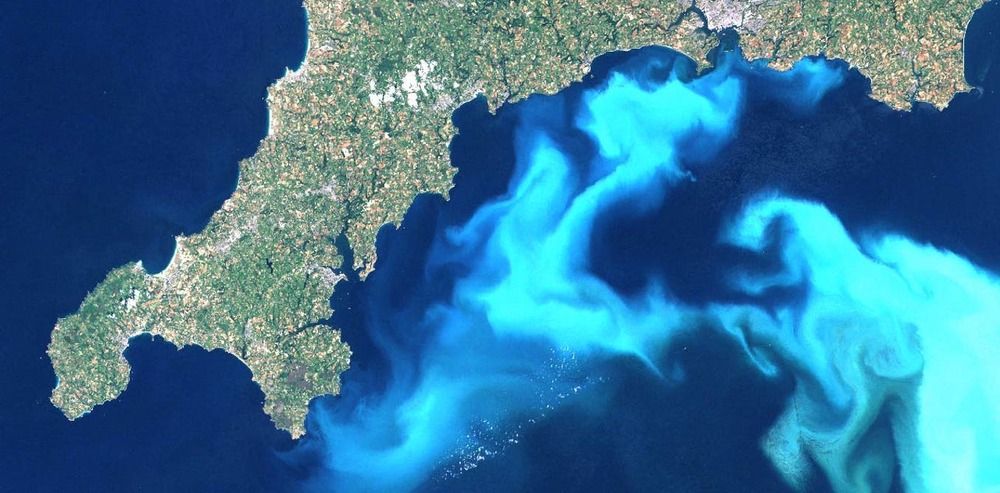
Rechargeable batteries are at the heart of many new technologies involving, for example, the increased use of renewable energies. More specifically, they are employed to power electric vehicles, cell phones, and laptops. Scientists at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) and the Helmholtz Institute Mainz (HIM) in Germany have now presented a non-contact method for detecting the state of charge and any defects in lithium-ion batteries. For this purpose, atomic magnetometers are used to measure the magnetic field around battery cells. Professor Dmitry Budker and his team usually use atomic magnetometry to explore fundamental questions of physics, such as the search for new particles. Magnetometry is the term used to describe the measurement of magnetic fields. One simple example of its application is the compass, which the Earth’s magnetic field causes to point north.
Non-contact quality assurance of batteries using atomic magnetometers
The demand for high-capacity rechargeable batteries is growing and so is the need for a form of sensitive, accurate diagnostic technology for determining the state of a battery cell. The success of many new developments will depend on whether batteries can be produced that can deliver sufficient capacity and a long effective life span. “Undertaking the quality assurance of rechargeable batteries is a significant challenge. Non-contact methods can potentially provide fresh stimulus for improvement in batteries,” said Dr. Arne Wickenbrock, a member of Professor Dmitry Budker’s work group at the JGU Institute of Physics and the Helmholtz Institute Mainz. The group has achieved a breakthrough by using atomic magnetometers to take measurements. The idea came about during a teleconference between Budker and his colleague Professor Alexej Jerschow of New York University. They developed a concept and, with close cooperation between the two groups, carried out the related experiments in Mainz.