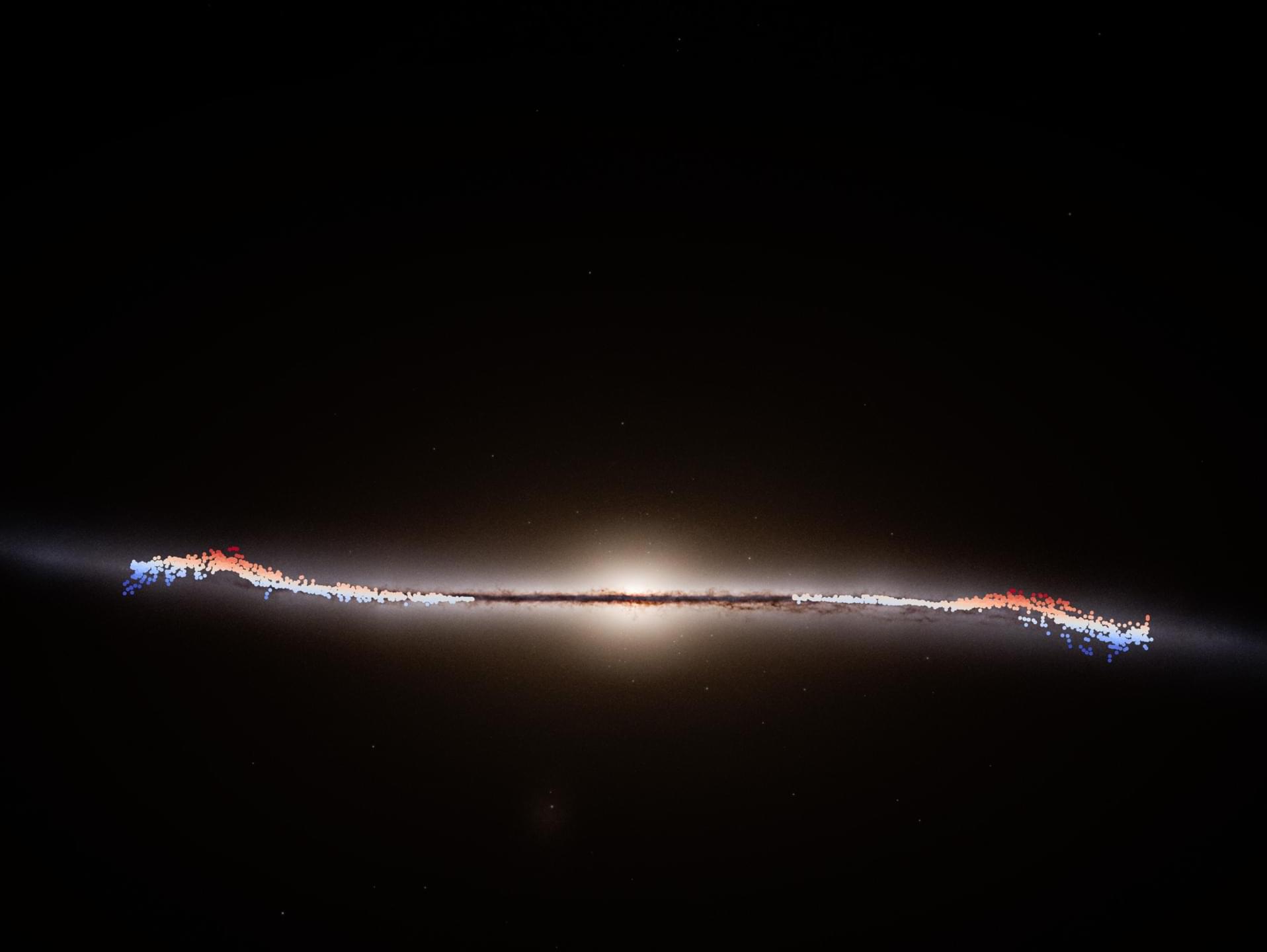
Our Milky Way galaxy never sits still: it rotates and wobbles. And now, data from the European Space Agency’s Gaia space telescope reveal that our galaxy also has a giant wave rippling outwards from its centre.



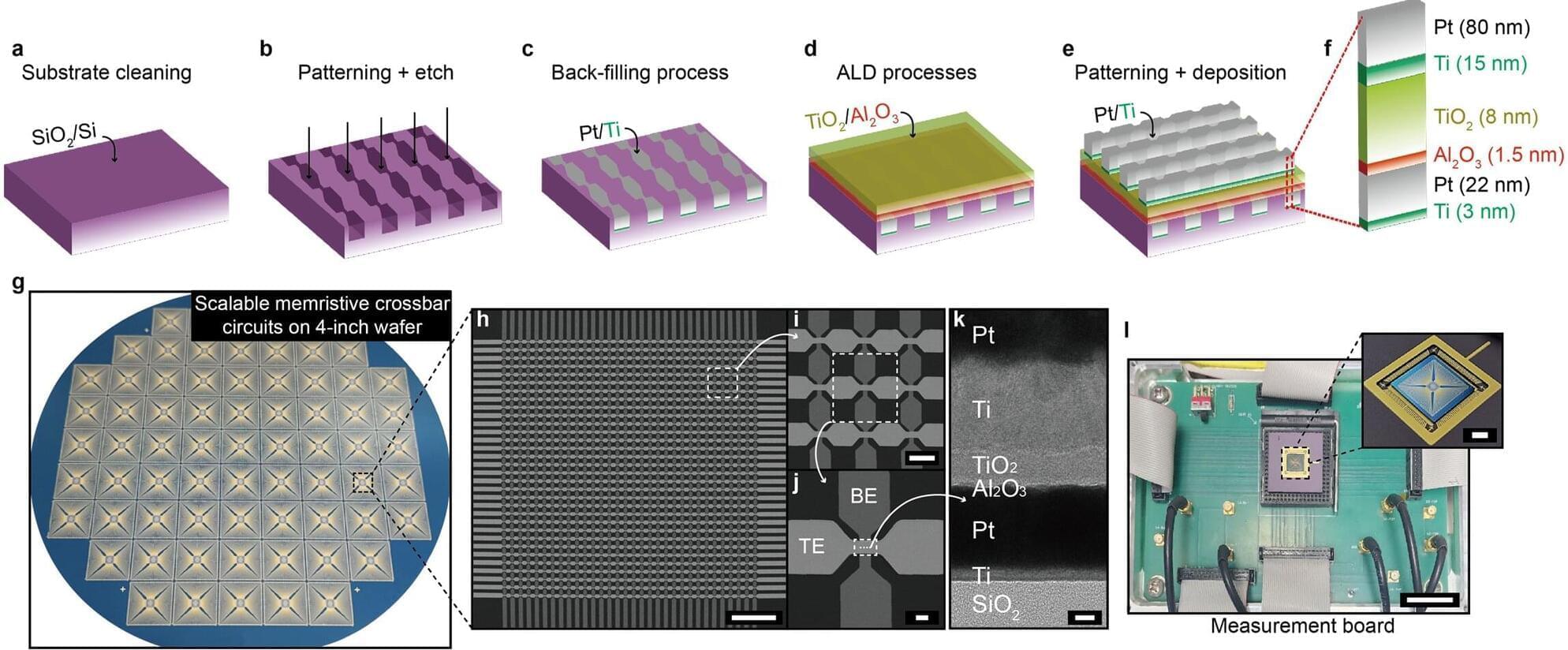
A research team led by Professor Sanghyeon Choi from the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at DGIST has successfully developed a memristor, which is gaining recognition as a next-generation semiconductor device, through mass-integration at the wafer scale.
The study, published in the journal Nature Communications, proposes a new technological platform for implementing a highly integrated AI semiconductor replicating the human brain, overcoming the limitations of conventional semiconductors.
The human brain contains about 100 billion neurons and around 100 trillion synapses, allowing it to store and process enormous amounts of information within a compact space.
Perhaps no existential question looms larger than that of our ultimate cosmic origins. At long last, science has provided the answers.

A question that has vexed physicists for the past century may finally have a solution – but perhaps not the one everyone was hoping for.
In a new, detailed breakdown of current theory, a team of physicists led by Mir Faizal of the University of British Columbia has shown that there is no universal “Theory of Everything” that neatly reconciles general relativity with quantum mechanics – at least, not an algorithmic one.
A natural consequence of this is that the Universe can’t be a simulation, since any such simulations would have to operate algorithmically.
Behind the Sun, the comet appears to show signs of acceleration beyond what is expected by gravity. And for reasons not yet clear, it appears to have changed color.
Full episode with Michael Levin: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c8iFtaltX-s.
As a listener of TOE you can get a special 20% off discount to The Economist and all it has to offer! Visit https://www.economist.com/toe.
Join My New Substack (Personal Writings): https://curtjaimungal.substack.com.
Listen on Spotify: https://tinyurl.com/SpotifyTOE
Become a YouTube Member (Early Access Videos):
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCdWIQh9DGG6uhJk8eyIFl1w/join.
Support TOE on Patreon: https://patreon.com/curtjaimungal.


In the mid-nineteenth century, the Harvard College Observatory began employing women as calculators, or “human computers,” to interpret the observations their male counterparts made via telescope each night. At the outset this group included the wives, sisters, and daughters of the resident astronomers, but soon the female corps included graduates of the new women’s colleges —Vassar, Wellesley, and Smith. As photography transformed the practice of astronomy, the ladies turned from computation to studying the stars captured nightly on glass photographic plates.
The “glass universe” of half a million plates that Harvard amassed over the ensuing decades—through the generous support of Mrs. Anna Palmer Draper, the widow of a pioneer in stellar photography—enabled the women to make extraordinary discoveries that attracted worldwide acclaim. They helped discern what stars were made of, divided the stars into meaningful categories for further research, and found a way to measure distances across space by starlight. Their ranks included Williamina Fleming, a Scottish woman originally hired as a maid who went on to identify ten novae and more than three hundred variable stars; Annie Jump Cannon, who designed a stellar classification system that was adopted by astronomers the world over and is still in use; and Dr. Cecilia Helena Payne, who in 1956 became the first ever woman professor of astronomy at Harvard—and Harvard’s first female department chair.
