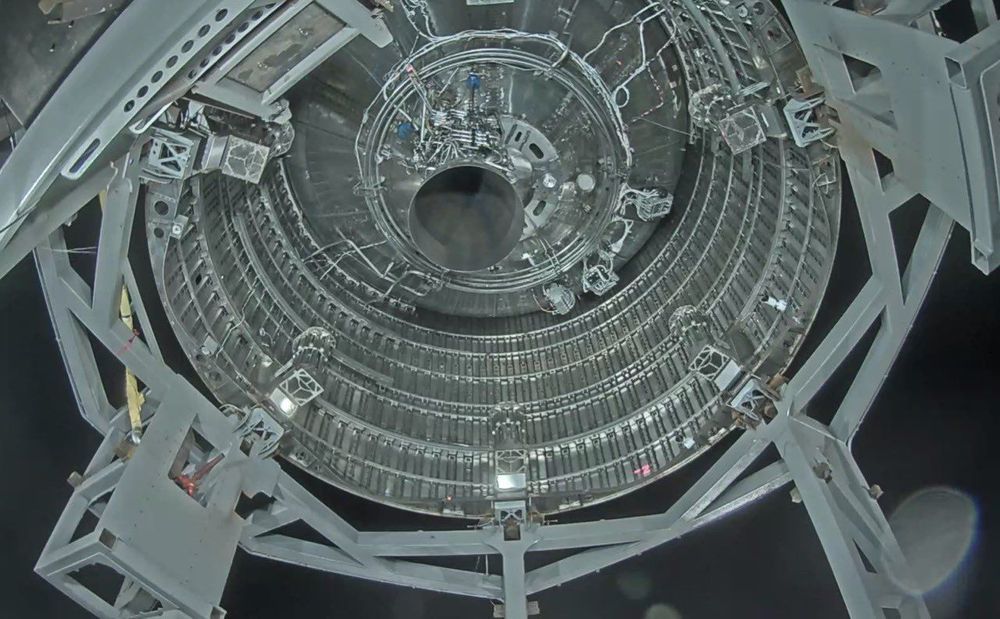
SpaceX has put the Starship SN4 through its paces ahead of an expected launch.

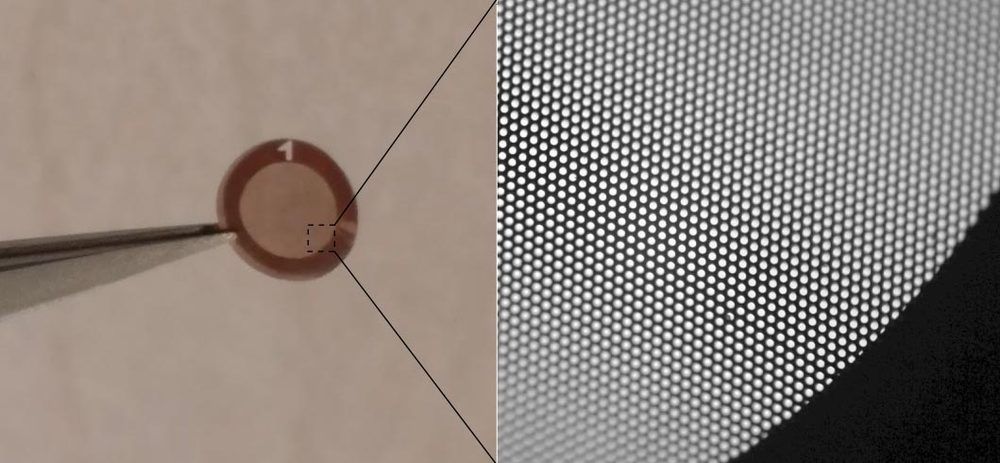
Graphene light sail of 3mm in diameter with a mass of 0.25 mg ‘sets sail’ when pointed with a 1W laser. The prototype has a graphene micromembrane design that reduces the overall mass while keeping functional the complete area of the sail. Credit: Dr. Santiago Jose Cartamil-Bueno.
Overseas exploration and trade during the Age of Discovery (15th-17th centuries) were possible by sail technology, and deep-space exploration will require the same for the coming Age of NewSpace. This time, however, the new sails shall move with light instead of wind, for which these light sails need to be extremely large, thin, lightweight, reflective, and strong.
In a light-hearted leap for humankind, ESA-backed researchers demonstrate the laser-propulsion of graphene sails in microgravity.

New spacecraft experience setbacks all the time. SpaceX Starship prototype violently disassembled several times. Boeing launched the CST-100 but ended up in the wrong orbit. China isn’t a stranger to setbacks either.
China tested a prototype spacecraft on May 5th, 2020 in efforts to prove the technology was ready. It’s good it was a test and not an actual mission since the spacecraft did not perform as expected. The news agency Xinhua reported the spacecraft launched from Hainan China, operated abnormally during its return.
Spacecraft experience tremendous heat during the last minutes of their mission. The heat shield protects the spacecraft from that heat. NASA looked at lots of materials and tested many before using for heat shields.
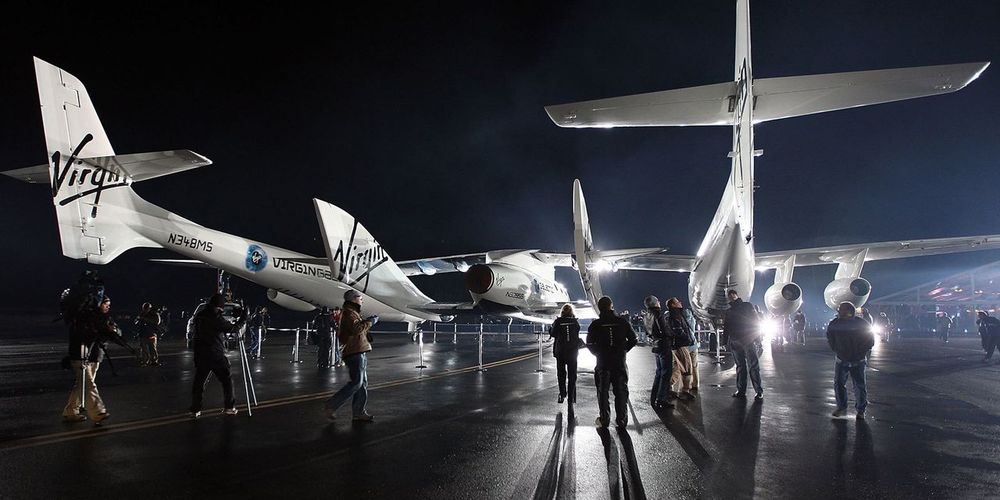

Virgin Galactic reported first-quarter earnings and the stock is surging in premarket trading. People, it seems, can’t wait to leave Earth. That’s a good thing for the fledgling space-tourism company.
Virgin (ticker: SPCE) reported $238,000 in first-quarter sales. But sales and earnings don’t matter yet. Virgin is “presales” at this stage of its life. The company is working with aviation authorities to approve its spacecraft and its plans for ferrying customers to the edge of Earth’s atmosphere. It completed two test flights from its New Mexico spaceport in the first quarter.
But sales are coming. During the quarter, the company launched an initiative for tourist-astronauts to reserve a place in Galactic’s flight queue, attracting commitments for up to $100 million in sales.
Circa 2016
Researchers say the new ‘impossible’ drive could carry passengers and their equipment to the moon in as little as four hours.
A trip to Alpha Centauri, which would take tens of thousands of years now, could be reached in just 100 years.
The system is based on electromagnetic drive, or EMDrive, which converts electrical energy into thrust without the need for rocket fuel.
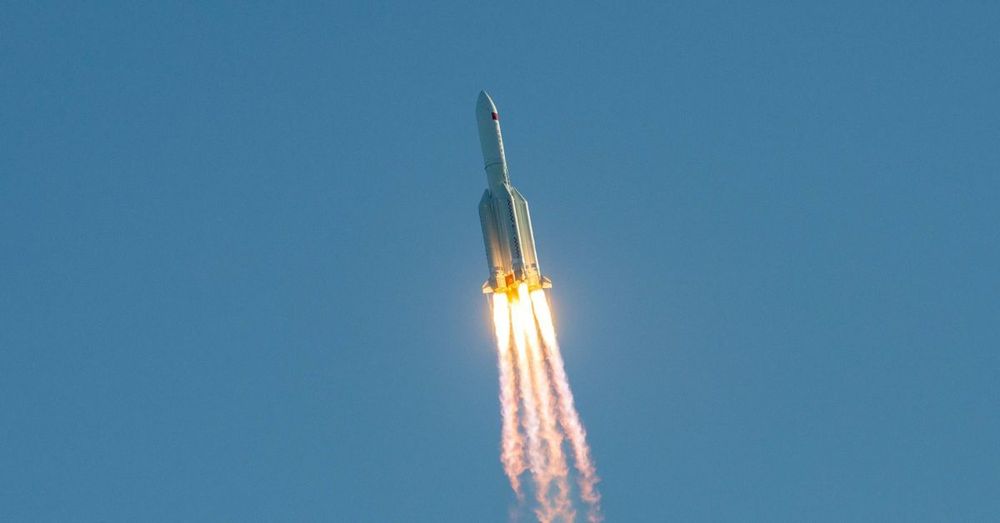

On May 4th, China launched a pivotal new rocket called the Long March 5B, carrying a prototype deep-space spacecraft into orbit around Earth. The successful launch is meant to test out the country’s plans for sending humans to deep space, and it paves the way for the country’s ambitious space projects in the year ahead.

Tom Cruise is going to film in space thanks to Elon Musk.
EXCLUSIVE: I’m hearing that Tom Cruise and Elon Musk’s Space X are working on a project with NASA that would be the first narrative feature film – an action adventure – to be shot in outer space. It’s not a Mission: Impossible film and no studio is in the mix at this stage but look for more news as I get it. But this is real, albeit in the early stages of liftoff.
Mission: Impossible Fallout took a break, literally when he broke his ankle in a leap from one rooftop to the other and he also hung from a helicopter; he hung from the side of a jet plane during takeoff in Mission: Impossible Rogue Nation, and in Mission: Impossible: Ghost Protocol he scaled the Burj Khalifa, the Dubai skyscraper, and executed stunts 123 floors up. He is meticulous in preparing these stunts he does, which are frightening just to watch.
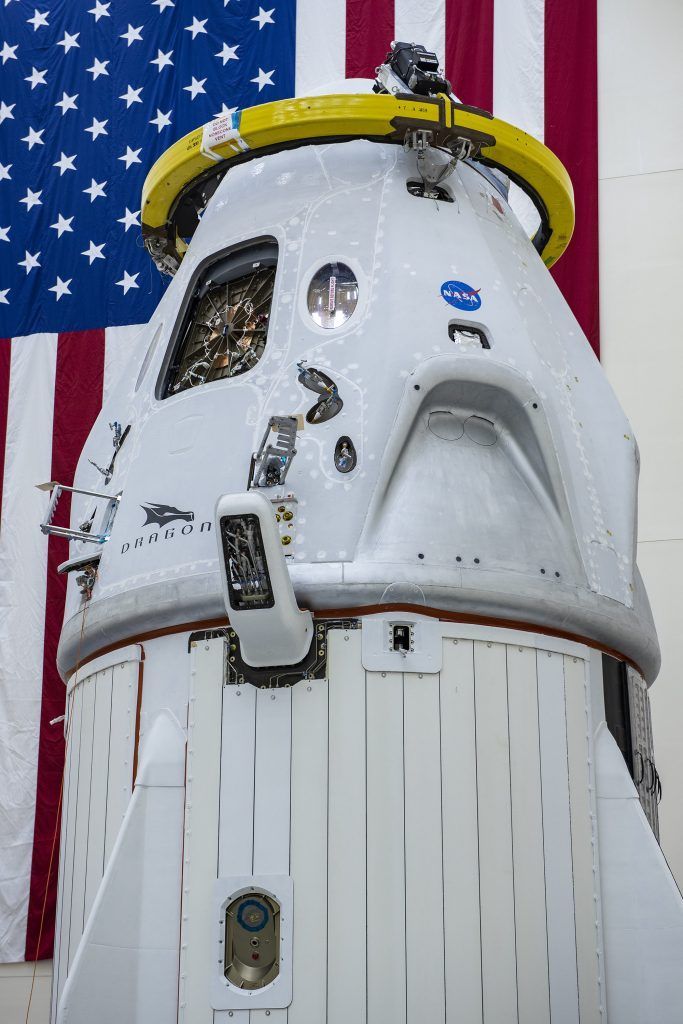

The SpaceX Crew Dragon trunk was secured to the spacecraft on Thursday, April 30, at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, in preparation for launch of NASAfs SpaceX Demo-2 mission.
NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley will fly to the International Space Station aboard the Crew Dragon spacecraft launched atop a Falcon 9 rocket. Liftoff from Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A is slated for May 27 at 4:32 p.m. EDT.
Demo-2 will serve as an end-to-end test of SpaceX’s crew transportation system, paving the way for NASA to certify the system for regular crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory as a part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. NASA’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission will be the first crewed flight to launch from U.S. soil since the conclusion of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011.
