A strange new robot from South Korea could be the key to exploring parts of the Moon no one has ever reached, and it’s built to survive the impossible.



Help us help the kids of Ukraine to dream about the future.
Space, hope, and a great cause on the side of freedom. Follow the links. Make the donation, put a telescope, model rocket or robot in the hands of a kid who very badly needs Permission to Dream!
Space4 Ukraine empowers young Ukrainians whose education has been disrupted by war, giving them access to the tools, training, and opportunities they need to rebuild their future—and ours. Because no human potential should ever be wasted.
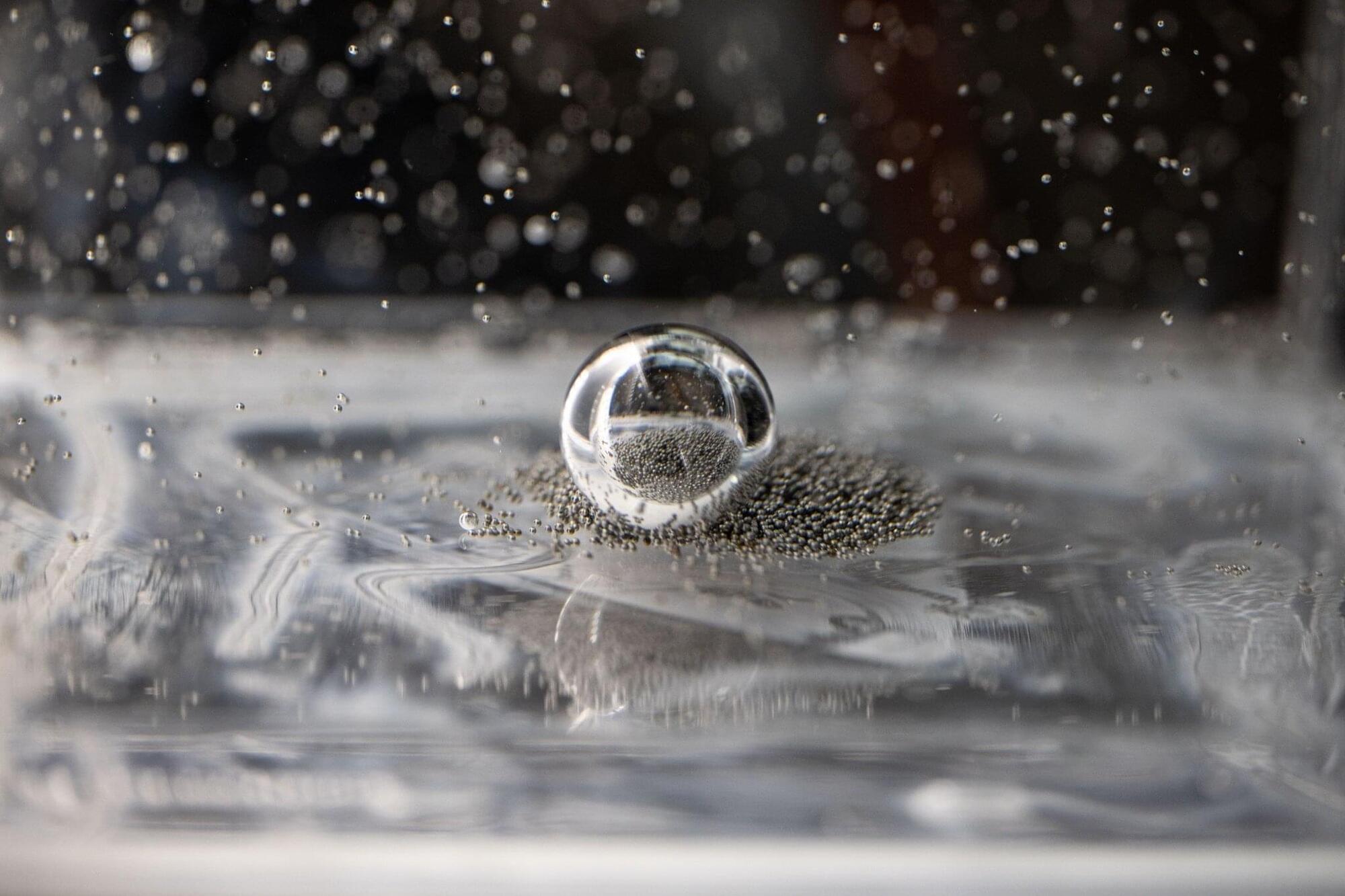


In this Oct. 20, 2025, photo, tiny ball bearings surround a larger central bearing during the Fluid Particles experiment, conducted inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) aboard the International Space Station’s Destiny laboratory module.
A bulk container installed in the MSG, filled with viscous fluid and embedded particles, is subjected to oscillating frequencies to observe how the particles cluster and form larger structures in microgravity. Insights from this research may advance fire suppression, lunar dust mitigation, and plant growth in space. On Earth, the findings could inform our understanding of pollen dispersion, algae blooms, plastic pollution, and sea salt transport during storms.
In addition to uncovering potential benefits on Earth, research done aboard the space station helps inform long-duration missions like Artemis and future human expeditions to Mars.
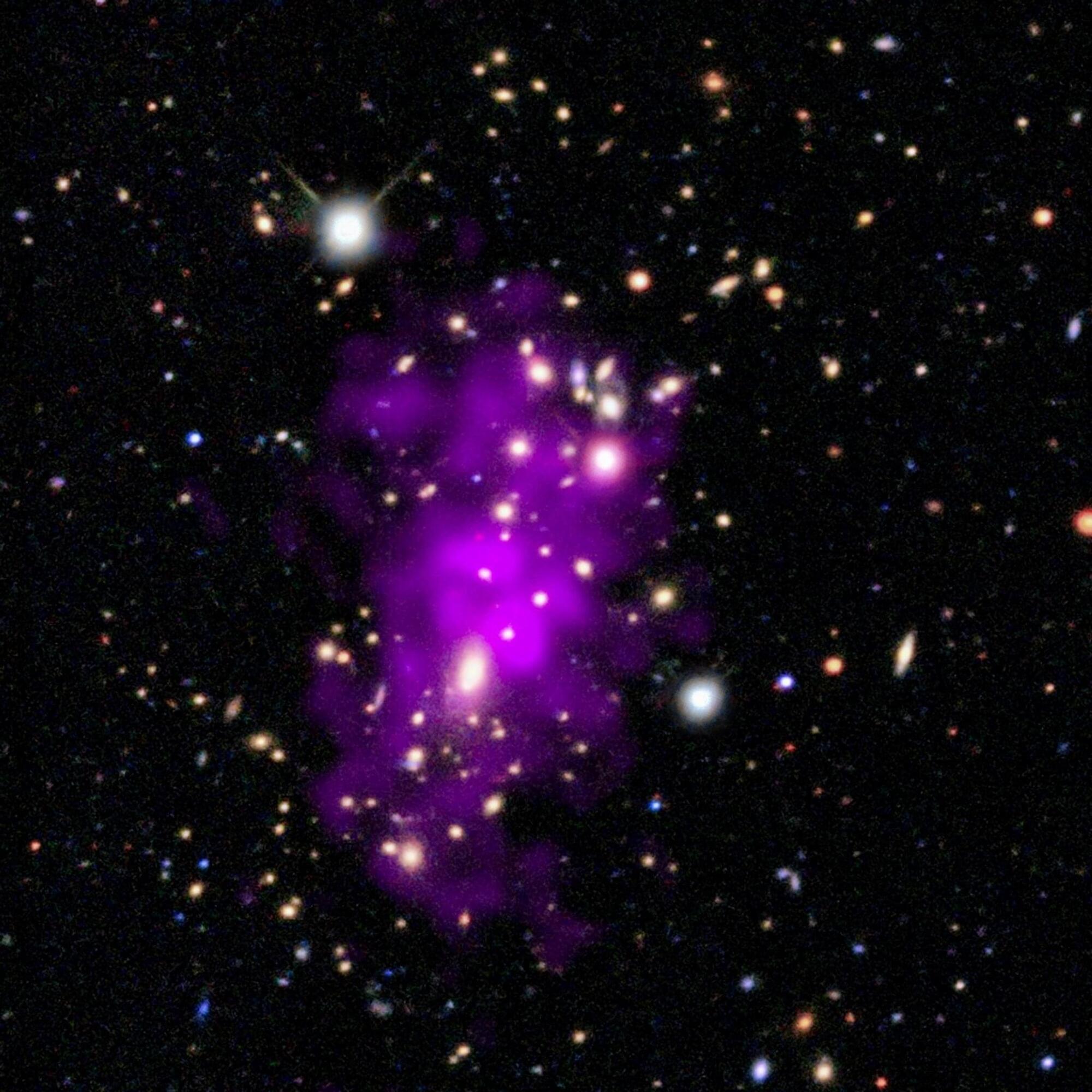


Celebrate the New Year with the “Champagne Cluster,” a galaxy cluster seen in this new image from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and optical telescopes.
Astronomers discovered this galaxy cluster on Dec. 31, 2020. The date, combined with the bubble-like appearance of the galaxies and the superheated gas seen with Chandra observations (represented in purple), inspired the scientists to nickname the galaxy cluster the Champagne Cluster, a much easier-to-remember name than its official designation of RM J130558.9+263048.4.
The new composite image shows that the Champagne Cluster is actually two galaxy clusters in the process of merging to form an even larger cluster.
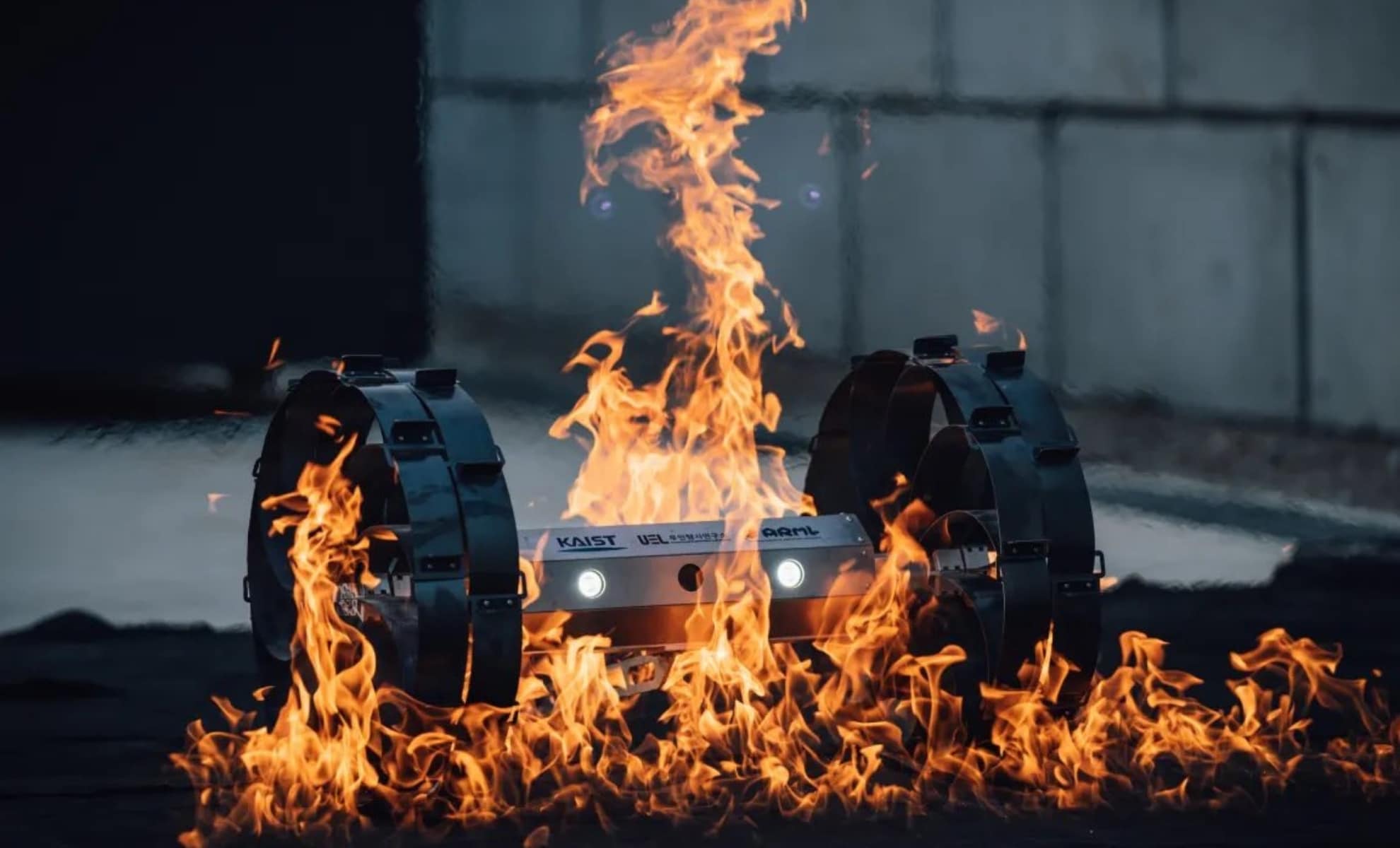
Beneath the moon’s cratered surface lie networks of lava tubes and deep pits, natural caves that could shelter future lunar bases from cosmic radiation and wild temperature swings. These underground structures represent some of the most scientifically valuable areas in the solar system, but they come with the very real challenge of simply getting there.
The entrances to these caves feature steep, rugged terrain with rocks and loose regolith. Small rovers, preferred for lunar exploration because you can deploy many of them to reduce mission risk, face an inherent limitation. Their compact wheels simply can’t climb over obstacles much larger than the wheel diameter itself. Send a swarm of small rovers and even if some fail, others continue the mission. Send one large rover and a single failure ends everything.
Variable diameter wheels are a new thing in lunar exploration and could solve this, expanding when needed to overcome obstacles, then contracting for efficient transport. But building such a wheel for the moon has proven nearly impossible. The lunar environment is uniquely hostile to mechanical systems. Fine, abrasive dust infiltrates everything, and in the airless vacuum, exposed metal surfaces stick together through a process called cold welding. Traditional hinges and joints don’t last long under these conditions.

Many researchers have spent decades attempting to decode biblical descriptions and link them to verifiable historical events. One such description is that of the Star of Bethlehem—a bright astronomical body that was said to lead the Magi to Jesus shortly after his birth.
Although many attempts have been made to link the Star of Bethlehem to astronomical bodies, the unique motion of the “star” did not quite fit any known object. However, a new research study, published in Journal of the British Astronomical Association, describes a likely candidate for the bright object seen above Bethlehem over 2000 years ago—a comet described in an ancient Chinese text.

Astronomers have employed the Very Energetic Radiation Imaging Telescope Array System (VERITAS) to observe a mysterious gamma-ray emitting source designated HESS J1857+026. Results of the observational campaign, published December 19 on the pre-print server arXiv, shed more light on the nature of this source.
