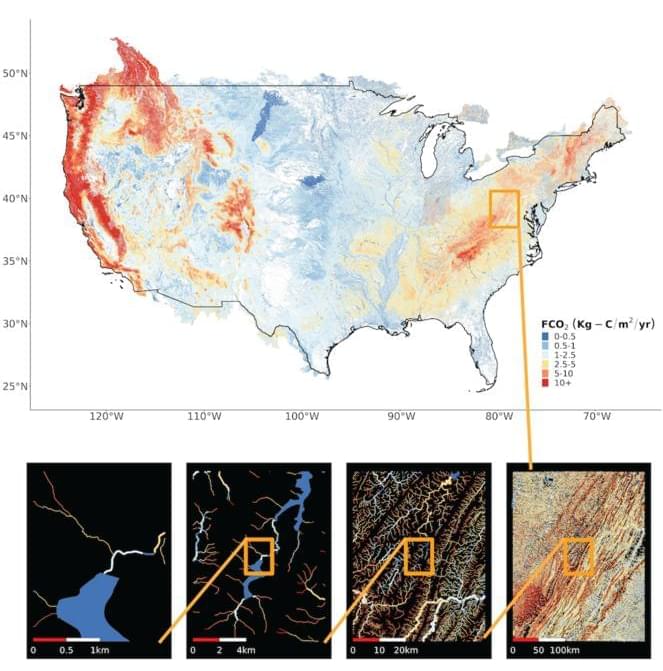
What is the level of carbon emissions across the United States? This is what a recent study published in AGU Advances hopes to address as a team of researchers from the University of Massachusetts Amherst conducted the first nationwide analysis of carbon emissions across the United States with the goal of putting constraints on previous analyses regarding the amount of carbon emissions across the United States, also known as the carbon cycle. This study holds the potential to help researchers, climate scientists, and the public better understand the United States’ contribution to climate change and the steps that can be taken to mitigate them.
“We need to know how much CO2 is being generated so we can predict how it will respond to climate change,” said Dr. Matthew Winnick, who is an assistant professor of Earth, Geographic and Climate Sciences at the University of Massachusetts Amherst and a co-author on the study. “As temperature rises, we tend to think that a lot of the natural carbon cycle processes will respond to that and potentially amplify climate change.”
For the study, the researchers collected data on carbon emissions across more than 22 million rivers, lakes, and water reservoirs with the goal of developing a model that could put tighter constraints on previous carbon cycle models. In the end, the researchers’ models estimated approximately 120 million metric tons of carbon, which is approximately 25 percent lower than previous models which estimated approximately 159 million metric tons of carbon. The researchers note these more accurate findings could benefit carbon capturing methods to mitigate climate change.