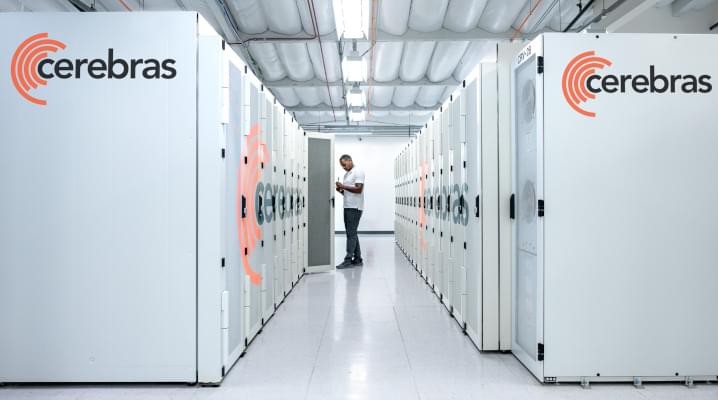
Chip startup Cerebras Systems Inc. today debuted Andromeda, a supercomputer optimized to run artificial intelligence applications that features more than 13.5 million processor cores.
Sunnyvale, California-based Cerebras Systems is backed by more than $720 million in venture funding. The startup sells a chip called the WSE-2 that is specifically designed to run AI software. The new Andromeda supercomputer that Cerebras Systems debuted today is based on the WSE-2 chip.
According to Cerebras Systems, Andromeda can provide performance in excess of one exaflop when running AI applications. One exaflop equals 1 million trillion calculations per second. The startup says that Andromeda’s performance makes it suitable for, among other use cases, training large language models, which are complex neural networks that can perform tasks such as translating text and generating software code.