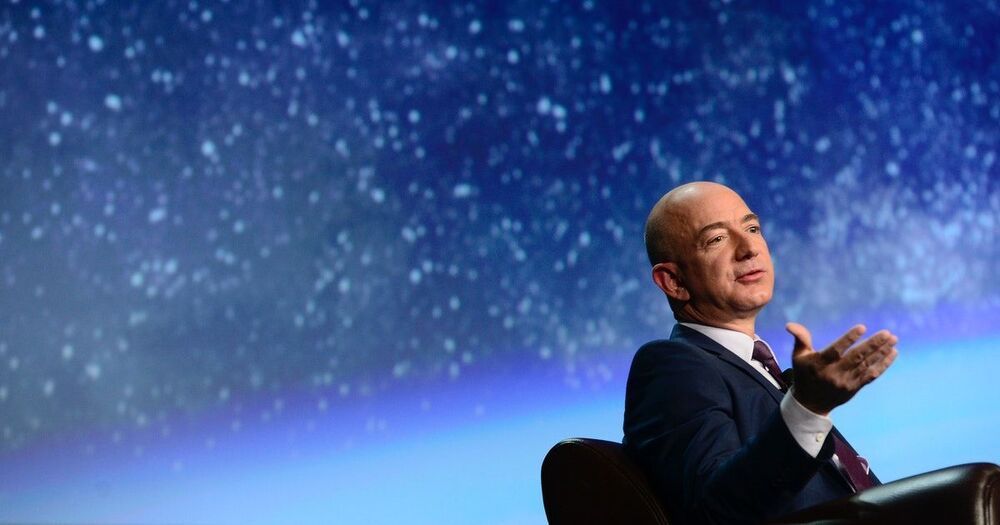
Blue Origin is set to host its first crewed flight next Tuesday, and the firm has finally revealed its full passenger lineup.




The CASC announced its plans to build a reusable space transport system last year, which would involve building a series of spacecraft that take off and land like regular planes, but can reach any corner of the earth within an hour by flying at least five times the speed of sound at a suborbital altitude.
Friday’s test of an experimental vessel is a step towards the development of a hypersonic vehicle that could reach any corner of the Earth within an hour.


The Juno Waves instrument “listened” to the radio emissions from Jupiter’s immense magnetic field to find their precise locations.
By listening to the rain of electrons flowing onto Jupiter from its intensely volcanic moon Io, researchers using NASA’s Juno spacecraft have found what triggers the powerful radio emissions within the monster planet’s gigantic magnetic field. The new result sheds light on the behavior of the enormous magnetic fields generated by gas-giant planets like Jupiter.
Jupiter has the largest, most powerful magnetic field of all the planets in our solar system, with a strength at its source about 20000 times stronger than Earth’s. It is buffeted by the solar wind, a stream of electrically charged particles and magnetic fields constantly blowing from the Sun. Depending on how hard the solar wind blows, Jupiter’s magnetic field can extend outward as much as two million miles (3.2 million kilometers) toward the Sun and stretch more than 600 million miles (over 965 million kilometers) away from the Sun, as far as Saturn’s orbit.


Universe Today.
Space may be pretty, but it’s dangerous. Astronauts face a much higher dose of ionizing radiation than us Earth-bound folks, and a new report says that NASA’s current guidelines and risk assessment methods are in serious need of an update.
On the surface of the Earth, protected by our extensive magnetic field and layers of thick atmosphere, we experience about 2–3 milliSieverts (mSv) of radiation exposure every year. Even that background level is enough to trigger the occasional cancer growth.
But astronauts, especially those hoping to go on upcoming long-term missions to the Moon and Mars, face a much greater risk due to the high-energy, ionizing radiation constantly soaking every cubic centimeter of space. To mitigate that risk, NASA currently implements a system based on “risk of exposure-induced death” (REID). The space agency estimates the exposure for each astronaut based on their sex, and if the REID exceeds 3%, their spacefaring careers are over.
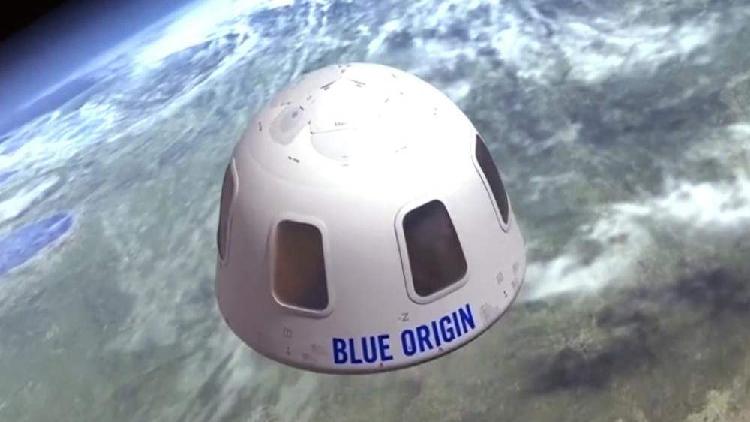

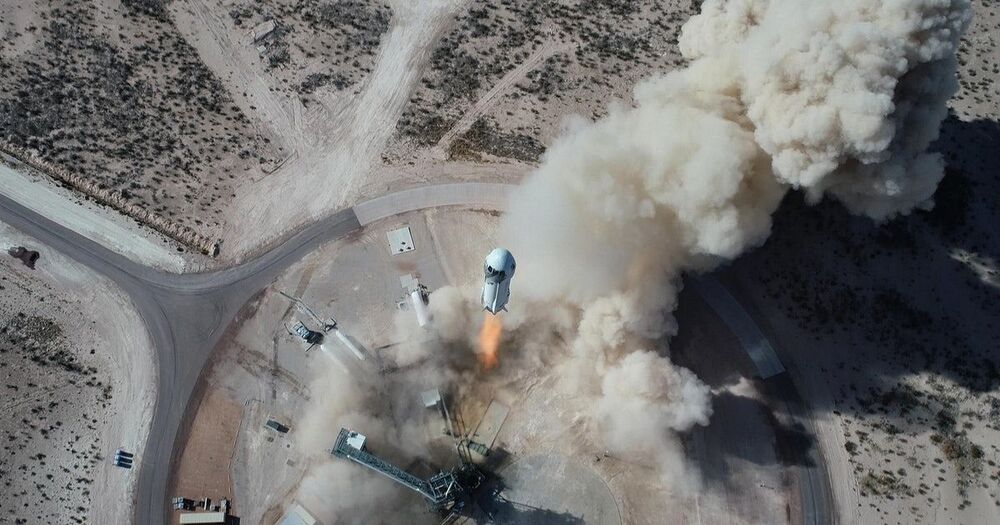
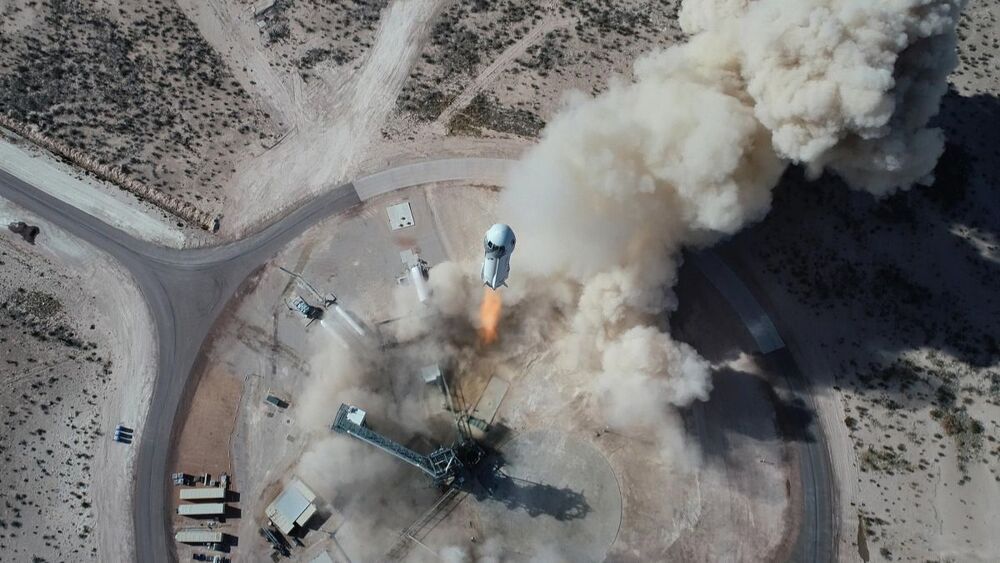
An 18-year-old is about to become the youngest person in space, rocketing away with an aviation pioneer who will become the oldest at age 82.
Blue Origin announced Thursday that instead of a $28 million auction winner launching with founder Jeff Bezos on Tuesday, the Dutch son of another bidder will be on board. The company said Oliver Daemen will be the first paying customer, but did not disclose the price of his ticket. A family spokesperson said it will be considerably less than the winning bid.
Daemen snagged the fourth and last seat on the space capsule after the auction winner stepped aside because of a scheduling conflict. The offer came in a surprise phone call from Blue Origin last week, he said.
Circa 2012 One day ice from could be transformed to metal the be transported anywhere even into space.
Researchers have combined high-powered computing and ‘chemical intuition’ to discover new phases of ice at extremely high pressures nonexistent on Earth, but probably abundant elsewhere in the solar system. (Jan. 16, 2012)