Galaxies can collect in large filamentary structures that have—until now—been considered rigid. A new study suggests one filament may be rotating.


Using an advanced machine-learning algorithm, researchers in the UK and Japan have identified several promising candidate locations for the long-lost landing site of the Soviet Luna 9 spacecraft. Publishing their results in npj Space Exploration, the team, led by Lewis Pinault at University College London, hope that their model’s predictions could soon be tested using new observations from India’s Chandrayaan-2 orbiter.
In 1966, the USSR’s Luna 9 mission became the first human-made object to land safely on the moon’s surface and to transmit photographs from another celestial body. Compared with modern missions, the landing was dramatic: shortly before the main spacecraft itself struck the lunar surface, it deployed a 58-cm-wide, roughly 100-kg spherical landing capsule from above, then maneuvered away to crash at a safe distance.
Equipped with inflatable shock absorbers, the capsule bounced several times before coming to rest, stabilizing itself by unfurling four petal-like panels. Although Luna 9 operated for just three days, it transmitted a wealth of valuable data back to Earth, helping to inspire confidence in crewed space exploration, that would see humanity take its first steps on the moon just three years later.
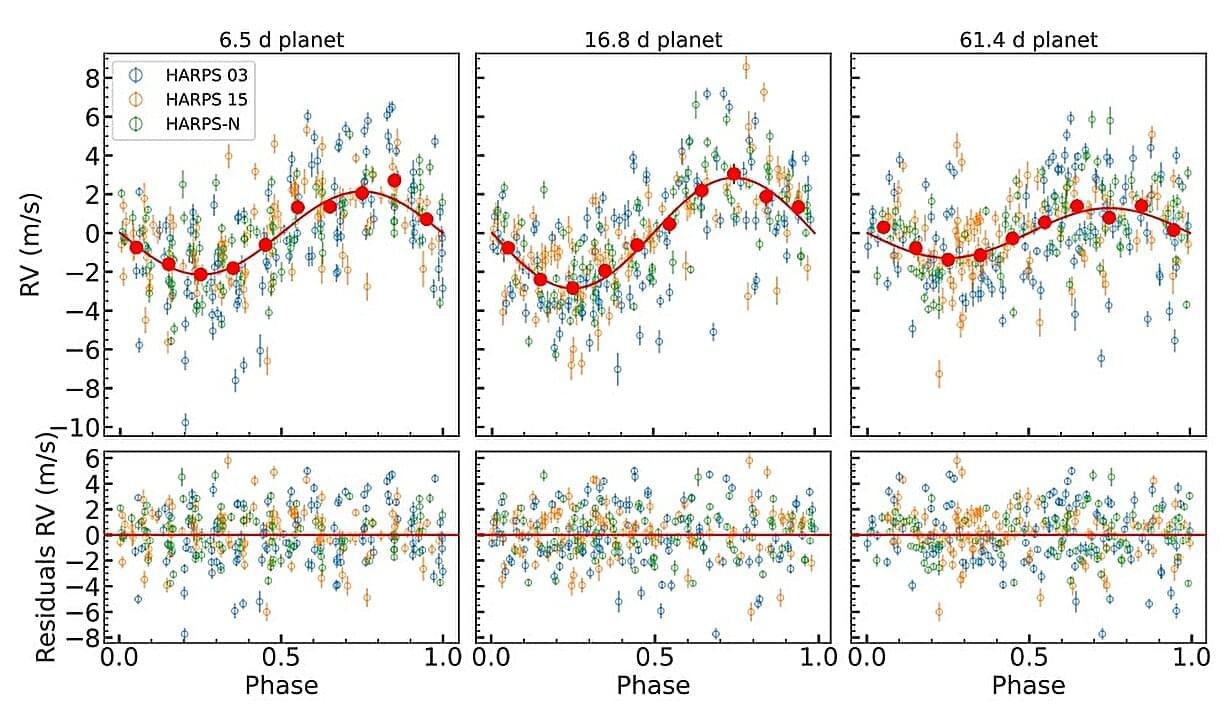
Using HARPS and HARPS-N spectrographs, astronomers have observed a nearby K-type star designated HD 176986, known to host two super-Earth exoplanets. The observations resulted in the discovery of another planet in the system at least several times more massive than Earth. The finding was detailed in a paper published January 28 in the Astronomy & Astrophysics journal.
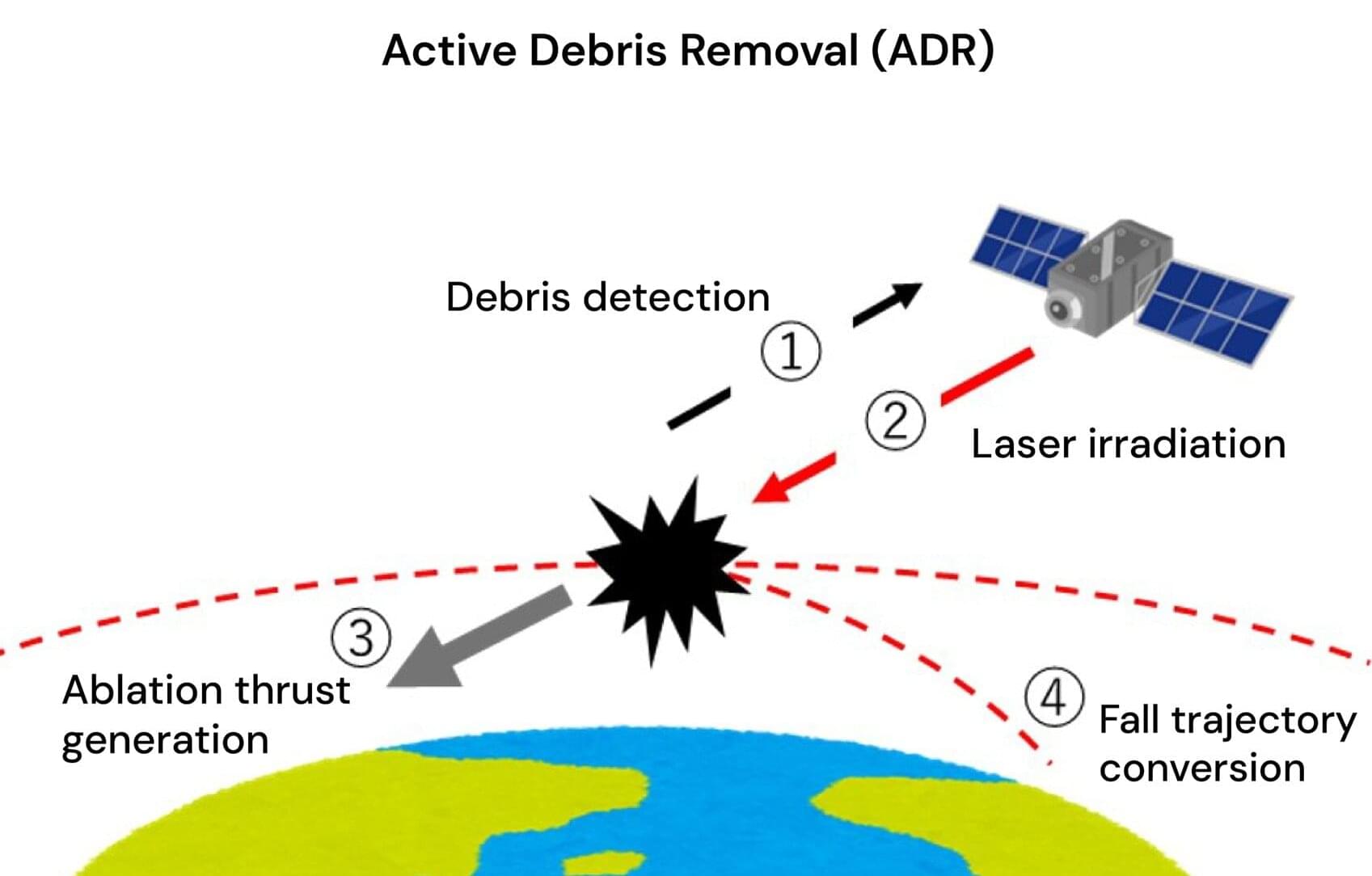
A possible alternative to active debris removal (ADR) by laser is ablative propulsion by a remotely transmitted electron beam (e-beam). The e-beam ablation has been widely used in industries, and it might provide higher overall energy efficiency of an ADR system and a higher momentum-coupling coefficient than laser ablation. However, transmitting an e-beam efficiently through the ionosphere plasma over a long distance (10 m–100 km) and focusing it to enhance its intensity above the ablation threshold of debris materials are new technical challenges that require novel methods of external actions to support the beam transmission.
Therefore, Osaka Metropolitan University researchers conducted a preliminary study of the relevant challenges, divergence, and instabilities of an e-beam in an ionospheric atmosphere, and identified them quantitatively through numerical simulations. Particle-in-cell simulations were performed systematically to clarify the divergence and the instability of an e-beam in an ionospheric plasma.
The major phenomena, divergence and instability, depended on the densities of the e-beam and the atmosphere. The e-beam density was set slightly different from the density of ionospheric plasma in the range from 1010 to 1012 m−3. The e-beam velocity was changed from 106 to 108 m/s, in a nonrelativistic range.


Why NASA Built SLS — And Why It Couldn’t Have Happened Any Other Way.
(https://youtu.be/LRwQqZGascs)
The inside scoop you never heard before.
Tired of toxins in your consumer products?
GoldBacks from Galactic/Green Greg’s affiliate link:
How big could space habitats really get? From O’Neill cylinders to Ringworlds and Topopolises, we explore the true limits of megastructure scale.
Get Nebula using my link for 50% off an annual subscription: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Watch my exclusive video Chronoengineering: https://nebula.tv/videos/isaacarthur–… Join this channel to get access to perks: / @isaacarthursfia 🛒 SFIA Merchandise: https://isaac-arthur-shop.fourthwall… 🌐 Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net ❤️ Support us on Patreon:
/ isaacarthur ⭐ Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a… 👥 Facebook Group:
/ 1,583,992,725,237,264 📣 Reddit Community:
/ isaacarthur 🐦 Follow on Twitter / X:
/ isaac_a_arthur 💬 SFIA Discord Server:
/ discord Credits: How Big Could a Space Habitat Get? Written, Produced & Narrated by: Isaac Arthur Editor: Tim Liusko Graphics from Fishy Tree, Jarred Eagley, Jeremy Jozwik, J. Dixon, Ken York, Udo Schroeter Music Courtesy of Chris Zabriskie & Stellardrone Select imagery/video supplied by Getty Images Music by Epidemic Sound: http://nebula.tv/epidemic & Stellardrone Chapters 0:00 Intro 2:03 Basics of Habitat Scaling 9:30 Cylinder & Ring Habitats — Linear and Radial Extremes 11:00 Banks Orbitals 12:42 Ringworlds 16:24 Chrono-Engineering 17:24 The Topopolis 21:03 Planet-Wrapping Habitats 22:55 Matrioshka Shellworlds 26:17Alternative & Exotic Designs.
🚀 Join this channel to get access to perks: / @isaacarthursfia.
🛒 SFIA Merchandise: https://isaac-arthur-shop.fourthwall…
🌐 Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
❤️ Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur.
⭐ Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a…
👥 Facebook Group: / 1583992725237264
📣 Reddit Community: / isaacarthur.
🐦 Follow on Twitter / X: / isaac_a_arthur.
💬 SFIA Discord Server: / discord.
Credits:
Hubble captures a dazzling stellar nursery where newborn stars light up and carve their way through glowing clouds in a nearby galaxy.
This striking image from the Hubble Space Telescope offers a fresh perspective on a faraway region where stars are actively forming. The view was captured alongside a recently released image and focuses on a nearby section of the N159 star-forming complex in the Large Magellanic Cloud, located about 160,000 light-years from Earth.
Glowing Gas and Emerging Stars.