Less than a millionth of a billionth of a second long, attosecond X-ray pulses allow researchers to peer deep inside molecules and follow electrons as they zip around and ultimately initiate chemical reactions.
Scientists at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory devised a method to generate X-ray laser bursts lasting hundreds of attoseconds (or billionths of a billionth of a second) in 2018. This technique, known as X-ray laser-enhanced attosecond pulse generation (XLEAP), enables researchers to investigate how electrons racing about molecules initiate key processes in biology, chemistry, materials science, and other fields.
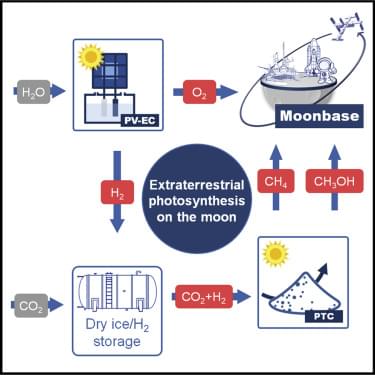
“Electron motion is an important process by which nature can move energy around,” says SLAC scientist James Cryan. “A charge is created in one part of a molecule and it transfers to another part of the molecule, potentially kicking off a chemical reaction. It’s an important piece of the puzzle when you start to think about photovoltaic devices for artificial photosynthesis, or charge transfer inside a molecule.”