A new system enables optimization of perovskite materials for the production of technology that could make solar energy ubiquitous.

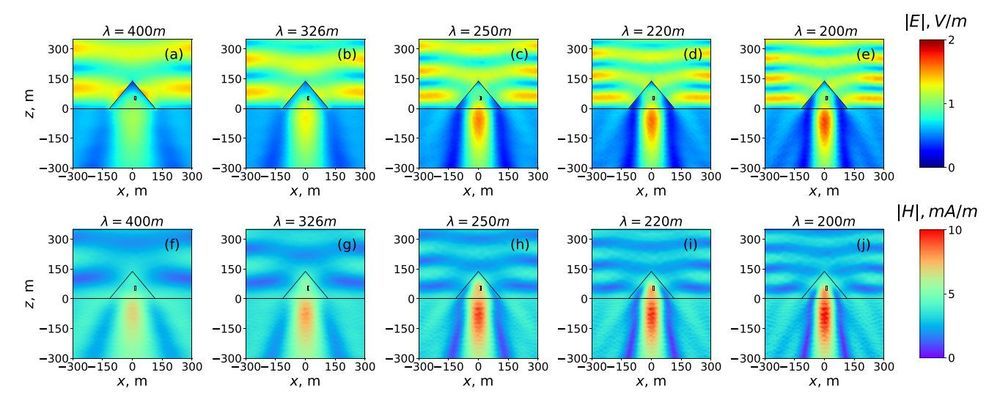
An international research group has applied methods of theoretical physics to investigate the electromagnetic response of the Great Pyramid to radio waves. Scientists predicted that under resonance conditions, the pyramid can concentrate electromagnetic energy in its internal chambers and under the base. The research group plans to use these theoretical results to design nanoparticles capable of reproducing similar effects in the optical range. Such nanoparticles may be used, for example, to develop sensors and highly efficient solar cells. The study was published in the Journal of Applied Physics.
While Egyptian pyramids are surrounded by many myths and legends, researchers have little scientifically reliable information about their physical properties. Physicists recently took an interest in how the Great Pyramid would interact with electromagnetic waves of a resonant length. Calculations showed that in the resonant state, the pyramid can concentrate electromagnetic energy in the its internal chambers as well as under its base, where the third unfinished chamber is located.
These conclusions were derived on the basis of numerical modeling and analytical methods of physics. The researchers first estimated that resonances in the pyramid can be induced by radio waves with a length ranging from 200 to 600 meters. Then they made a model of the electromagnetic response of the pyramid and calculated the extinction cross section. This value helps to estimate which part of the incident wave energy can be scattered or absorbed by the pyramid under resonant conditions. Finally, for the same conditions, the scientists obtained the electromagnetic field distribution inside the pyramid.
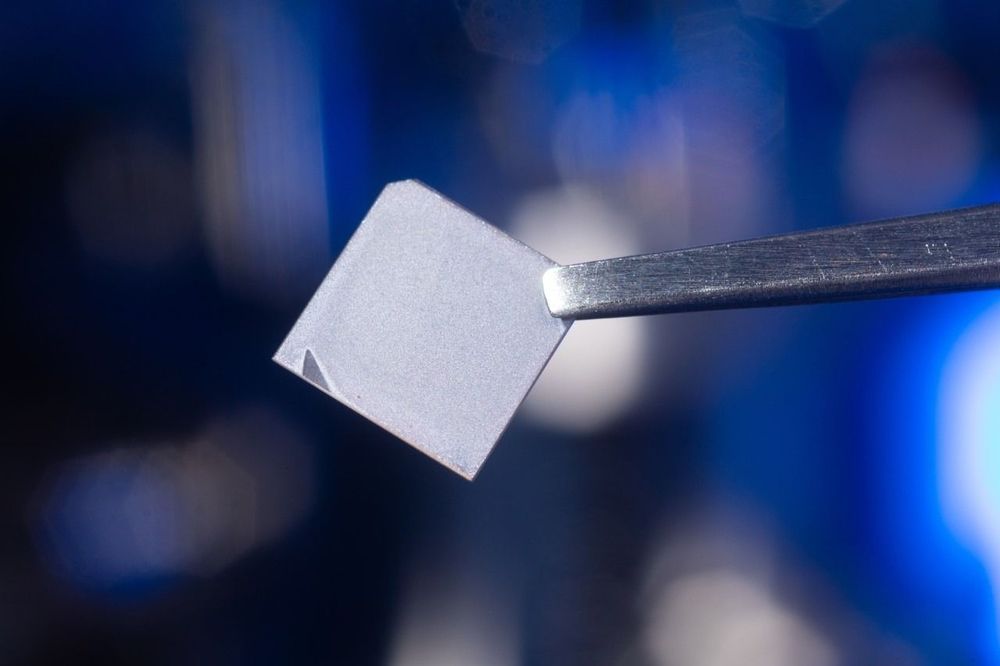

Scientists have created thin films made from barium zirconium sulfide (BaZrS3) and confirmed that the materials have alluring electronic and optical properties predicted by theorists.
The films combine exceptionally strong light absorption with good charge transport—two qualities that make them ideal for applications such as photovoltaics and light-emitting diodes (LEDs).
In solar panels, for example, experimental results suggest that BaZrS3 films would be much more efficient at converting sunlight into electricity than traditional silicon-based materials with identical thicknesses, says lead researcher Hao Zeng, Ph.D., professor of physics in the University at Buffalo College of Arts and Sciences. This could lower solar energy costs, especially because the new films performed admirably even when they had imperfections. (Manufacturing nearly flawless materials is typically more expensive, Zeng explains.)
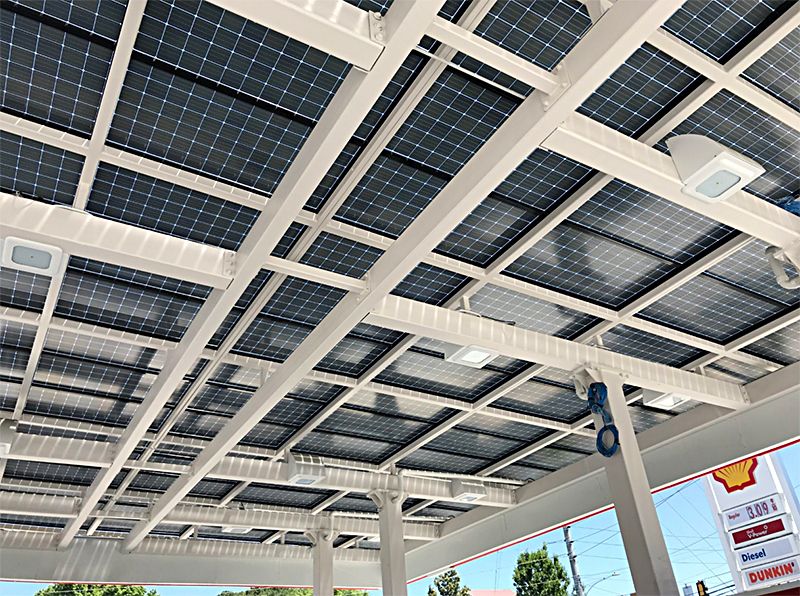

Engineers calculate the ultimate potential of next-generation solar panels
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — Most of today’s solar panels capture sunlight and convert it to electricity only from the side facing the sky. If the dark underside of a solar panel could also convert sunlight reflected off the ground, even more electricity might be generated.
Double-sided solar cells are already enabling panels to sit vertically on land or rooftops and even horizontally as the canopy of a gas station, but it hasn’t been known exactly how much electricity these panels could ultimately generate or the money they could save.
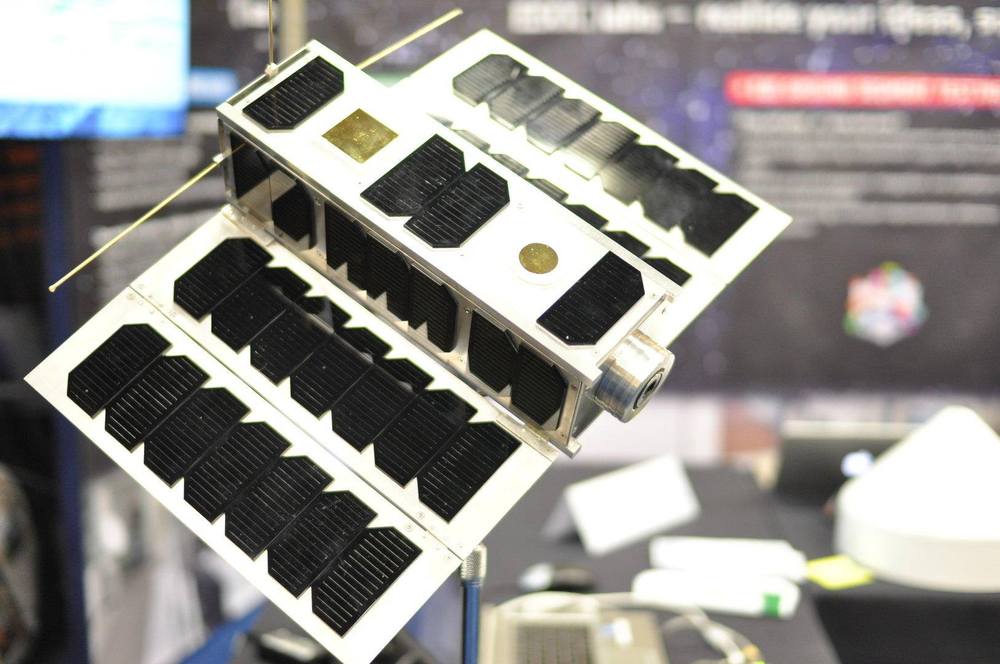

Calling all radio amateurs! We’re challenging anyone with amateur radio equipment to catch the first signals from #OPS –SAT, ESA’s brand new space software lab. On 17 December, OPS-SAT will be launched into space with ESA’s #Cheops exoplanet satellite.
Once launched, the satellite will deploy its solar panels and ultra-high frequency antenna, and then start to send signals back home. Could you be the first on Earth to catch them? ESA’s mission control team in Darmstadt are asking for your help to find the fledgling #CubeSat 👉 http://www.esa.int/Enabling_Support/Operations/Calling_radio…nd_OPS-SAT

Elon Musk has revived his idea to power the entire U.S. with one single, giant solar farm. In a recent tweet evidently directed at fellow mega-billionaire Bill Gates, Musk insinuated that his grand solar plan is actually quite simple (hat-tip to Inverse):
Decision-making algorithms transform how automated systems evaluate and synthesize novel compounds.

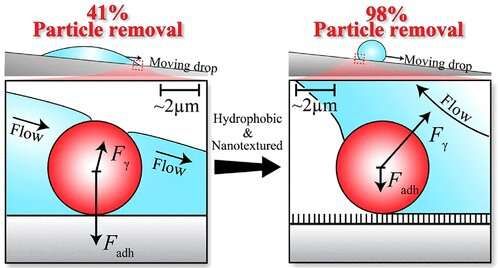
Taking a cue from the self-cleaning properties of the lotus leaf, researchers at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev have shed new light on microscopic forces and mechanisms that can be optimized to remove dust from solar panels to maintain efficiency and light absorption. The new technique removed 98 percent of dust particles.
In a new study published in Langmuir, the researchers confirmed that modifying the surface properties of solar panels may greatly reduce the amount of dust remaining on the surface, and significantly increase the potential of solar energy harvesting applications in the desert.
Dust adhesion on solar panels is a major challenge to energy harvesting through photovoltaic cells and solar thermal collectors. New solutions are necessary to maintain maximum collection efficiency in high dust density areas such as the Negev desert in Israel.