Perovskite has broad application prospects in solar cells, light-emitting diodes (LEDs), and detectors due to its high luminescent efficiency and low cost. However, electrons and holes in traditional perovskite materials often struggle to effectively recombine and emit light. As a result, the strongly space-confined method is commonly employed to improve luminescence efficiency. Furthermore, how to enhance the brightness of LEDs and extend their lifespan has become a top research priority in this field.
In a study published in Nature, Prof. Xiao Zhengguo’s team from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has proposed a novel strategy based on weakly space-confined, large-grain crystals of all-inorganic perovskite to prepare perovskite films with larger crystalline grains and higher temperature resistance. Researchers increased the brightness of perovskite LEDs (PeLEDs) to over 1.16 million nits and extended their lifespan to more than 180,000 hours.
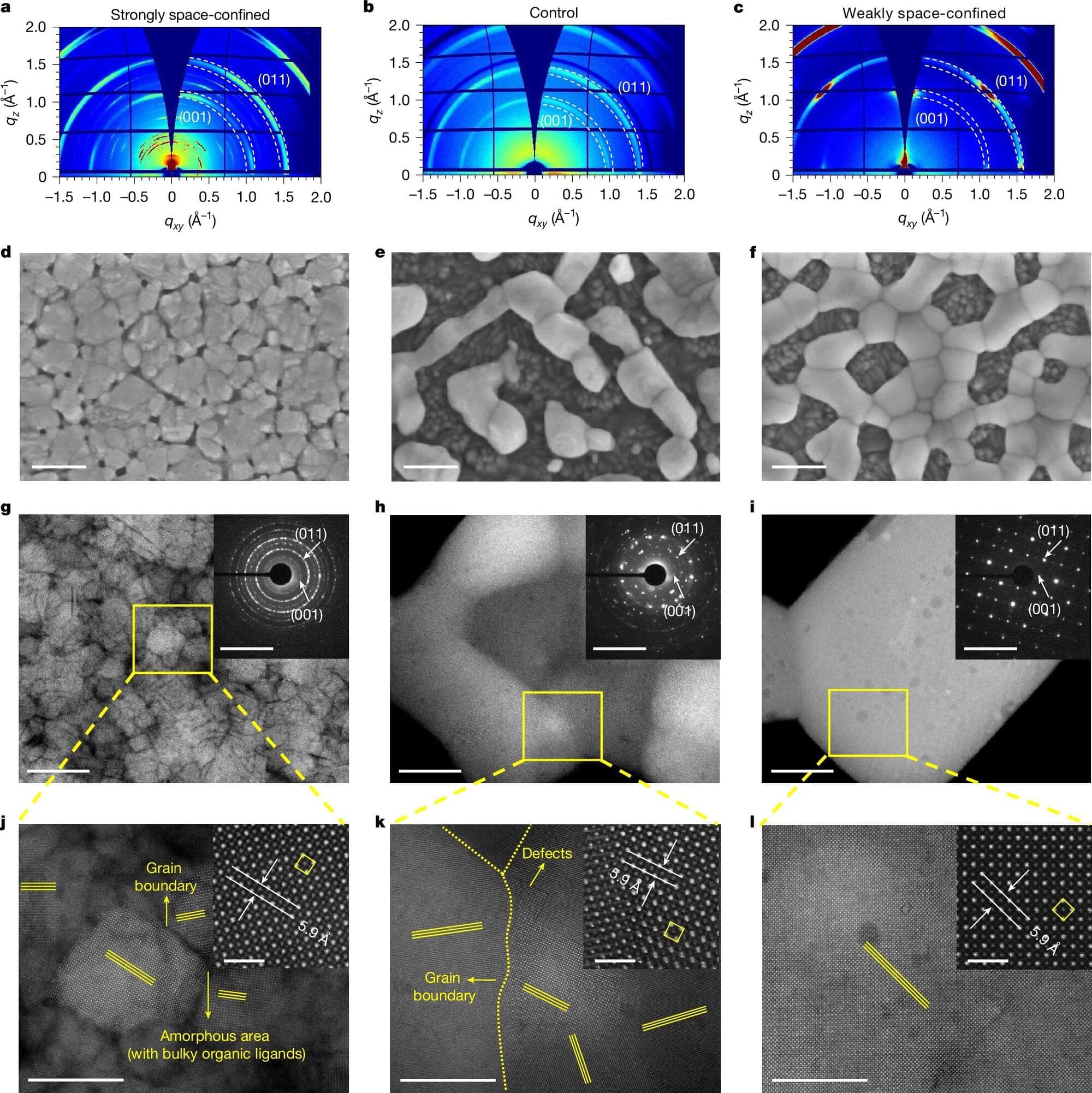
Researchers developed the strategy based on the weakly space-confined technique. They first added specific compounds—hypophosphorous acid and ammonium chloride—to the perovskite material. Then, they prepared a new type of perovskite thin film with larger crystalline grains and fewer defects using a high-temperature annealing process.