The probe will map the surface, deploy rovers and collect pristine samples that could contain clues about the origins of life on Earth.
- By Elizabeth Tasker on June 29, 2018

The probe will map the surface, deploy rovers and collect pristine samples that could contain clues about the origins of life on Earth.

Based on posts I’ve seen from techies, militarizing space is a total fail. However, space is already militarized — Nothing goes into air space without Air Force approval… ANY organization developed to “regulate” Space has the potential for corruption whether that be collaborative, international entities which always panders to herd think, or stale governmental organizations. I’m undecided on this.
The White House, Air Force and Defense Secretary James Mattis had disapproved of creating a sixth branch of the military last year.

Very interesting.
“It is possible for a computer to become conscious. Basically, we are that. We are data, computation, memory. So we are conscious computers in a sense.”
— Tom Campbell, NASA, Author of My Big TOE
If the universe is a computer simulation, virtual reality, or video game, then a few unusual conditions seem to necessarily fall out from that reading. One is what we call consciousness, the mind, is actually something like an artificial intelligence. If the universe is a computer simulation, we are all likely one form of AI or another. In fact, we might come from the same computer that is creating this simulated universe to begin with. If so then it stands to reason that we are virtual characters and virtual minds in a virtual universe.

Astronomers have found iron and titanium in the atmosphere of the Jupiter-sized world KELT-9b, the hottest known exoplanet.
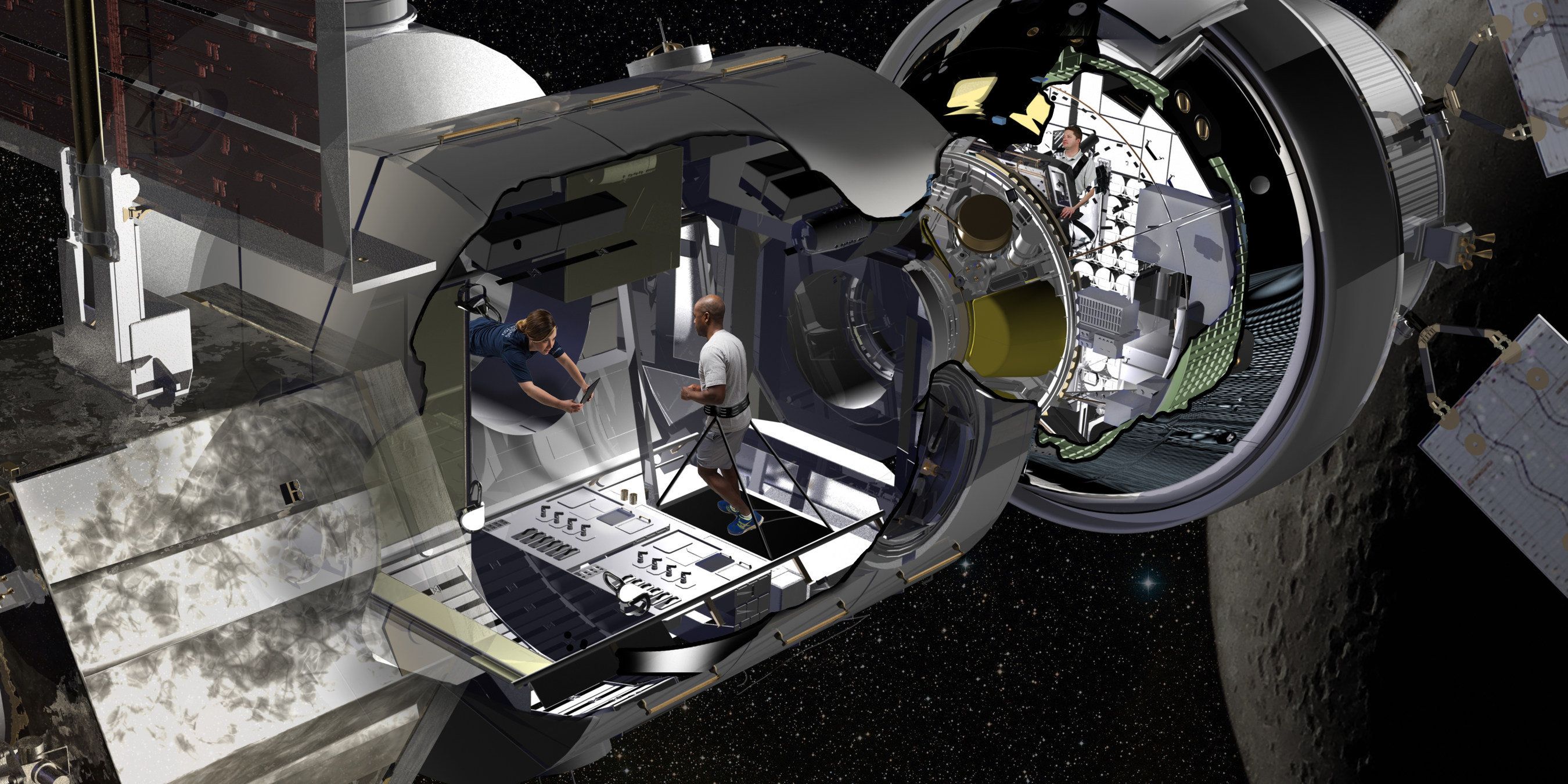

A massive cylindrical habitat may one day house up to four astronauts as they make the trek to deep space.
Lockheed Martin gave a first look at what one of these habitats might look like Thursday at the Kennedy Space Center, where the aerospace giant is under contract with NASA to build a prototype of the living quarters.
Lockheed is one of six contractors—the others are Boeing, Sierra Nevada Corp.‘s Space Systems, Orbital ATK, NanoRacks and Bigelow Aerospace—that NASA awarded a combined $65 million to build a habitat prototype by the end of the year. The agency will then review the proposals to reach a better understanding of the systems and interfaces that need to be in place to facilitate living in deep space.


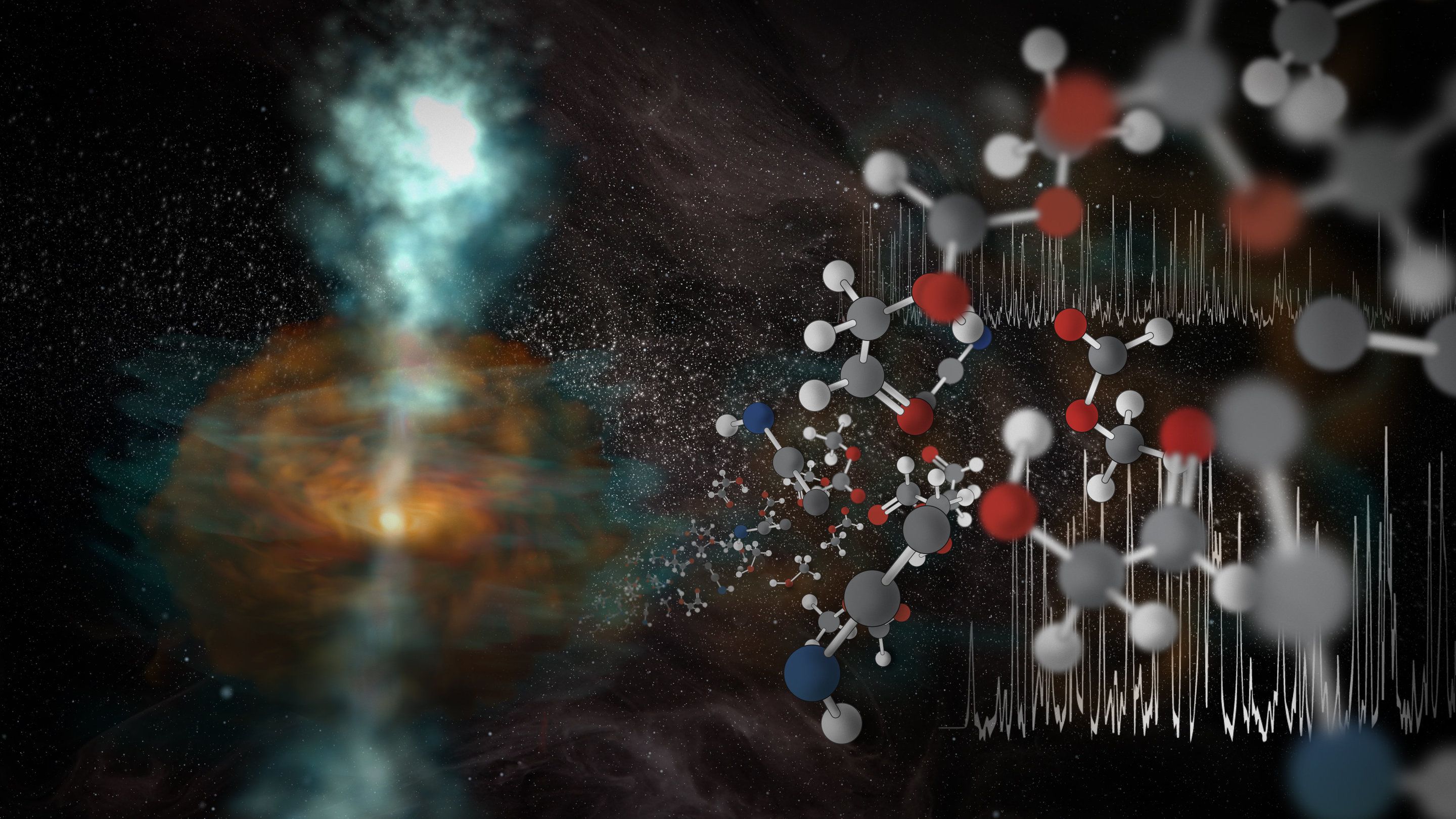
The ALMA telescope in Chile has transformed how we see the universe, showing us otherwise invisible parts of the cosmos. This array of incredibly precise antennas studies a comparatively high-frequency sliver of radio light: waves that range from a few tenths of a millimeter to several millimeters in length. Recently, scientists pushed ALMA to its limits, harnessing the array’s highest-frequency (shortest wavelength) capabilities, which peer into a part of the electromagnetic spectrum that straddles the line between infrared light and radio waves.
“High-frequency radio observations like these are normally not possible from the ground,” said Brett McGuire, a chemist at the National Radio Astronomy Observatory in Charlottesville, Virginia, and lead author on a paper appearing in the Astrophysical Journal Letters. “They require the extreme precision and sensitivity of ALMA, along with some of the driest and most stable atmospheric conditions that can be found on Earth.”
Under ideal atmospheric conditions, which occurred on the evening of 5 April 2018, astronomers trained ALMA’s highest-frequency, submillimeter vision on a curious region of the Cat’s Paw Nebula (also known as NGC 6334I), a star-forming complex located about 4,300 light-years from Earth in the direction of the southern constellation Scorpius.
Here are 4 crazy exoplanets you’ve never heard of.
