Brighter with Herbert.
Category: transportation – Page 83
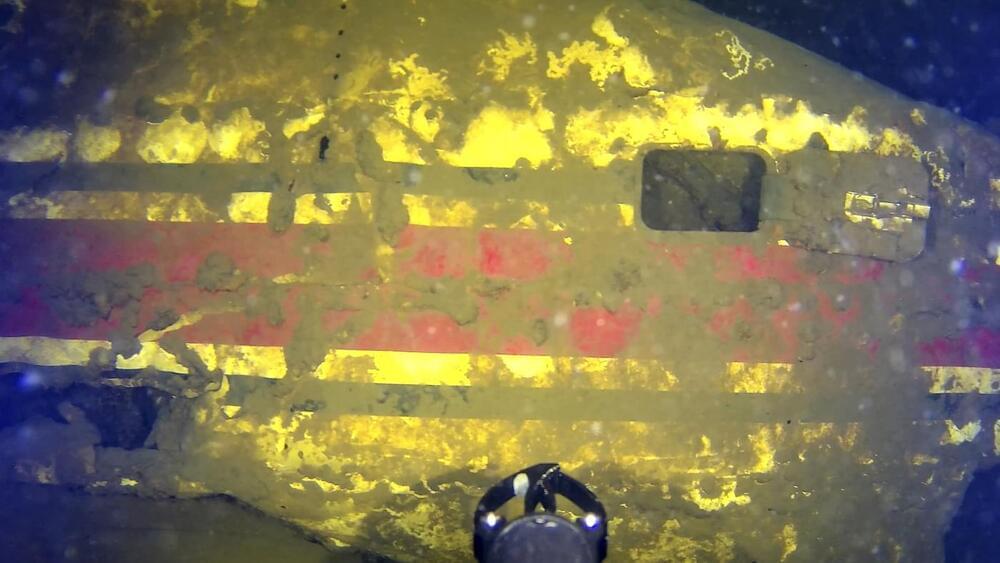

A jet missing since 1971 has been found at the bottom of Vermont’s Lake Champlain
Fifty-three years after a private plane carrying five men disappeared on a snowy Vermont night, experts believe they have found the wreckage of the long lost jet in Lake Champlain.
The corporate jet disappeared shortly after departing the Burlington airport for Providence, Rhode Island, on Jan. 27, 1971. Those aboard included two crew members and three employees of a Georgia development company Cousins Properties, who were working on a development project in Burlington.
Initial searches for the 10-seat Jet Commander turned up no wreckage and the lake froze over four days after the plane was lost. At least 17 other searches happened, until underwater searcher Garry Kozak and a team using a remotely operated vehicle last month found wreckage of a jet with the same custom paint scheme in the lake close to where the radio control tower had last tracked the plane before it disappeared. Sonar images were taken of the wreck found in 200 feet of water near Juniper Island.
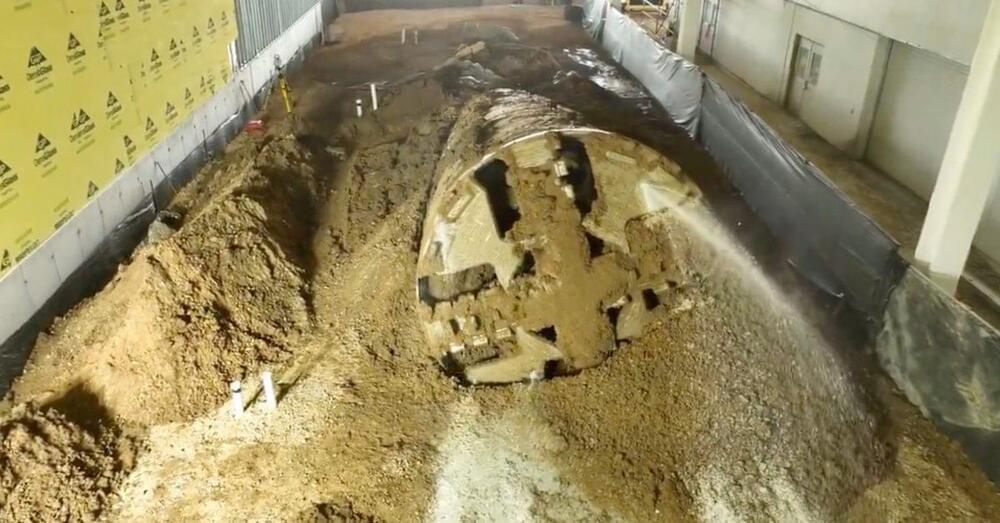
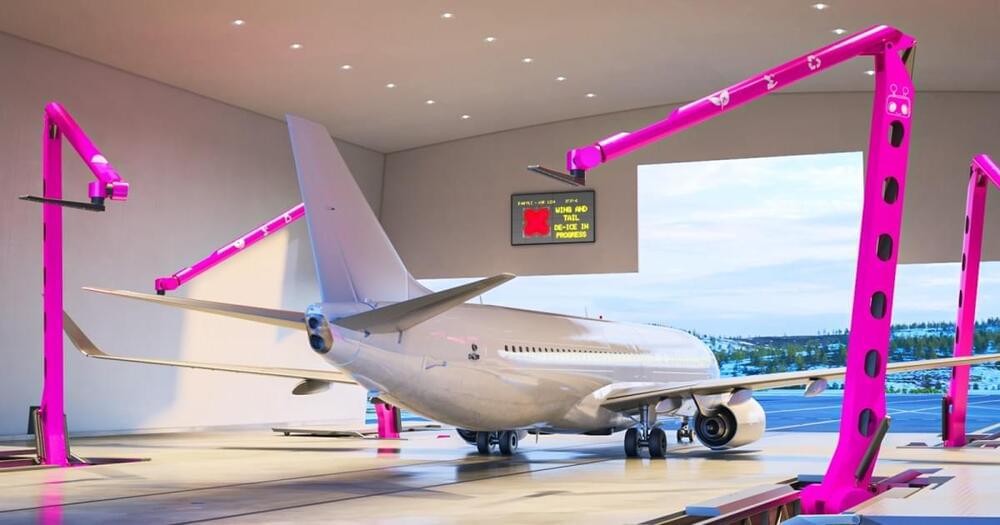


World’s largest robots will help airlines cut carbon emissions
A Norwegian startup is building massive AI robots to help airlines reduce their carbon emissions, save water, and inspect their planes in a fraction of the time it usually takes.
The challenge: The aviation industry is responsible for about 2.5% of global carbon emissions, and while sustainable jet fuels or electric propulsion systems could one day slash that figure, airlines can reduce their emissions right now — simply by cleaning their planes more often.
Washing an airplane’s exterior reduces air resistance, which means it can decrease the amount of jet fuel a plane needs to burn by up to 2% — while that’s not a huge difference, it can add up when you consider there are about 28,000 commercial jets in the global fleet.

Germany is No 1 in Europe for EV production, No 2 in the world
Germany’s automakers manufactured around 1.27 million BEVs and PHEVs in 2023, putting it at No. 2 behind China, but 2024 will be bumpy.
The German automotive industry association VDA says that 995,000 purely electric vehicles rolled off German assembly lines in 2023.
China dominates global EV production, but most of its cars are sold domestically. By contrast, 76% of German EVs are sold abroad. The US holds the spot for the world’s third-largest EV maker. And Germany, the home of key automakers such as Volkswagen, BMW, and Mercedes-Benz, leads Europe with more EVs produced than second-placed Spain (256,000) and France (225,000) combined.
Tesla’s Robotaxi Event: Potential Partnership Announcement to Boost $TSLA
Brighter with Herbert.
New method optimizes lithium extraction from seawater and groundwater
As the electric vehicle market booms, the demand for lithium—the mineral required for lithium-ion batteries—has also soared. Global lithium production has more than tripled in the last decade. But current methods of extracting lithium from rock ores or brines are slow and come with high energy demands and environmental costs. They also require sources of lithium which are incredibly concentrated to begin with and are only found in a few countries.


China’s humanoid robots to tackle tricky car chores at Dongfeng Motor
Chinese state-owned automaker Dongfeng Motor is partnering with robotics firm UBTech to introduce the latter’s humanoid into its manufacturing process.
The industrial version of the Walker S humanoid robot from Ubtech will be used on the production line of Dongfeng Motor to carry out various manufacturing duties.
According to reports, it will involve conducting safety belt inspection, door lock testing, body quality checks, oil filling, and label application. The robot will integrate with traditional automated machinery to handle complex scenarios in unmanned manufacturing.