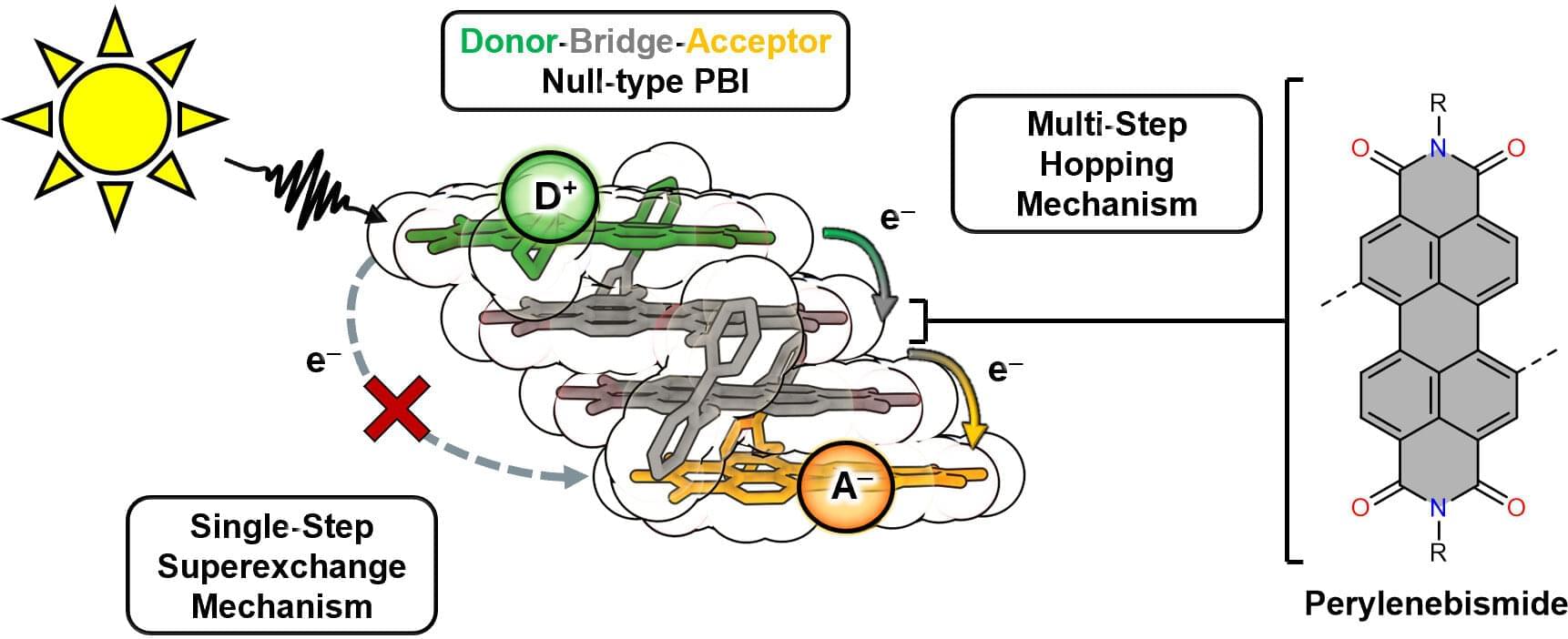
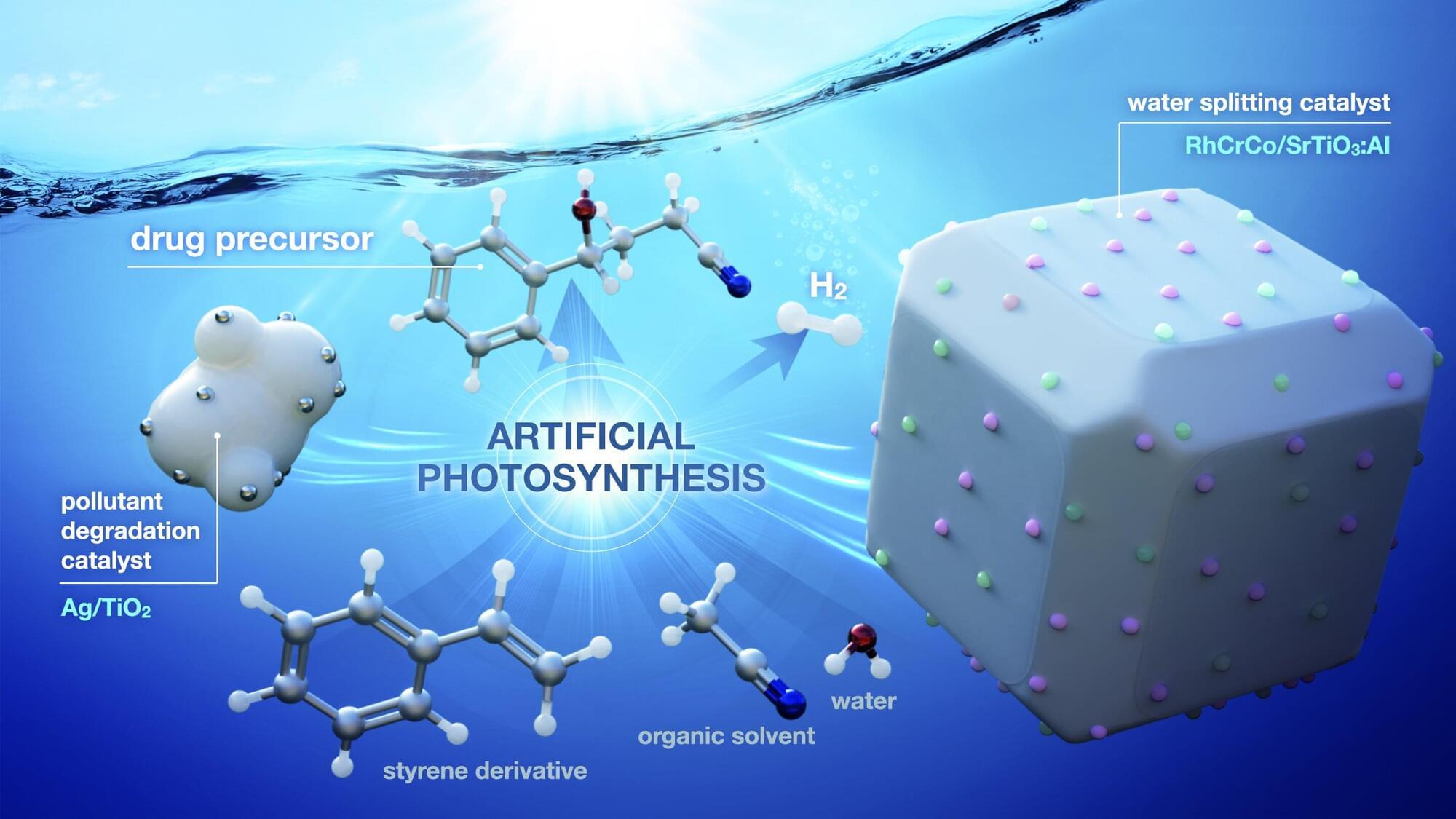
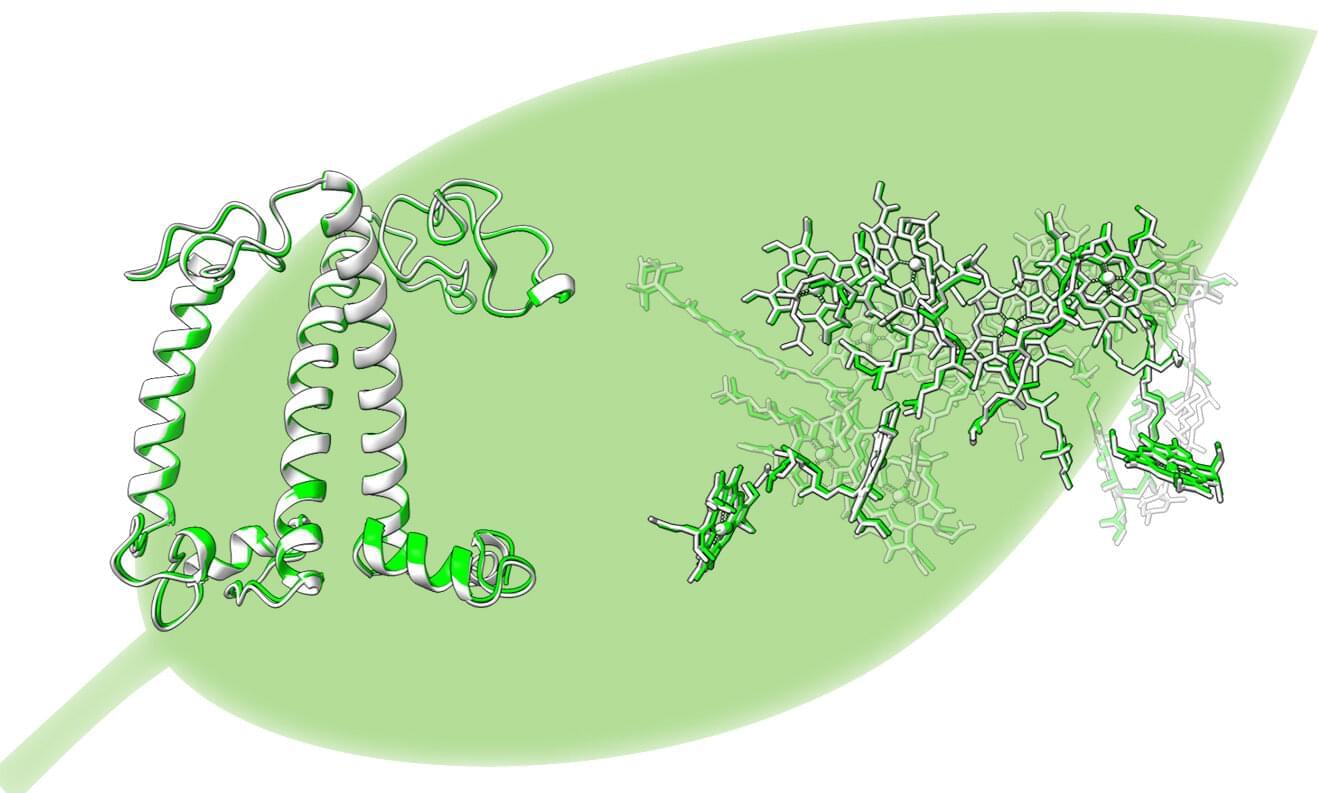
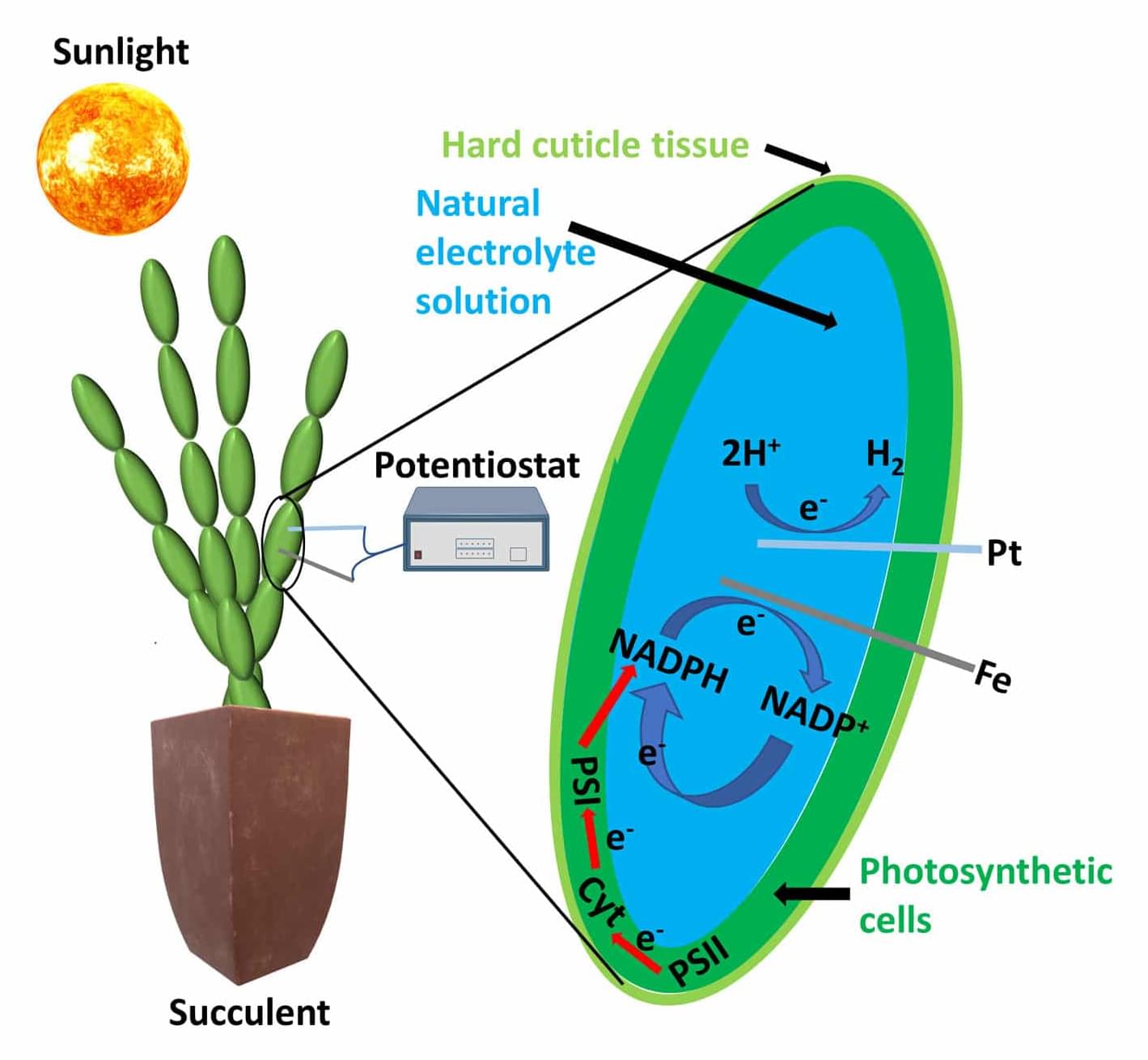
With artificial photosynthesis, mankind could utilize solar energy to bind carbon dioxide and produce hydrogen. Chemists from Würzburg and Seoul have taken this one step further: They have synthesized a stack of dyes that comes very close to the photosynthetic apparatus of plants. It absorbs light energy, uses it to separate charge carriers and transfers them quickly and efficiently in the stack.
Photosynthesis is a marvelous process: plants use it to produce sugar molecules and oxygen from the simple starting materials carbon dioxide and water. They draw the energy they need for this complex process from sunlight.
If humans could imitate photosynthesis, it would have many advantages. The free energy from the sun could be used to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and use it to build carbohydrates and other useful substances. It would also be possible to produce hydrogen, as photosynthesis splits water into its components oxygen and hydrogen.