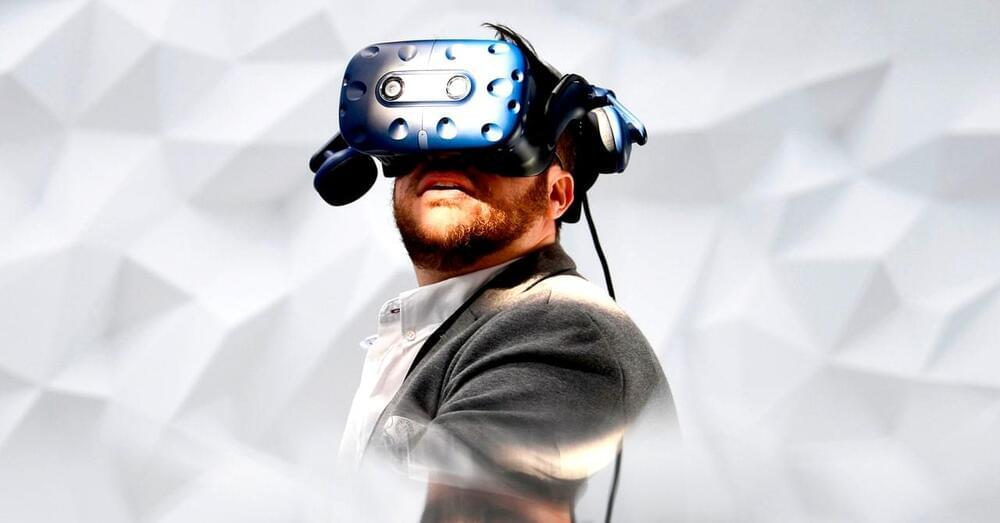
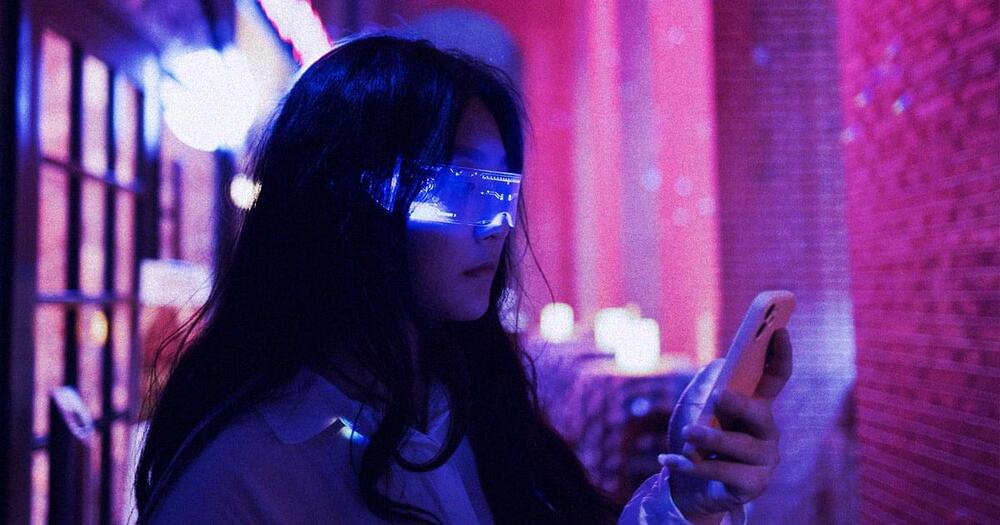
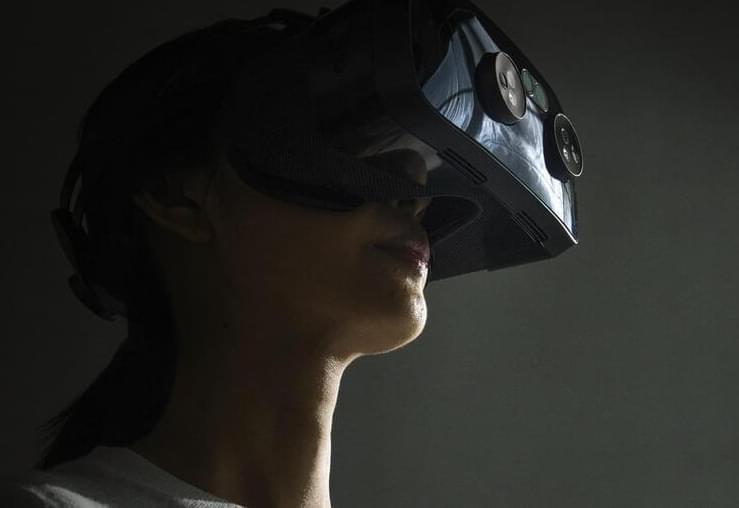
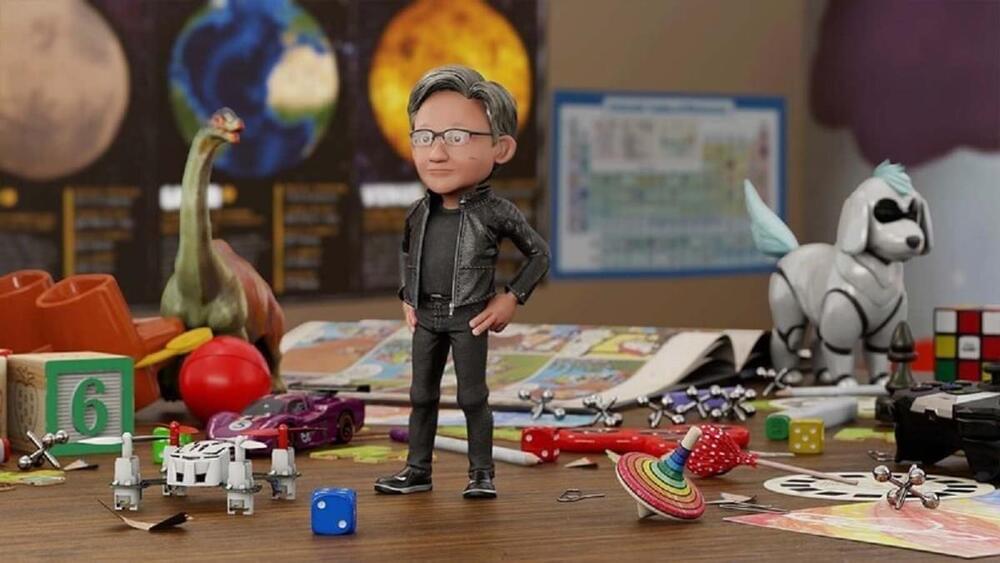
As part of its recently announced rebranding, Facebook is doubling down on its vision of the metaverse, an immersive virtual-reality environment for gaming, work meetings, and socializing. In promotional materials, Mark Zuckerberg and his friends enter the metaverse via the company’s own Oculus headsets, and are transformed into cartoon-y animated torsos, often while arranged around a virtual boardroom.
According to Zuckerberg, the metaverse promises an at-work reality better than our own, with lush backdrops and infinite personal customization (as long as that customization stops at the waist for humanoid characters). Borrowing elements from world-building games and environments like Second Life and Fortnite, and inspiration from science-fiction referents like Ready Player One and the Matrix, the insinuation is that working within the metaverse will be fun. (This despite the irony that all of these virtual worlds are positioned as dystopias by their creators.)
Full Story: