How did meteorite impacts on the Moon influence water being delivered to Earth when both planetary bodies were forming? This is what a recent study publish | Space



Read “” by Myk Eff on Medium.
When Freud first mapped the territories of the unconscious, he could only speak in the metaphors available to him — hydraulic pressures, economic systems, topographical layers. Yet the phenomena he described possess a striking affinity with concepts that would not emerge until decades later, when Claude Shannon formalized information theory and computing science revealed the architecture of data itself. What if the mechanisms Freud, Jung, and their successors laboriously documented are, at their foundation, information processing operations? What if repression is encryption, condensation is compression, and the deepest strata of the psyche represent not mystical depths but maximal data density?
The proposition is not merely metaphorical. Consider Freud’s description of repression in Repression (1915): the mechanism whereby the ego refuses admittance to consciousness of ideational content that threatens its equilibrium. Freud wrote that repression lies simply in turning something away, and keeping it at a distance, from the conscious (p. 147). Yet this keeping at a distance operates through a curious transformation. The repressed content does not vanish; it persists, inaccessible yet influential, distorting thought and behavior through its very concealment.
This is precisely analogous to encrypted data. Encryption transforms information into a form that resists interpretation without the proper key, yet the information remains fully present, its structure intact but rendered opaque. The encrypted file occupies space, exerts influence on system resources, and can corrupt or destabilize processes that attempt to access it incorrectly. Similarly, repressed material occupies psychic space and generates symptoms — failed decryption attempts, as it were — when consciousness approaches without the therapeutic key.


The team, led by NUY Abu Dhabi’s Panče Naumov, developed a material they dubbed smart molecular crystals. In a paper published in the journal Nature Materials, they outlined the observation process that allowed them to identify the material’s impressive properties.
During experiments, they observed that the material could be mechanically damaged in extreme cold and then repair itself. Importantly, it also recovered its ability to transmit light after being damaged. This is essential for low-temperature flexible optical and electronic devices.
According to a press statement, the material can restore its structure even at temperatures as low as −196°C (−320°F), the boiling temperature of liquid nitrogen. The material also remains functional throughout a wide temperature range, going up to 150°C (302°F).

Morten E. Iversen, partner at Sandwater, said that Filics technology offers not only substantial space efficiency but also a flexible, scalable path to the automation of warehouses:
For Sandwater, it represents a transformative solution that can redefine warehouse operations—reducing space needs, boosting productivity, and achieving a smaller footprint through a smart hardware/software combination. We have been truly impressed by the team.
The Filics Unit will be further developed for use in floor block warehouses by the end of 2025, enabling up to 66 per cent space savings to be achieved. In the medium term, the company plans to develop the technology further to enable fully autonomous truck loading in under five minutes.
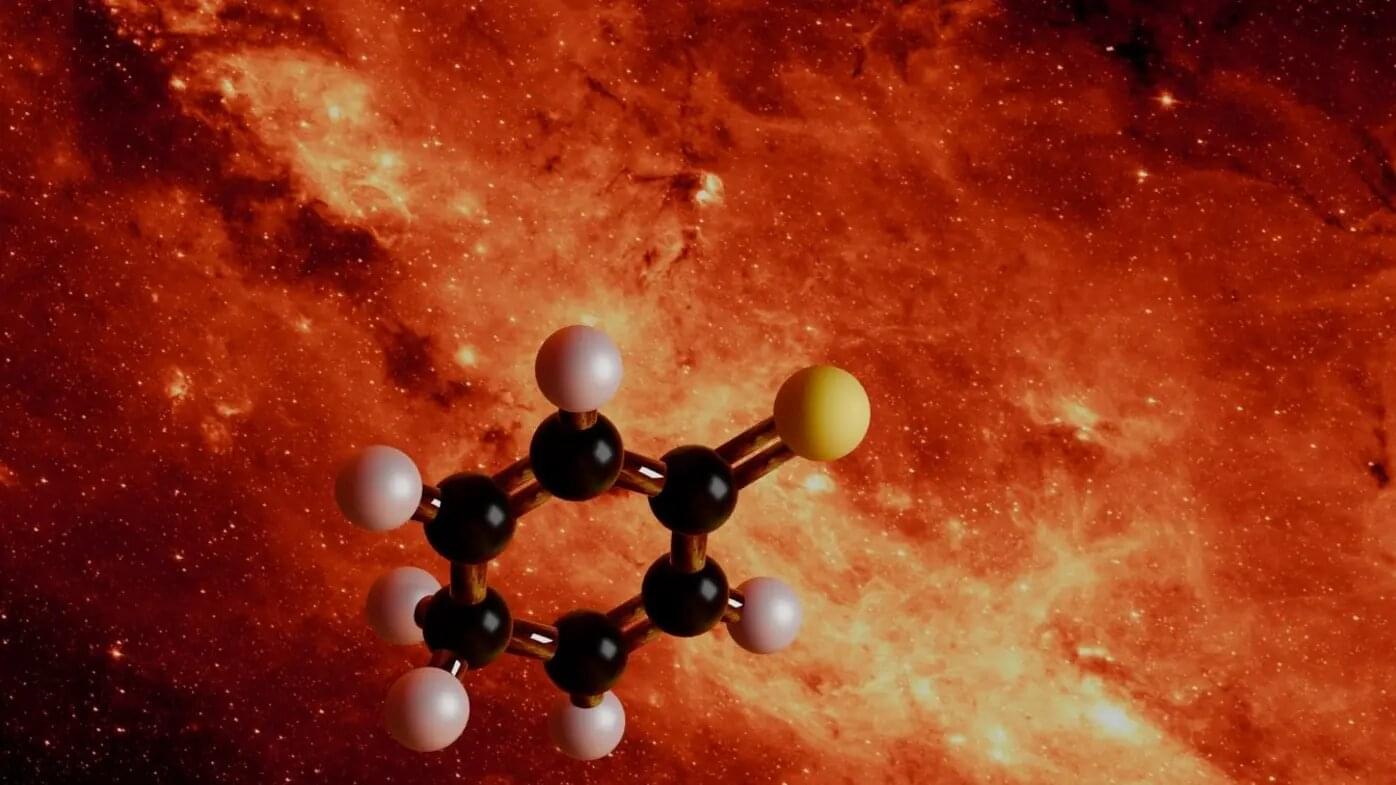
Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics (MPE), in collaboration with astrophysicists from the Centro de Astrobiología (CAB), CSIC-INTA, have identified the largest sulfur-bearing molecule ever found in space: 2,5-cyclohexadiene-1-thione (C₆H₆S). They made this breakthrough by combining laboratory experiments with astronomical observations. The molecule resides in the molecular cloud G+0.693–0.027, about 27,000 light-years from Earth near the center of the Milky Way.
With a stable six-membered ring and a total of 13 atoms, it far exceeds the size of all previously detected sulfur-containing compounds in space. The study is published in Nature Astronomy.
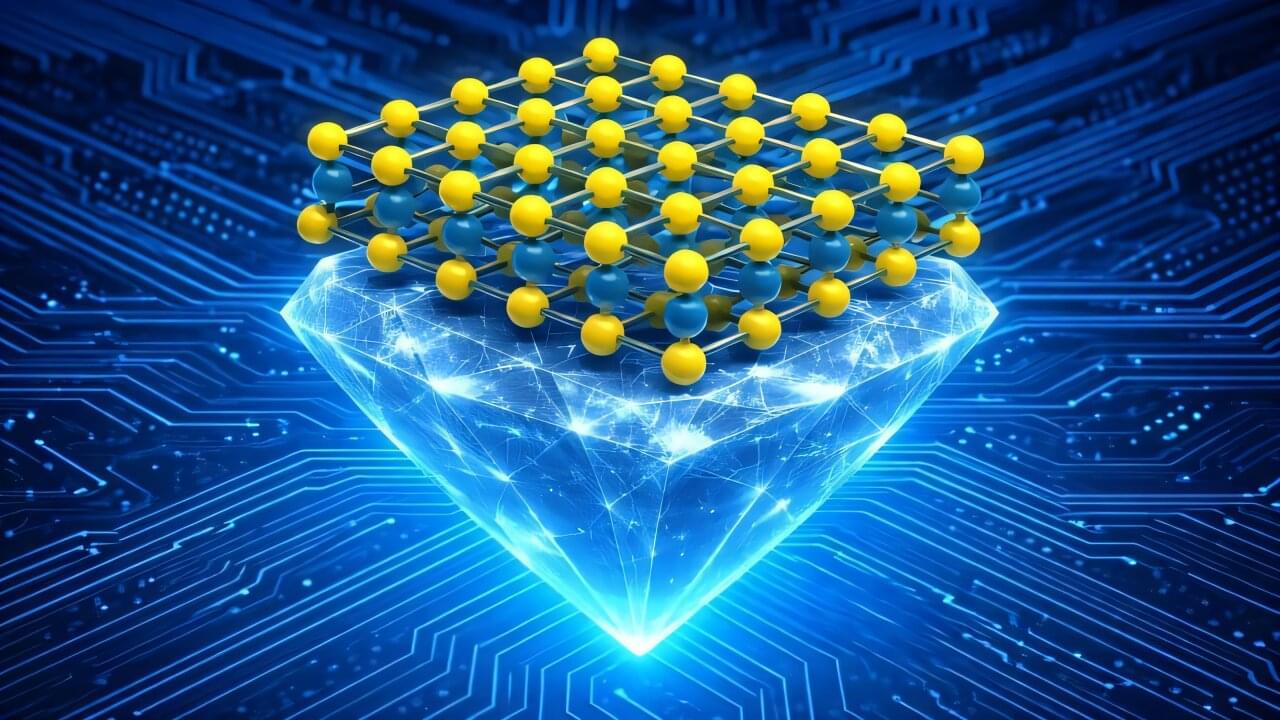
Beyond their sparkle, diamonds have hidden talents. They shed heat better than any material, tolerate extreme temperatures and radiation, and handle high voltages while wasting almost no electricity—ideal traits for compact, high-power devices. These properties make diamond-based electronics promising for applications in the power grid, industrial power switches, and places with high radiation, such as space or nuclear reactors.
Diamond’s ability to quickly carry heat away from electronic components allows devices to handle large currents and voltages without overheating. This means smaller devices can be used to switch to high power in the grid or in industrial settings. Diamond’s natural resistance to radiation and extreme temperatures could enable electronics to work reliably in places where traditional silicon devices fail.
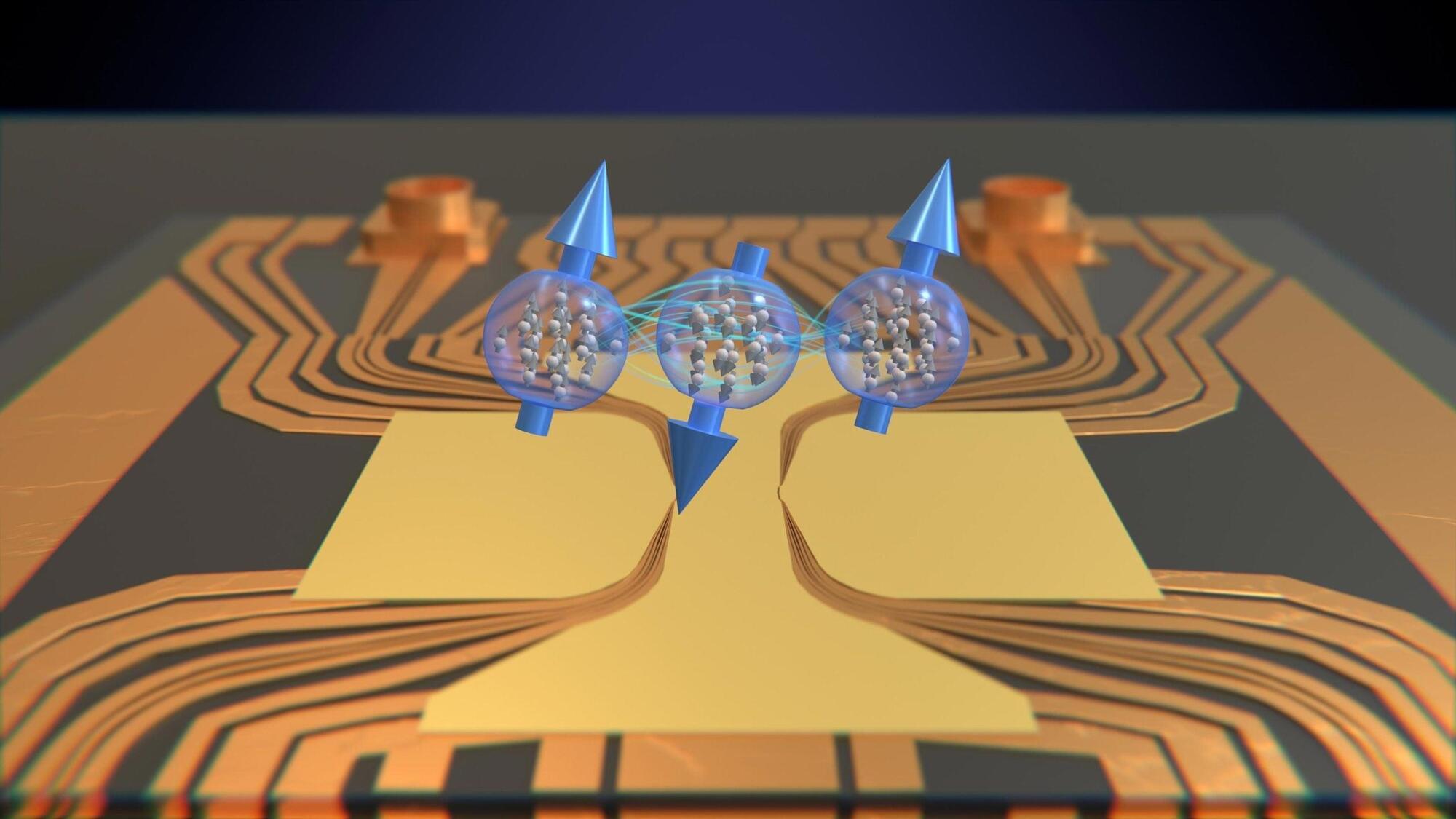
Entangled atoms, separated in space, are giving scientists a powerful new way to measure the world with stunning precision.
Researchers from the University of Basel and the Laboratoire Kastler Brossel have shown that quantum entanglement can be used to measure multiple physical quantities at the same time with greater accuracy than previously possible.
What makes quantum entanglement so unusual.
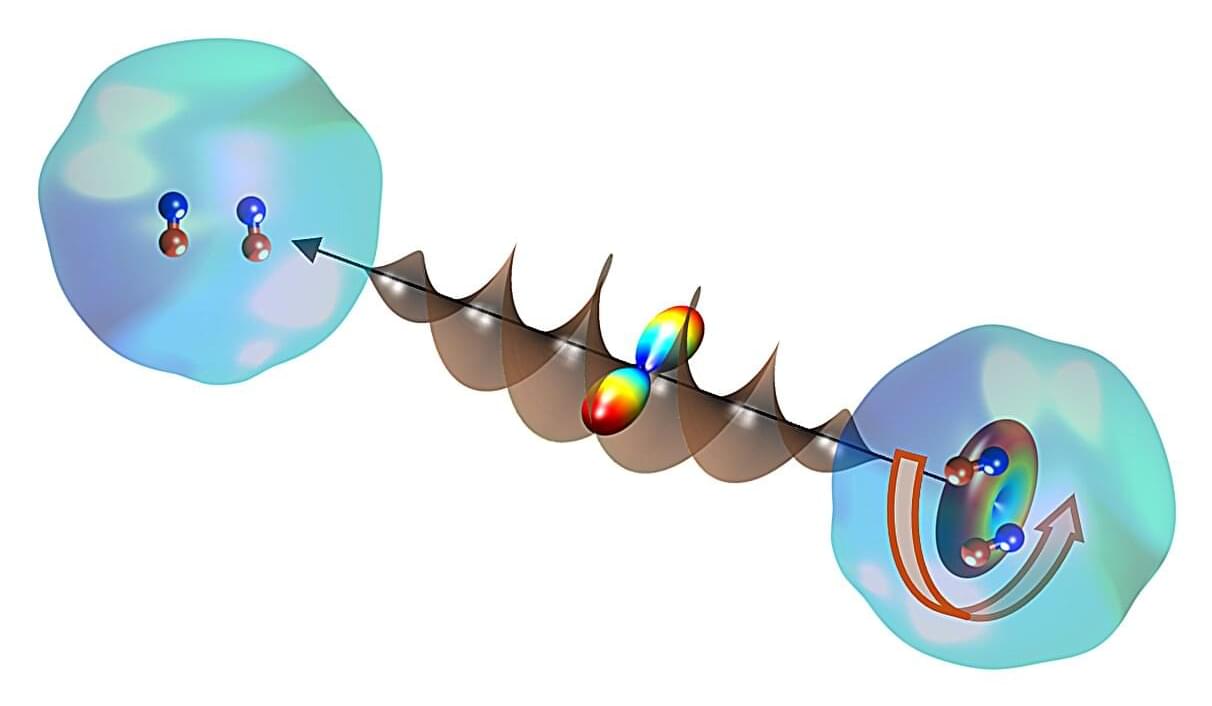
Physicists have used a new optical centrifuge to control the rotation of molecules suspended in liquid helium nano-droplets, bringing them a step closer to demystifying the behavior of exotic, frictionless superfluids.
It’s the first demonstration of controlled spinning inside a superfluid—researchers can now directly set the direction and frequency of the molecule’s rotation, which is vital in studying how molecules interact with the quantum environment at various rotational frequencies. The method was outlined this week by researchers at the University of British Columbia (UBC) and colleagues at the University of Freiburg in the journal Physical Review Letters.
“Controlling the rotation of a molecule dissolved in any fluid is a challenge,” said Dr. Valery Milner, associate professor with UBC Physics and Astronomy and lead author on the paper.