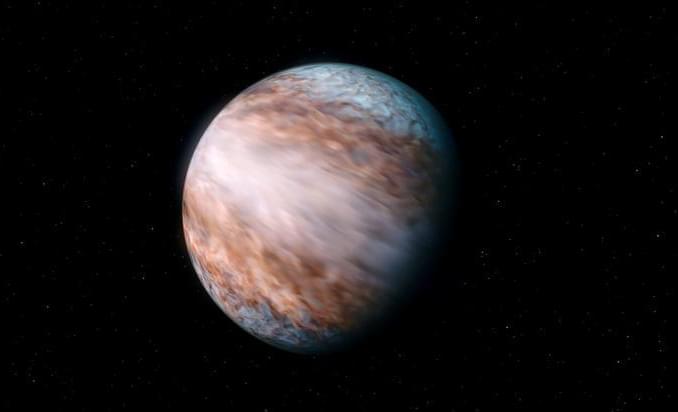
“Part of the atmosphere of this planet is moving towards us at a high velocity while another part is moving away from us at the same speed,” said Dr. Lisa Nortmann.
Do habitable exoplanets exist that possess life as we know it? Scientists have pondered this longstanding question ever since the first exoplanet was confirmed in the mid-1990s, and this will be the goal of NASA’s upcoming Pandora mission, which is due for launch in the second half of 2025. In preparation for its launch, engineers recently finished assembly of the spacecraft bus, which will house the primary systems of the spacecraft, including its power.
“This is a huge milestone for us and keeps us on track for a launch in the fall,” said Dr. Elisa Quintana, who is the principal investigator for Pandora at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, although the mission operations center for Pandora will be located at the University of Arizona (U of A) Space Institute. “The bus holds our instruments and handles navigation, data acquisition and communication with Earth – it’s the brains of the spacecraft.”
The primary science objectives for Pandora will be to analyze the atmospheres of 20 confirmed exoplanets during the science operations phase of the mission, which is slated to last approximately one year. This will be accomplished when the exoplanet passes in front of its parent star, known as a transit, resulting in light passing through the exoplanet’s atmosphere which Pandora will analyze for the presence of water, hazes, and clouds.