KANSAS CITY, Mo. (KCTV) — Part of rolling out trash carts to Kansas City homes included a fully automated trash truck.
The City of Kansas City tweeted out a video of the truck hitting the road on it’s first day.

KANSAS CITY, Mo. (KCTV) — Part of rolling out trash carts to Kansas City homes included a fully automated trash truck.
The City of Kansas City tweeted out a video of the truck hitting the road on it’s first day.

The approach addresses key challenges in visible light communication, including pulse distortion and sunlight interference.
Scientists have developed a low-cost visible light communication (VLC) system using commercially available hardware that enables stable data transmission even under strong ambient light.
The team achieved reliable outdoor VLC at data rates of up to 3.48 Mbit/s over distances of several meters by implementing a newly designed 8B13B coding scheme on an FPGA and interfacing it with a Raspberry Pi.
The approach addresses key challenges in VLC, including pulse distortion and sunlight interference, and offers a practical path toward intelligent transportation system (ITS) applications.
In response to the findings, Google has blocked the phishing efforts that abuse the email notification feature within Google Cloud Application Integration, adding that it’s taking more steps to prevent further misuse.
Check Point’s analysis has revealed that the campaign has primarily targeted manufacturing, technology, financial, professional services, and retail sectors, although other industry verticals, including media, education, healthcare, energy, government, travel, and transportation, have been singled out.
“These sectors commonly rely on automated notifications, shared documents, and permission-based workflows, making Google-branded alerts especially convincing,” it added. “This campaign highlights how attackers can misuse legitimate cloud automation and workflow features to distribute phishing at scale without traditional spoofing.”

A research team led by Professor Kanghyun Nam from the Department of Robotics and Mechanical Engineering at DGIST has developed a physical AI-based vehicle state estimation technology that accurately estimates the driving state of electric vehicles in real time.
This technology is viewed as a key advancement that can improve the core control performance of electric vehicles and greatly enhance the safety of autonomous vehicles. The work was conducted through international joint research with Shanghai Jiao Tong University in China and the University of Tokyo in Japan.
The work is published in the journal IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics.
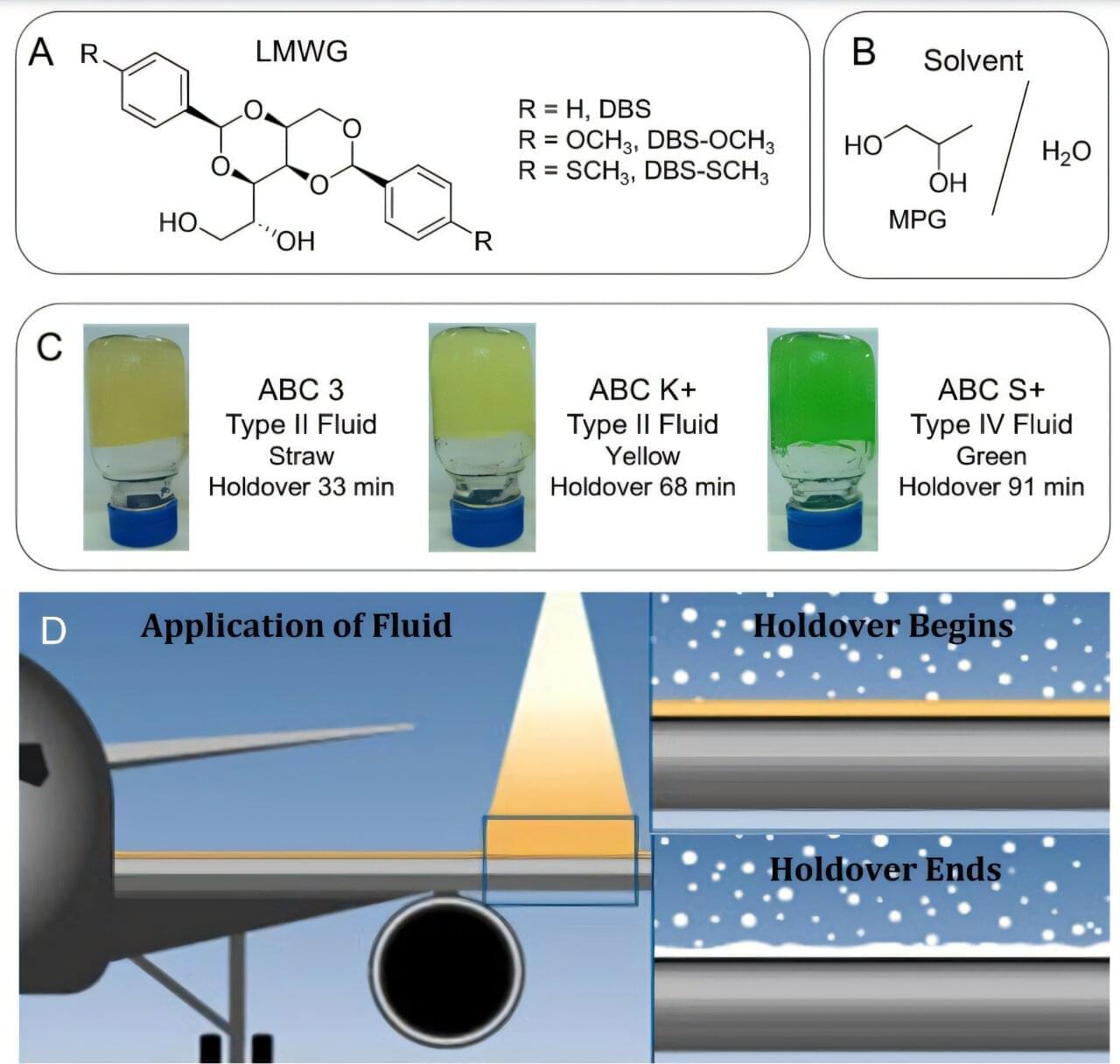
Tiny molecules already used to thicken everyday products like lotions and adhesives may soon help keep aircraft safe in icy conditions. These molecules, known as low-molecular-weight gelators (LMWGs), can self-assemble into soft, gel-like structures and have long been used in industrial formulations.
In a study published in Langmuir, researchers report that adding just small amounts of these molecules can significantly improve the performance of aircraft anti-icing fluids.
The team modified commercial deicing and anti-icing fluids—which already contain polymers for protective coating—by incorporating LMWG molecules to produce a hybrid gel formulation. They tested three variants of a gelator, known as DBS (1,3:2,4-dibenzylidenesorbitol), at varying levels of aviation-grade agents used to remove existing ice and prevent new ice formation on aircraft surfaces during ground operations.
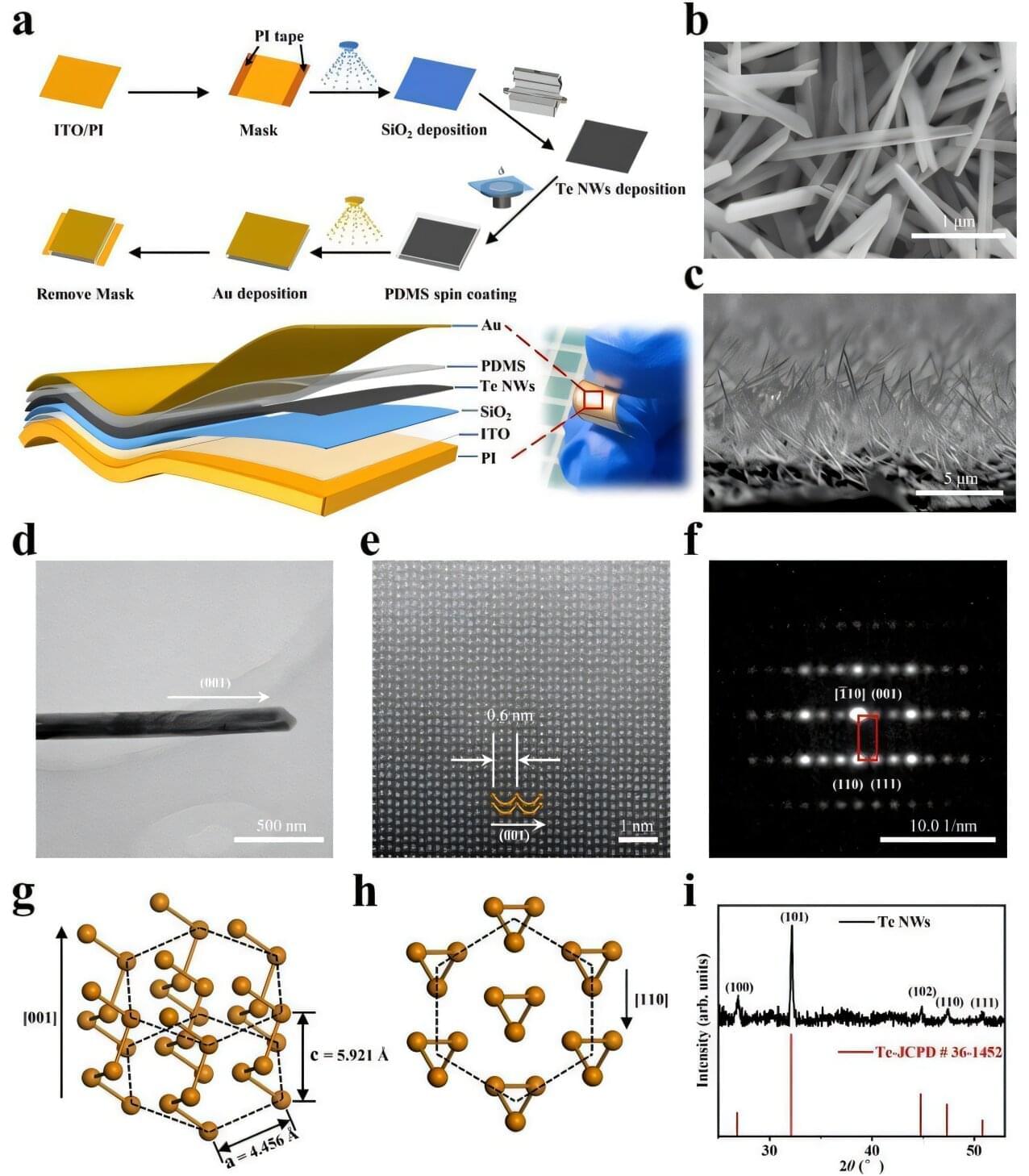
Researchers from the Institute of Metal Research (IMR) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed an innovative flexible sensor that can simultaneously detect strain, strain rate, and temperature using a single active material layer, representing a significant advance in multimodal sensing technology.
The study, published in Nature Communications, addresses the longstanding challenge of conventional sensors requiring complex multilayer designs that integrate different materials for distinct sensing functions. These traditional approaches often involve complicated signal acquisition and external power supplies, limiting their reliability in continuous monitoring applications.
Led by Prof. Tai Kaiping, the researchers designed the sensor based on a specially designed network of tilted tellurium nanowires (Te-NWs). Through material and structural engineering, they overcame a fundamental limitation where thermoelectric and piezoelectric signals could not be collected in the same direction within conventional materials. In this unique architecture, both signals are simultaneously detected and output in the out-of-plane direction.

Even before entering production, Tesla’s Cybercab is already transforming the appearance of Austin’s streets, with multiple prototypes spotted testing in downtown areas recently.
Videos and photos showed the sleek, two-seat autonomous vehicles navigating traffic. Interestingly enough, the vehicles were equipped with temporary steering wheels and human safety drivers.
Over the weekend, enthusiasts captured footage of two Cybercabs driving together in central Austin, their futuristic silhouettes standing out amid regular traffic. While the vehicles featured temporary steering wheels and side mirrors for now, they retained their futuristic, production-intent exterior design.
Mode locking—a laser technique that revolutionized optical physics—has been extended to x rays, producing stable trains of attosecond pulses with unprecedented phase coherence.
X-ray free-electron lasers (XFELs) have transformed the study of matter by delivering femtosecond and attosecond pulses at angstrom wavelengths, enabling direct observation of ultrafast structural and electronic dynamics. Despite these successes, XFELs have long lacked a capability central to precision optical science: stable temporal phase coherence. Most XFEL facilities operate in the self-amplified spontaneous-emission (SASE) regime, in which radiation originates from microscopic shot noise in an electron beam. This mechanism produces extremely bright pulses, but shot-to-shot fluctuations in their temporal structure limit their use in phase-sensitive experiments useful for metrology, interferometry, and ultrafast spectroscopy [1].
A robot revolution, driven by advancements in robotics and AI, is imminent and will drastically transform the economy, labor, and society, leading to a post-labor, post-scarcity system with abundant energy and labor ##
## Questions to inspire discussion.
Investment & National Strategy.
🚀 Q: Why should governments prioritize humanoid robot investment now? A: Governments must treat humanoid robots as a national priority for transforming productivity and defense, with enormous investments justified because there’s no time to lose as both the US and China have already recognized this imperative.
💰 Q: What economic growth rates become possible with early humanoid robot adoption? A: Spinning up the humanoid robot flywheel early enables exponential economic growth rates of 20–100% per year, unlocking unprecedented prosperity and catapulting societies up the curve over the next 15 years.
⚡ Q: Which countries or entities will likely lead the humanoid robot transformation? A: Outsiders rather than incumbents or centers of power will lead the transformation to a new economic paradigm, as history shows leadership typically comes from the edge rather than the status quo.