The Invictus project is leveraging tech that the now-defunct British company Reaction Engines developed for a huge space plane called Skylon.


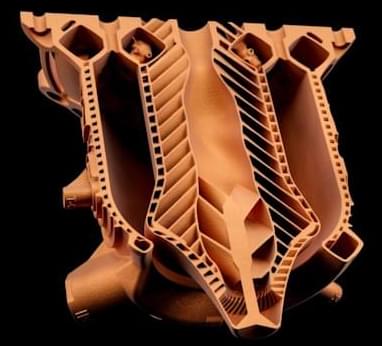
The reason these aerospike style engines haven’t been used more in the past is they’re difficult to design and make. While generally thought of as having the potential to be more efficient, they also require intricate cooling channels to help keep the spike cool. CEO and Co-Founder of LEAP 71, Josefine Lissner, credits the company’s computational AI, Noyron, with the ability to make these advancements.
“We were able to extend Noyron’s physics to deal with the unique complexity of this engine type. The spike is cooled by intricate cooling channels flooded by cryogenic oxygen, whereas the outside of the chamber is cooled by the kerosene fuel.” Said Lissner “I am very encouraged by the results of this test, as virtually everything on the engine was novel and untested. It’s a great validation of our physics-driven approach to computational AI.”
Lin Kayser, Co-Founder of LEAP 71, also believes the AI was paramount in achieving the complex design, explaining “Despite their clear advantages, Aerospikes are not used in space access today. We want to change that. Noyron allows us to radically cut the time we need to re-engineer and iterate after a test and enables us to converge rapidly on an optimal design.”
🧑🚀 Q: What are the details of the upcoming Crew-11 mission? A: Crew-11 is set to launch on July 31st, 2025, with NASA astronaut Zena Cartman as commander, for a 6-month stay on the ISS.
Technical Improvements.
🔧 Q: What new system has SpaceX installed at Pad A for Starship? A: SpaceX installed a new Ship Quick Disconnect (QD) system at Pad A, which is smaller, temporary, and designed for static fire tests only.
🪂 Q: What upgrades have been made to the Dragon spacecraft Endeavor? A: Endeavor now features the Drogue 3.1 parachute system with reinforced crown material and a new packing system for more controlled deployment.
Program Challenges.
🚁 Q: What issues is Boeing’s Starliner program facing? A: Starliner is experiencing helium leaks and thermal management problems affecting its thrusters, delaying the next mission.
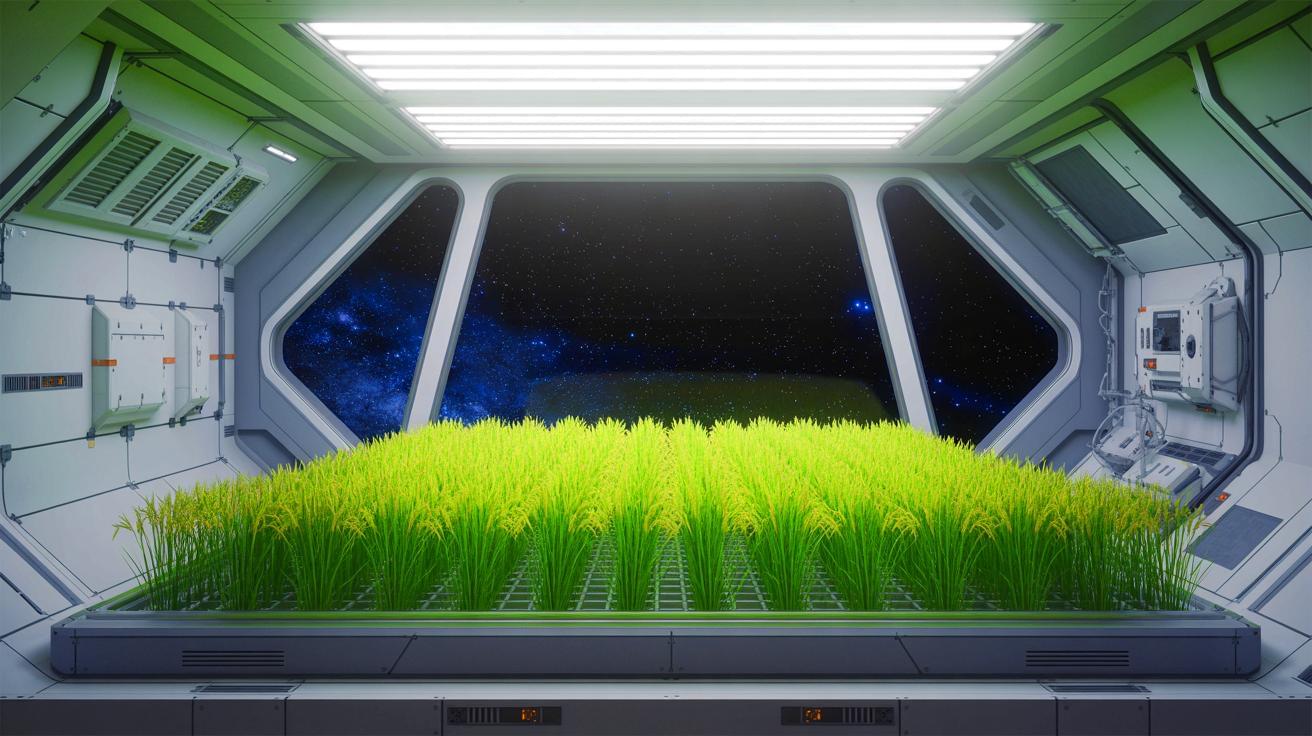
IN A NUTSHELL 🌾 The Moon-Rice project is developing “super-dwarf” rice to support long-duration space missions and extreme Earth environments. 🛰️ Led by the Italian Space Agency, the project involves collaboration between three Italian universities specializing in rice genetics, crop physiology, and space crop production. 🔬 The research focuses on using CRISPR-Cas technology to create

Questions to inspire discussion.
🚀 Q: How might Elon Musk’s diverse projects contribute to Tesla’s value? A: Musk’s involvement in AI, energy, transportation, and communication through projects like Tesla, SpaceX, and Neuralink demonstrates his capacity to make progress on multiple fronts, potentially creating significant value for Tesla.
Political Involvement and Economic Strategy.
🏛️ Q: Why is Elon Musk getting involved in politics? A: Musk’s political involvement aims to create a better political system on Earth, addressing the unsustainability of US government spending and debt to avoid a fiscal doom loop.
📊 Q: What is Musk’s strategy to improve the US economy? A: Musk plans to accelerate GDP growth through AI-driven growth, humanoid bots, and reducing government spending and waste, potentially breaking free from the constant 7% growth line of the US stock market.
💰 Q: How could reducing government spending benefit the economy? A: By cutting wasteful spending and implementing a balanced budget requirement, the US could potentially grow its economy faster than its spending, reducing interest costs and freeing up money for other investments.
In the year 2,525, humans, post-humans, and new species navigate a vast and vibrant future. Join us as we explore the lives, dreams, and struggles of a trillion-strong civilization.
Watch my exclusive video Antimatter Propulsion: Harnessing the Power of Annihilation — https://nebula.tv/videos/isaacarthur–… Nebula using my link for 40% off an annual subscription: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur Get a Lifetime Membership to Nebula for only $300: https://go.nebula.tv/lifetime?ref=isa… Use the link gift.nebula.tv/isaacarthur to give a year of Nebula to a friend for just $30. Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a… Facebook Group:
/ 1,583,992,725,237,264 Reddit:
/ isaacarthur Twitter:
/ isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content. SFIA Discord Server:
/ discord Credits: Life in 2525 A.D. Episode 500; May 22, 2025 Written, Produced & Narrated by: Isaac Arthur Editors: Merv Johnson II & Thomas Owens Graphics: Anthrofuturism Jarred Eagley Jeremy Jozwik Ken York YD Visual Space Resources CGI Udo Schroeter Select imagery/video supplied by Getty Images Music Courtesy of Epidemic Sound http://epidemicsound.com/creator Chris Zabriskie, “Unfoldment, Revealment”, “A New Day in a New Sector” Taras Harkavyi, “Alpha and…” Stellardrone, “Red Giant”, “Billions and Billions” Sergey Cheremisinov, “Labyrinth” 0:00 Intro 0:35 Dinner & Tales of the Future (Story Arc) 7:36 The Captain’s Concerns (Story Arc) 16:37 Episode 500 28:36 Antimatter Propulsion 30:08 On Colonizing Gas Giants and Energy Economics 44:45 Voyage Interrupted.
Get Nebula using my link for 40% off an annual subscription: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Get a Lifetime Membership to Nebula for only $300: https://go.nebula.tv/lifetime?ref=isa…
Use the link gift.nebula.tv/isaacarthur to give a year of Nebula to a friend for just $30.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur.
Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a…
Facebook Group: / 1583992725237264
Reddit: / isaacarthur.
Twitter: / isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: / discord.
Credits:
Life in 2525 A.D.
Episode 500; May 22, 2025
Written, Produced \& Narrated by: Isaac Arthur.
Editors: Merv Johnson II \& Thomas Owens.
Graphics:
Anthrofuturism.
Jarred Eagley.
Jeremy Jozwik.
Ken York YD Visual.
Space Resources CGI
Udo Schroeter.
Select imagery/video supplied by Getty Images.


In a bold move that could transform the future of clean energy and quantum computing, a Seattle-based startup, Interlune, is taking the first steps toward mining the Moon for a rare isotope called helium-3. This new venture has the potential to challenge the boundaries of technology, as well as the frameworks for space exploration and international resource management.