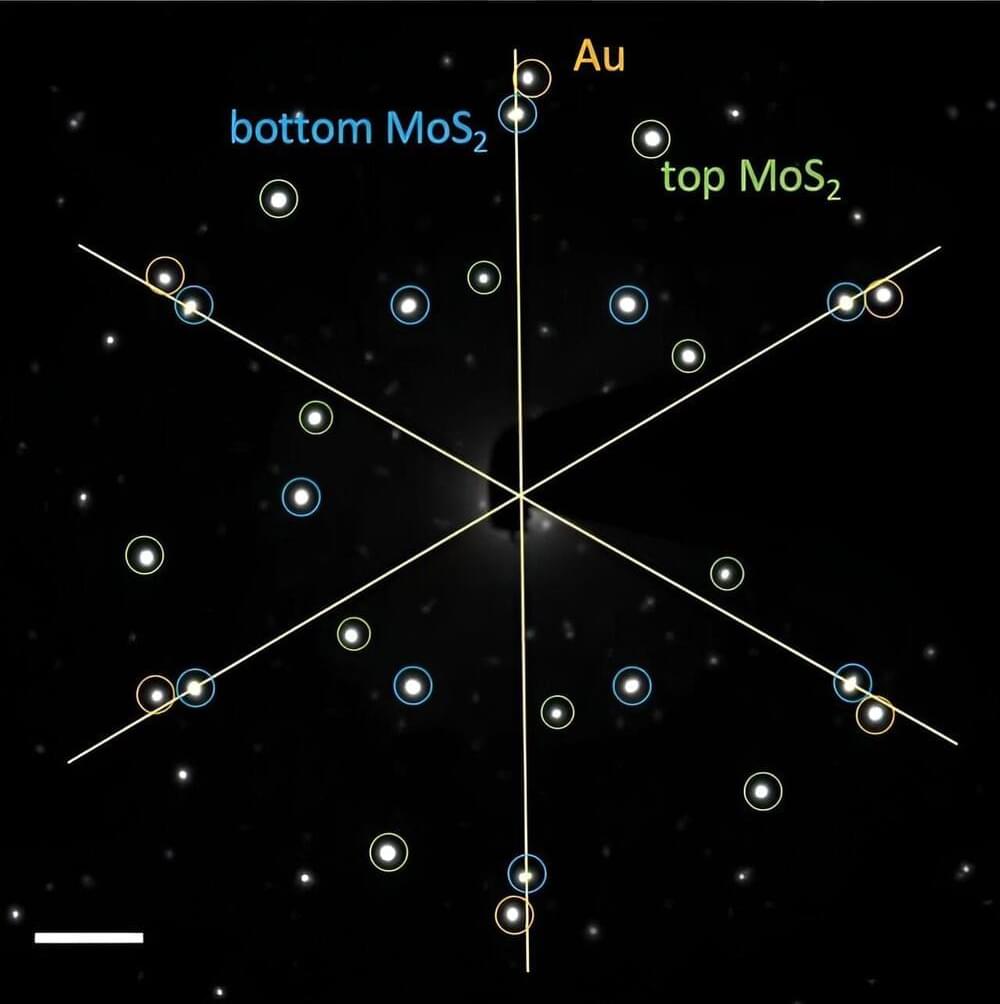
Hexagonal boron nitride coatings on metal alloys enhance durability, reduce friction, and protect against harsh conditions, paving the way for improvements in solar panels, semiconductors, and aerospace components.
Researchers demonstrated that stainless steel and other metal alloys coated with hexagonal boron nitride, or hBN, exhibit non-stick or low-friction qualities along with improved long-term protection against harsh corrosion and high-temperature oxidation in air.
Metal alloys — mixtures of two or more metals — are created to be strong, durable, and resistant to corrosion or oxidation. By adding coatings, or “armor,” to make those materials even tougher, scientists could enhance existing products and enable the creation of new, innovative ones.