Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Aubrey de Grey — Update on Anti-Aging Research
Hangout with Aubrey de Grey live on 6pm Feb 20th AU time / 11pm Feb 19th PST time: Bring your curiosity, an open mind!
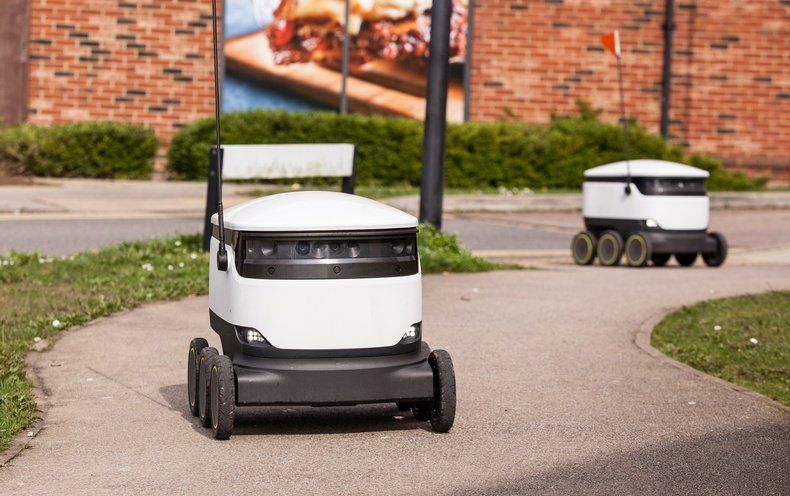

Out of the Way, Human! Delivery Robots Want a Share of Your Sidewalk
As automated delivery ramps up, cities must decide how to make the best use of public spaces.
- By Jeremy Hsu on February 19, 2019

Great white shark genome has been sequenced, revealing clues to longevity and cancer resistance
To many of us, the great white shark is a mysterious and scary creature from the deep – but now it’s a little less mysterious. A team of scientists has sequenced the entire genome of the great white shark, revealing a few clues as to how these animals are so good at healing wounds and resisting cancer.

Dozens of new Salmonella cases linked to turkey products in ongoing outbreak
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention just issued a new update to its ongoing investigation of a months-long Salmonella outbreak linked to turkey products. The update, which is the first since mid December of last year, adds over 60 new confirmed cases of Salmonella infection to the 200+ cases that were already logged.
A total of 279 cases have now been confirmed across 41 states, with over 100 hospitalized patients and one death resulting from the outbreak. Unfortunately, the bulletin brings more bad news as there’s still been no confirmed source of the Salmonella, and the investigation remains active.
Nano-droplets are the key to controlling membrane formation
Biological membranes, and man-made variants, consist of amphiphilic molecules, of which soap is an example. These molecules have a head that bonds with water, but a tail that turns away from water. You can imagine that a group of such molecules in water, preferably puts the tails together, and sticks the heads out, towards the water. Similar processes also dominate the creation of membranes. Often they are spherical, like liposomes, so you can, for example, put a medicine in it. And also the ultimate membrane, the cell wall, is constructed in a similar way.
How nano-droplets self-assemble
Until now, the formation of ‘micelles’ was considered to be the first step in membrane formation. A micelle is an extremely small spherical structure (about 100 nanometers) of amphiphilic molecules—all with the tails inwards and the heads outwards. However, researchers at Eindhoven University of Technology discovered a different beginning: the formation of nano-droplets in water with a higher concentration of amphiphilic molecules. At the interface of that drop, the amphiphilic molecules, as it were, take each others’ hands: first they form spheres, which then change into cylinders or plates, and then a closed membrane is created that encloses the nano-droplet. With this so-called ‘self-assembly’ process, the droplet has become a liposome.


Dementia eliminates the ability to daydream, sufferers are “stuck in the moment”
Daydreaming, thinking about the past, planning for the future, or just letting your mind wander off from the current moment occupies our thoughts for a large part of every day. However, a new study has revealed patients suffering from a specific kind of early-onset dementia may have completely lost the ability to do this and seem perpetually “stuck in the moment”.
Unraveling the Mystery of ‘Deadly Dreams’ Syndrome
In December 1981, the Centers for Disease Control (the name was amended to add “Prevention” in 1992) published a report detailing sudden, unexpected deaths during sleep among mostly young, male, Southeast Asian refugees in the United States. Thirty-three of those who died were from Laos, four were from Vietnam, and one was from Cambodia. “The abruptness of the deaths reported here is compatible with a cardiac dysrhythmia,” the report stated, “but the underlying mechanism remains unclear.” Proposed explanations included stress from immigration and resettlement, sleep abnormalities, undiagnosed heart defects, and dietary deficiencies, but nothing could be proven. So it began to be called sudden unexplained death syndrome, or SUDS, and was quickly recognized as a leading cause of death among young men from Southeast Asia.
What I left out is a recurring feature in which book authors are invited to share anecdotes and narratives that, for whatever reason, did not make it into their final manuscripts. In this installment, Sandeep Jauhar shares a story that didn’t make it into his latest book, “Heart: A History,” (Farrar, Straus and Giroux.)
Brugada syndrome is believed to be responsible for roughly 20 percent of deaths in patients with structurally normal hearts.