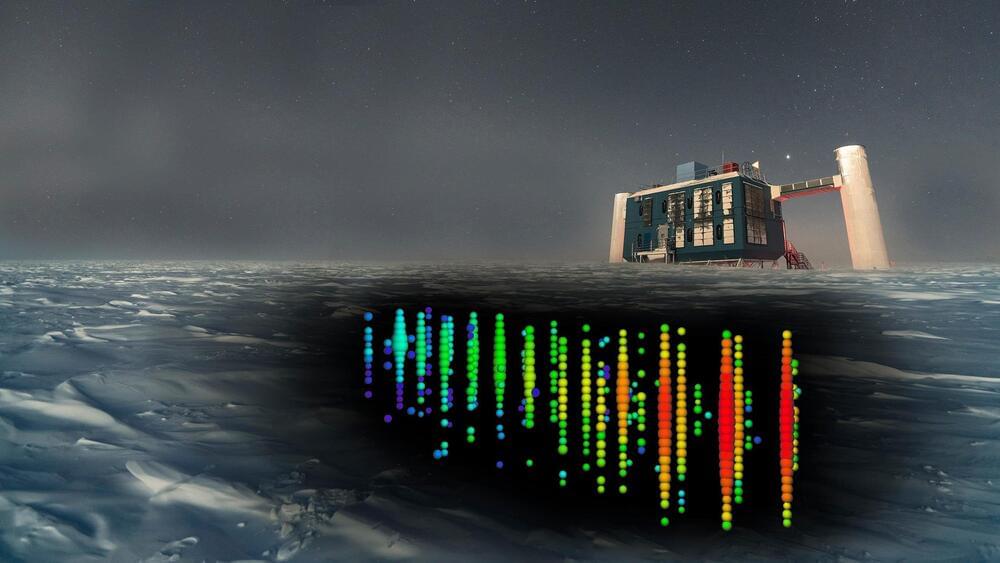
Whenever and wherever stars are born, which occurs whenever clouds of gas sufficiently collapse under their own gravity, they come in a wide variety of sizes, colors, temperatures, and masses. The largest, bluest, most massive stars contain the greatest amounts of nuclear fuel, but perhaps paradoxically, those stars are actually the shortest lived. The reason is straightforward: in any star’s core, where nuclear fusion occurs, it only occurs wherever temperatures exceed 4 million K, and the higher the temperature, the greater the rate of fusion.
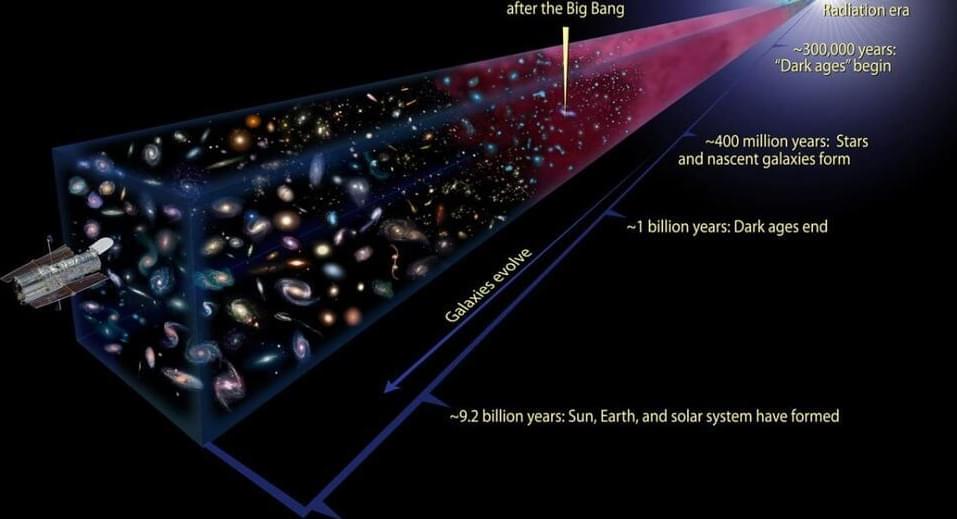
So the most massive stars might have the most fuel available at the start, but that means they shine brightly as they burn through their fuel quickly. In particular, the hottest regions in the core will exhaust their fuel the fastest, leading the most massive stars to die the most quickly. The best method we have for measuring “How old is a collection of stars?” is to examine globular clusters, which form stars in isolation often all at once, and then never again. By looking at the cooler, fainter stars that remain (and the lack of hotter, bluer, brighter, more massive stars), we can state with confidence that the Universe must be at least ~12.5–13.0 billion years old.