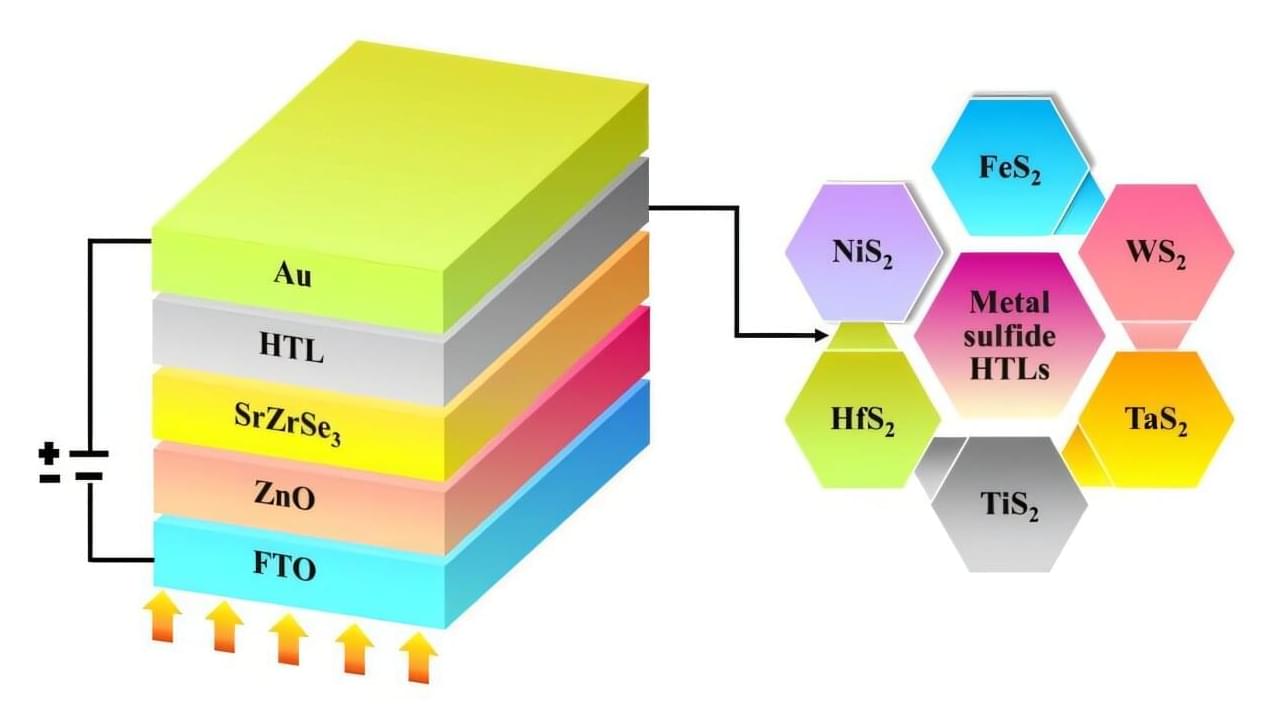
Photovoltaic (PV) solutions, which are designed to convert sunlight into electrical energy, are becoming increasingly widespread worldwide. Over the past decades, engineers specialized in energy solutions have been trying to identify new solar cell designs and PV materials that could achieve even better power conversion efficiencies, while also retaining their stability and reliably operating for long periods of time.
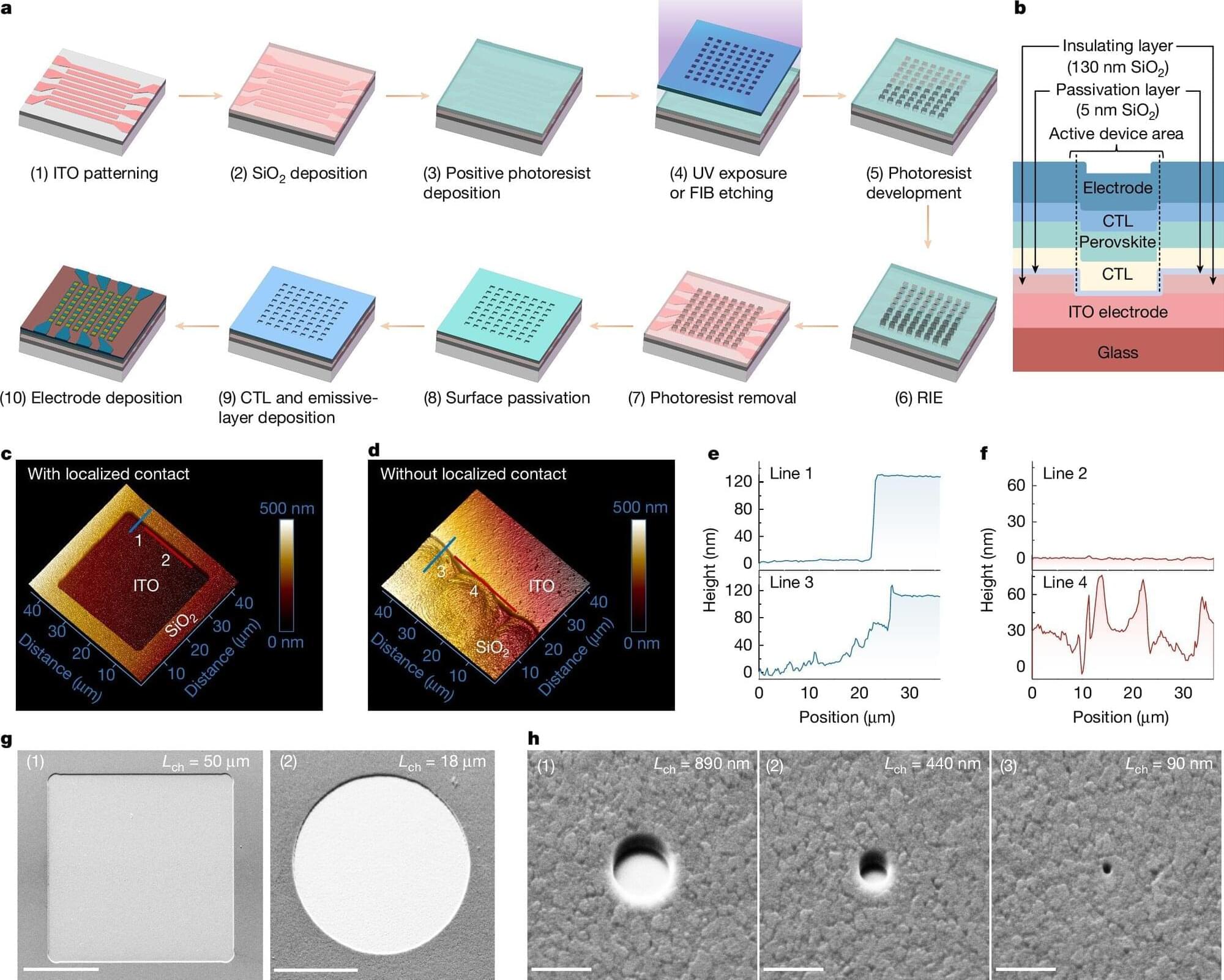
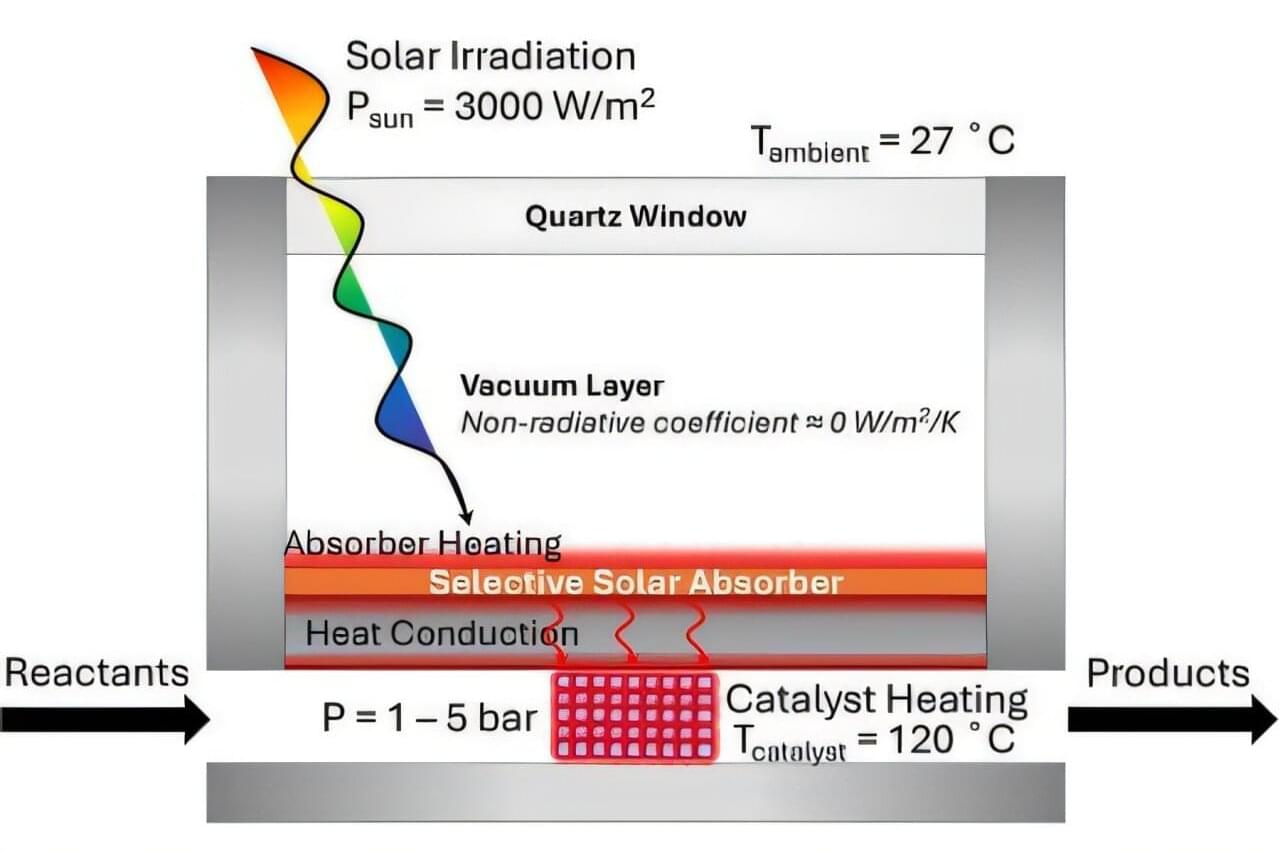
The many emerging PV solutions that have proven to be particularly promising include tandem solar cells based on both perovskites (a class of materials with a characteristic crystal structure) and organic materials. Perovskite/organic tandem solar cells could be more affordable than existing silicon-based solar cells, while also yielding higher power conversion efficiencies.
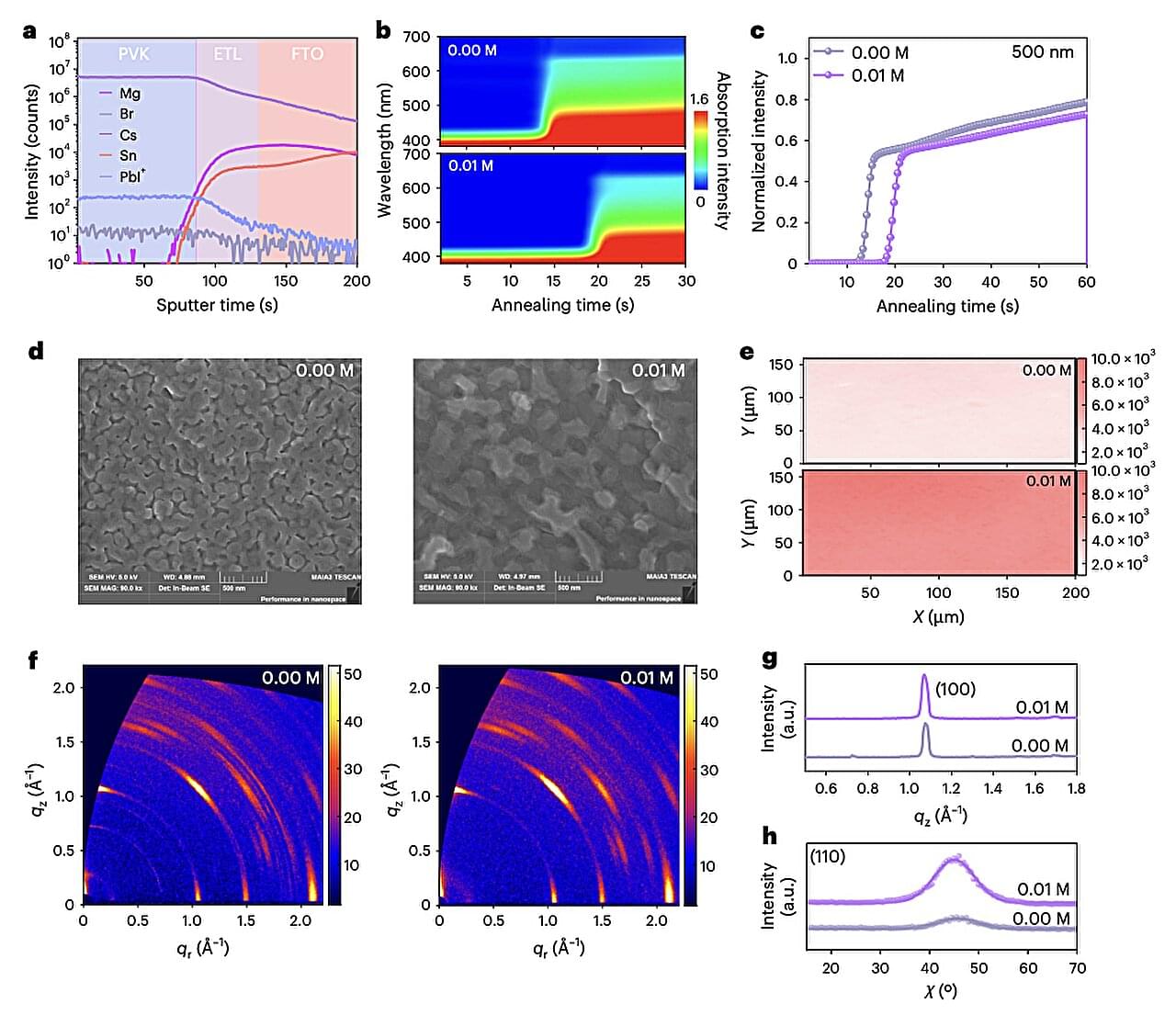
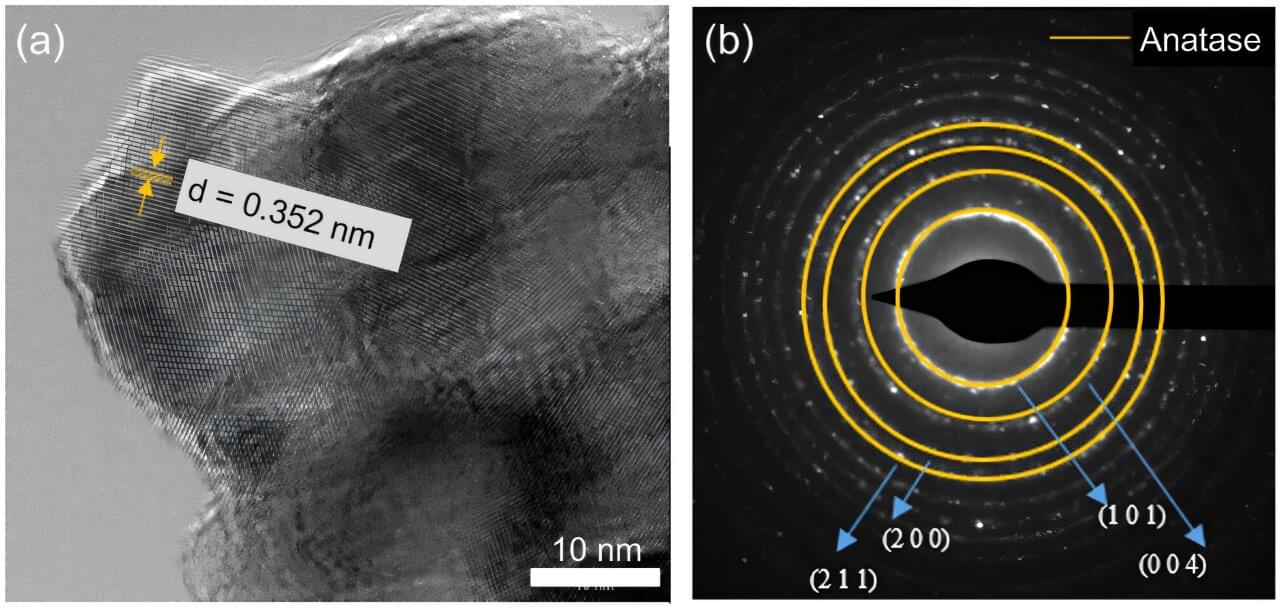
These solar cells are manufactured using wide-bandgap perovskites, which have an electronic bandgap greater than 1.6 electronvolts (eV) and can thus absorb higher-energy photons. Despite their enhanced ability to absorb high-energy light particles, these materials have significant limitations, which typically adversely impact the stability of solar cells.