Paving a potential industrial approach for effectively harvesting raindrop energy at a large scale.
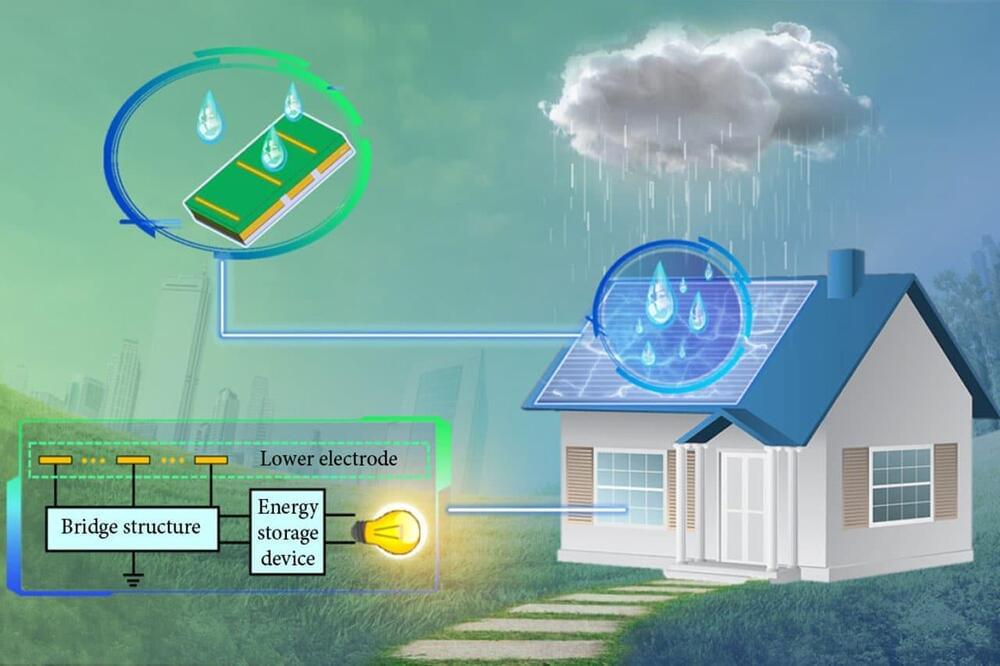

Now that’s something mach can use.
MIT researchers have recently developed a portable desalination unit that can remove particles and salts to turn seawater into drinking water.
The suitcase-sized device, weighing less than ten kilograms, requires less power to operate than a cell phone charger and can also be driven by a small, portable solar panel.
It automatically generates drinking water that exceeds World Health Organization quality standards. The technology is packaged into a user-friendly device that runs with the push of a button.
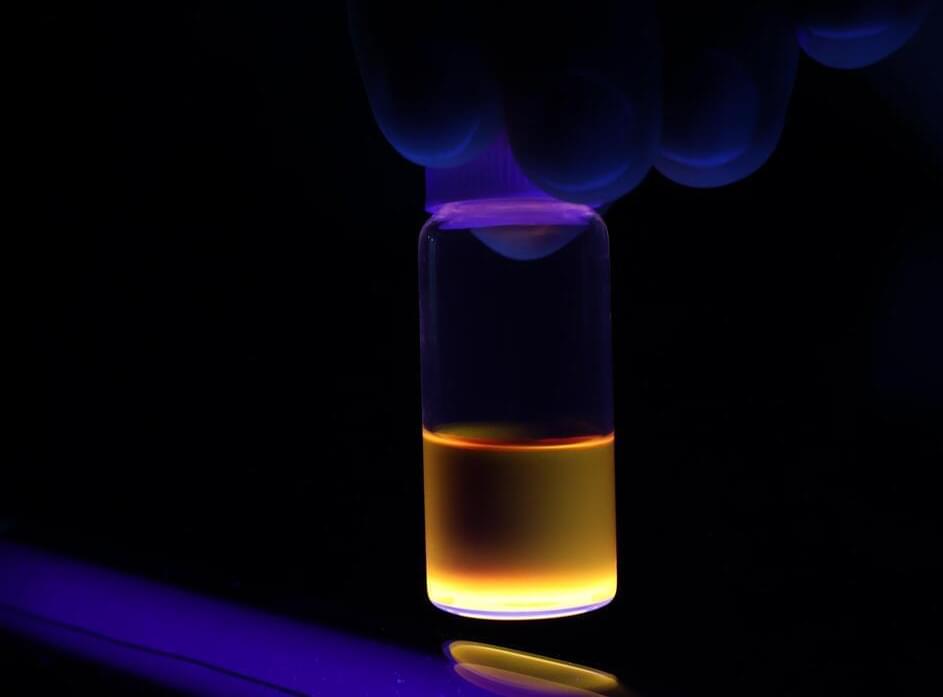

A team of researchers from the Instituto de Carboquímica of the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) has made a remarkable step forward in the development of efficient and sustainable electronic devices. They have found a special combination of two extraordinary nanomaterials that successfully results in a new hybrid product capable of turning light into electricity, and vice-versa, faster than conventional materials.
The research is published in the journal Chemistry of Materials.
This new material consists of a one-dimensional conductive polymer called polythiophene, ingeniously integrated with a two-dimensional derivative of graphene known as graphene oxide. The unique features exhibited by this hybrid material hold incredible promise for improving the efficiency of optoelectronic devices, such as smart devices screens, and solar panels, among others.
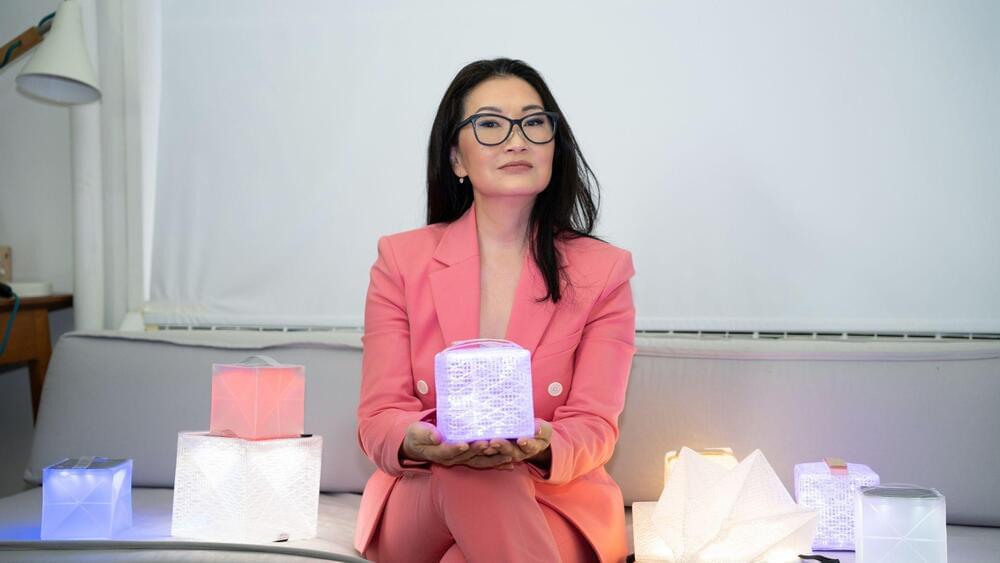

Innovative solar-powered light has helped earthquake victims around the world and now comes with phone-charging function.
As a little girl growing up in Seoul, Korea and then upstate New York, inventor Alice Min Soo Chun spent days with her mother learning origami and how a simple fold could become structured.
She went on to study Architecture at Penn State and earned her Masters at the University of Pennsylvania.
As we strive towards a more sustainable future, it’s becoming increasingly important to find innovative ways to decarbonize industry and facilitate clean energy storage.
One promising approach is the manufacture of valuable products and fuels using available, low-cost feedstocks like water, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and solar energy. By harnessing the power of these abundant resources, we can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and move towards a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.
In a similar effort, Rice University engineers have developed a device that can turn sunlight into hydrogen with record-breaking efficiency – a significant step forward for clean energy. The device combines next-generation halide perovskite semiconductors with electrocatalysts in a single, durable, cost-effective, and scalable device.


A plentiful supply of clean energy is lurking in plain sight. It’s the hydrogen that can be extracted from water (H2O) using renewable energy. Researchers are on the hunt for cost-effective strategies to generate clean hydrogen from water, with an aim to displace fossil fuels and battle climate change.
Hydrogen is a potent source of power for vehicles, emitting nothing more than water. It also plays a crucial role in several industrial processes, particularly in the production of steel and ammonia. The use of cleaner hydrogen in these industries would be extremely beneficial.
A multi-institutional team led by the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory has developed a low-cost catalyst for a process that yields clean hydrogen from water. Other contributors include DOE’s Sandia National Laboratories and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, as well as Giner Inc.
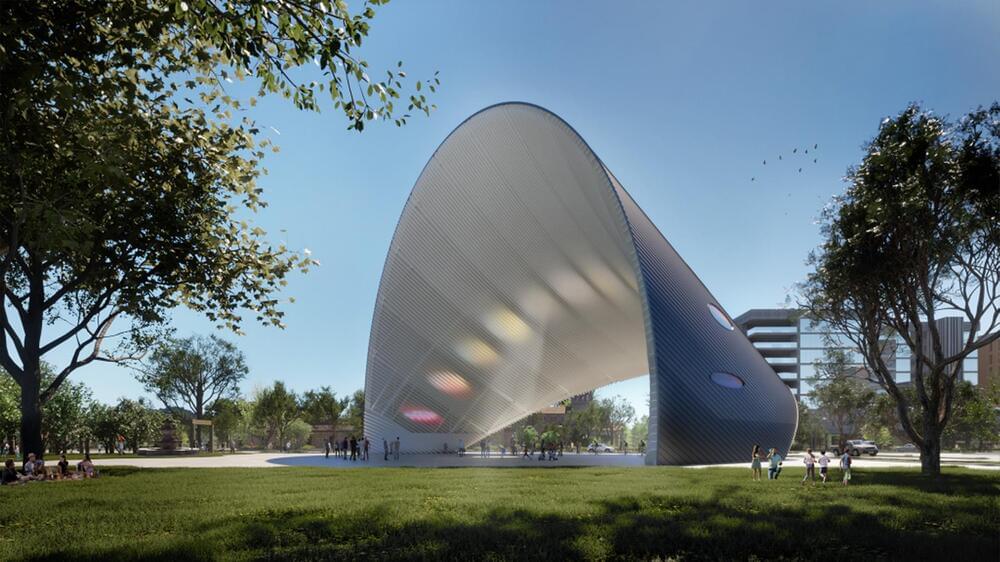

The project, called the Arch of Time, will stand 100 feet tall and generate enough solar power every year to offset 40 Texans’ home energy use.
Berlin architect Riccardo Mariano has designed an innovative new project for the city of Houston, Texas, that will generate nearly 400,000 kWh of electricity every year while acting as a public sundial.
The project, named the Arco del Tiempo (Arch of Time), will be a 100-foot-tall triumphal archway that will serve as the gateway to the city’s East End, part of the Second Ward district for the city. It will have a roof covered in photovoltaic modules to produce electricity as well.
It should be ready by the end of 2024 but can we take Musk’s word at face value when it comes to deadlines?
Tesla CEO Elon Musk has committed to spending a billion dollars to build the Dojo supercomputer over the next year, Bloomberg.
The FSD on Tesla is offered as a feature in “beta mode”, meaning it is far from being the advanced driver-assist system that Musk has declared it to be. Tesla has occasionally provided updates on the software, but many have pointed out the flaws in the design and how it cannot be trusted.
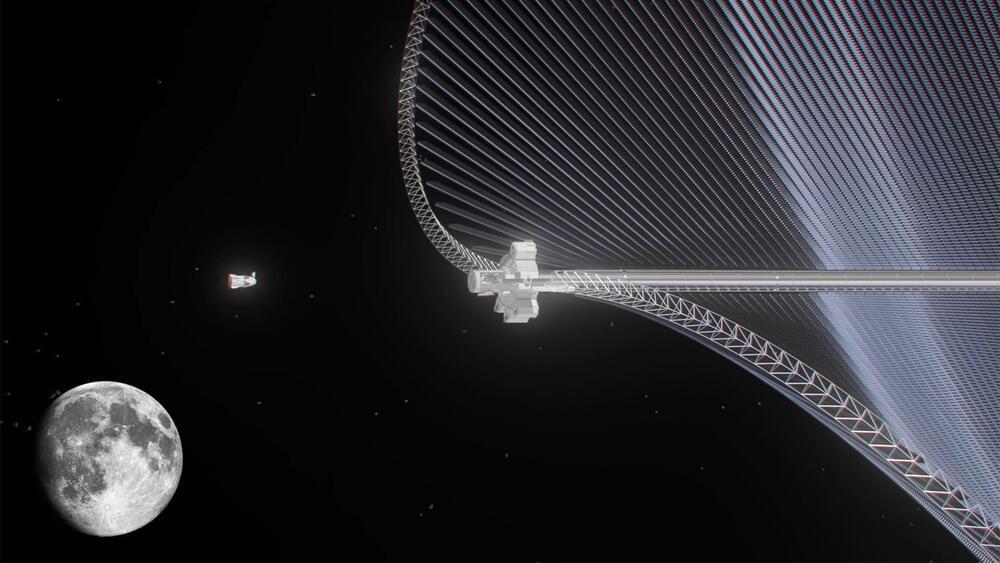
According to a study by Astrostrom for ESA, future Moon bases could be powered by a giant space butterfly called the Greater Earth Lunar Power Station (GEO-LPS) covered with solar panels made from lunar materials beaming microwaves to the surface.
One of the major design concerns in setting up a lunar base is finding a reliable means of powering it. Solar power might seem the obvious answer, but with lunar nights lasting 14 Earth days, it isn’t a practical option. However, though the most promising alternative is currently a small nuclear reactor, solar may not be out of the running.
The idea of solar power plants in space has been around for well over half a century. On Earth, solar panels are limited by night time, atmospheric haze, and bad weather, making them only capable of intermittent power generation with limited efficiency. On the other hand, in space, where there is no night and no atmosphere, solar power becomes very attractive.