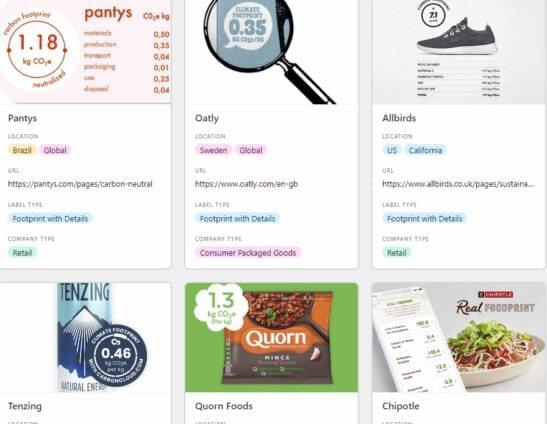
Carbon labelling gives consumers a weapon to fight climate change at the cash register.
What’s Involved with Carbon Labelling
Today, nutritional and content labelling can be found on packaged foods. The Government recently announced plans to enhance those labels. Why, because of concerns that Canadians need to learn more about what they eat so that they can make healthier choices.
Carbon labelling would serve a similar purpose by allowing Canadians to make healthier choices about carbon emissions. A carbon label would let consumers understand the environmental impact of items they purchase and consume. The label would contain the total carbon footprint of the product.