“Our microwave induction heating technology enables fast and easy preparation of hard carbon, which I believe will contribute to the commercialization of sodium-ion batteries,” said Dr. Daeho Kim.
Can sodium-ion batteries be improved to exceed the efficiency and longevity of traditional lithium-ion batteries? This is what a recent study published in Chemical Engineering Journal hopes to address as a team of researchers from South Korea investigated how microwave induction heating can produce sufficient carbon anodes used in sodium-ion batteries. This study holds the potential to help researchers and engineers better understand how to develop and produce efficient sodium-ion batteries, which have demonstrated greater abundancy and stability.
“Due to recent electric vehicle fires, there has been growing interest in sodium-ion batteries that are safer and function well in colder conditions. However, the carbonization process for anodes has been a significant disadvantage in terms of energy efficiency and cost,” said Dr. Jong Hwan Park, who is from the Korea Electrotechnology Research Institute (KERI) and a co-author on the study.
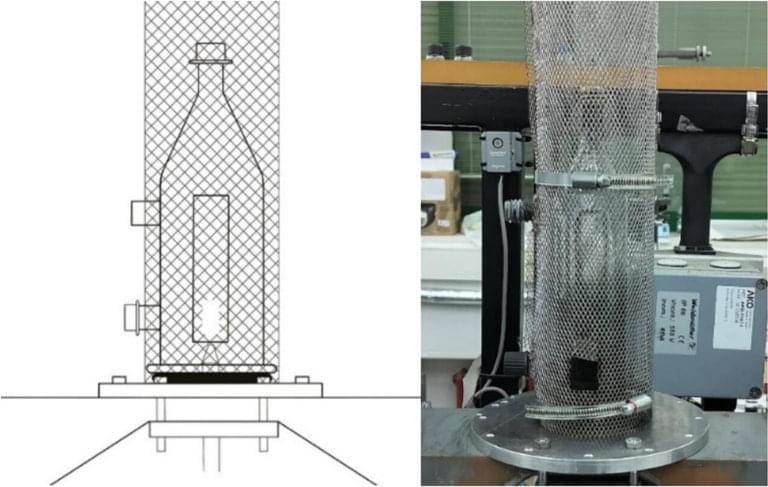
For the study, the KERI-led researchers improved upon existing sodium-ion batteries by using microwave technology, which involves heating carbon nanotubes using a microwave magnetic field, resulting in temperature exceeding 1,400 degrees Celsius (2,550 degrees Fahrenheit) in only 30 seconds. This breakthrough improves upon traditional methods for procuring carbon anodes, which typically require lengthy amounts of time to reach just 1,000 degrees Celsius (1,800 degrees Fahrenheit).