolved. So, this iron-rich ultrashort-period (USP) planet, dubbed GJ 367b should really boggle their minds.
It’s completely rocky, unlike most previously detected gaseous hot Jupiters on extremely short stellar orbits. As a result, the tiny planet is estimated to have a surface with temperatures of 1,500 degrees Celsius, hot enough to melt iron; hardly an Earth 2.0.
Full Story:
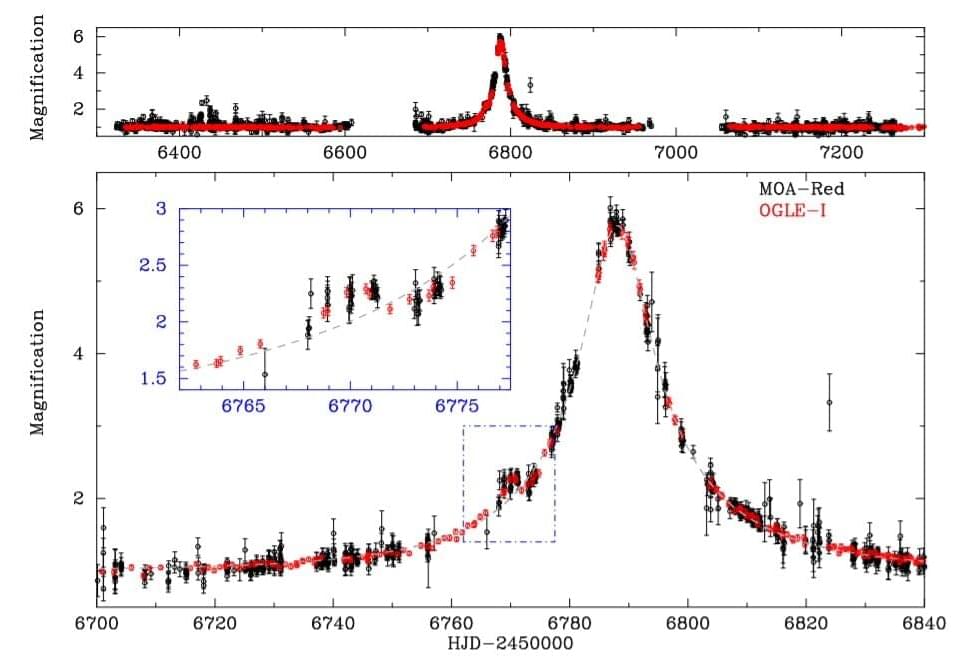
An international team of astronomers reports the detection of a new sub-Jupiter-mass alien world orbiting an M-dwarf star. The newly found exoplanet, designated OGLE-2014-BLG-0319Lb, turns out to be about half as massive as Jupiter. The discovery was detailed in a paper published December 30 on the arXiv pre-print repository.
Based on the gravitational lens effect, the microlensing method is mainly used to detect planetary and stellar-mass objects regardless of the light they emit. This technique is therefore sensitive to the mass of the objects, rather than their luminosity, which allows astronomers to study objects that emit little or no light at all.