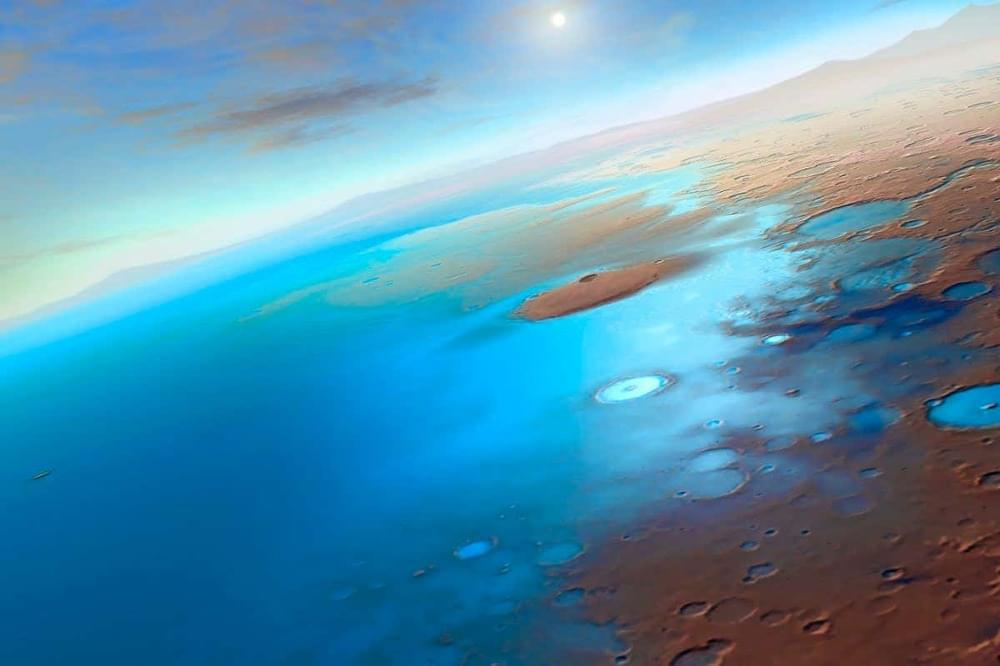
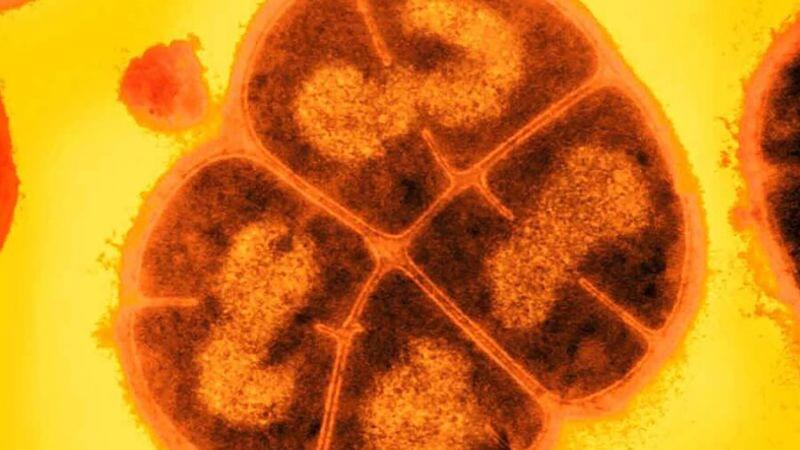
Ancient bacteria might be sleeping beneath the surface of Mars, where it has been shielded from the harsh radiation of space for millions of years, according to new research.
While no evidence of life has been found on the red planet, researchers simulated conditions on Mars in a lab to see how bacteria and fungi could survive. The scientists were surprised to discover that bacteria could likely survive for 280 million years if it was buried and protected from the ionizing radiation and solar particles that bombard the Martian surface.
The findings suggested that if life ever existed on Mars, the dormant evidence of it might still be located in the planet’s subsurface — a place that future missions could explore as they drill into Martian soil.