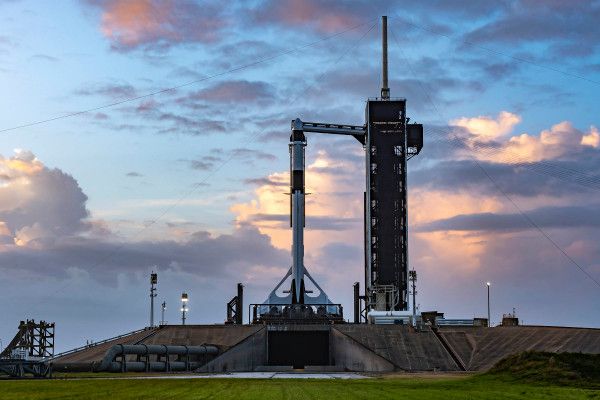
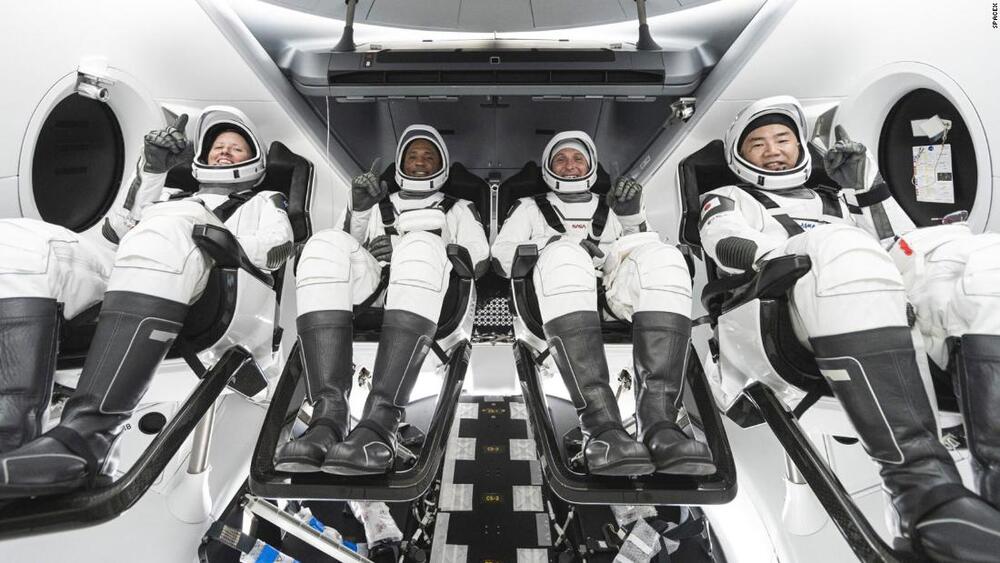
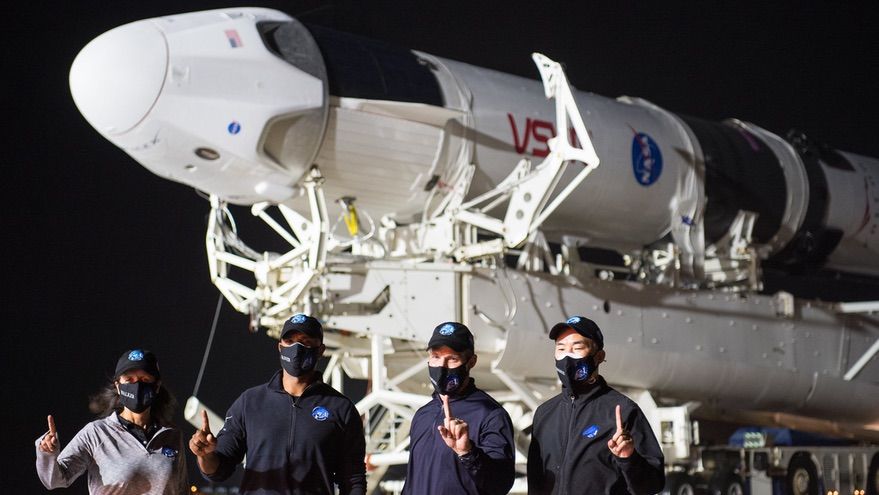
SpaceX and NASA have spent years working towards today’s Crew-1 mission, which is set to launch from Florida at 7:27 PM EST (4:27 PM PST). This is the first time that SpaceX’s Dragon capsule and Falcon 9 rocket will be officially used as a spacecraft certified by NASA for human flight on a regular astronaut transportation operation. NASA astronauts Mike Hopkins, Victor Glover and Shannon Walker, along with JAXA astronaut Soichi Noguchi, will also be aboard the Dragon spacecraft and, barring any weather delays, on their way to the International Space Station later Sunday night.
SpaceX has already flown people using Dragon – NASA astronauts Bob Behnken and Doug Hurley had the honor of being the first humans ever to be launched to the ISS aboard a commercial spacecraft when they took part in SpaceX’s Demo-2 mission earlier this year. That was obviously a historic achievement, but it was also technically the last stage in SpaceX’s test and demonstration program for Dragon and Falcon 9, whereas today’s Crew-1 launch no longer qualifies as a test. Think of it this way: If Demo-2 was akin to the Wright Brothers’ Kitty Hawk flight, Crew-1 will be the equivalent of the first U.S. scheduled commercial airline flight in 1914.
Crew-1 will be the first time that a full complement of astronauts are flown on Dragon (there are six total seats but NASA has said it will only ever fly a max of four of its and partner agency crew to the ISS on these flights). The astronauts will join the existing crew on the ISS for a regular tour of performing experiments, maintaining and upgrading the station, which will also see the active ISS population swell by one additional astronaut for the first time during a standard rotation, which means more science can get done according to the agency.