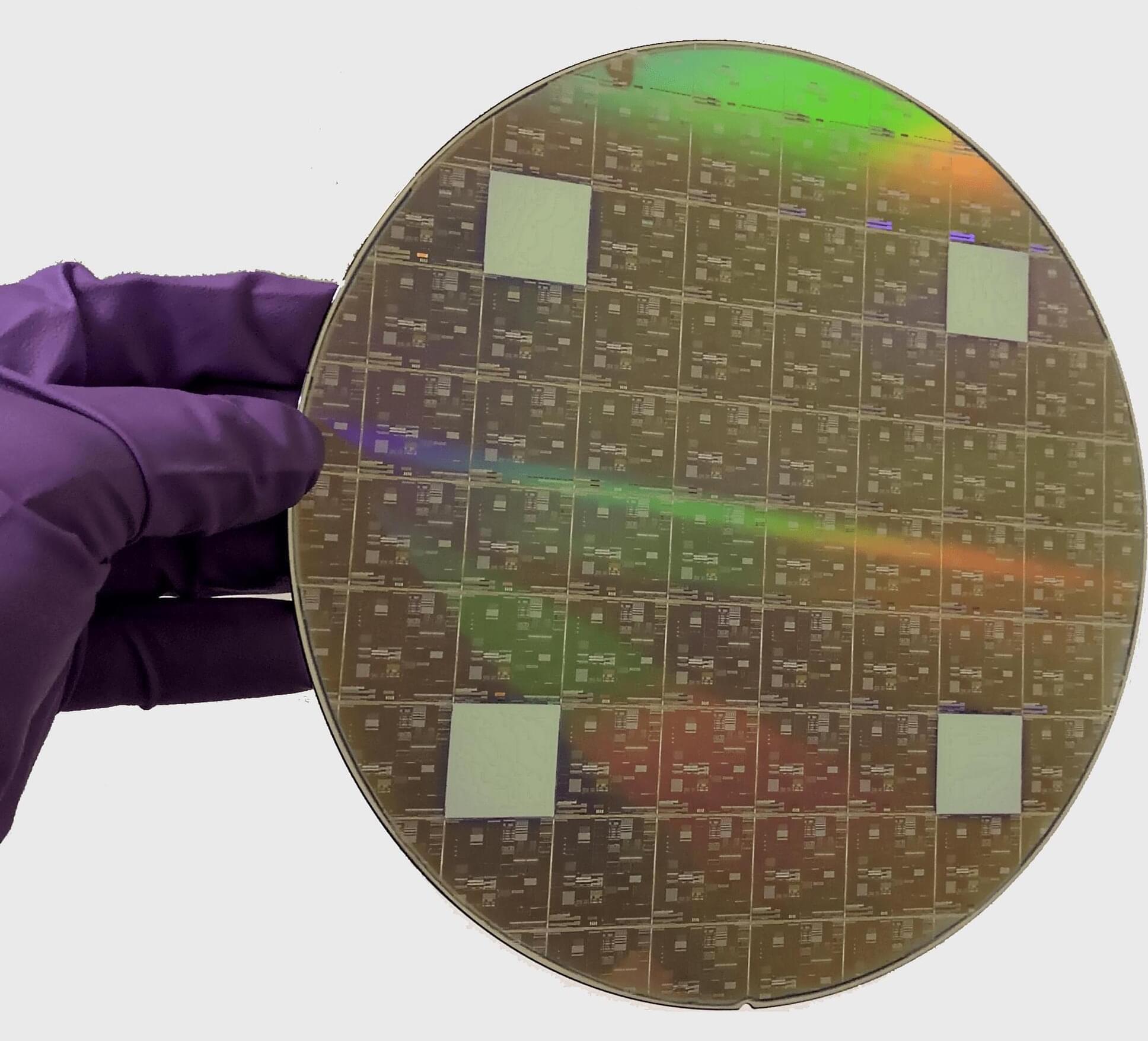
In the consumer electronics playbook, custom silicon is the final step in the marathon: you use off-the-shelf components to prove a product, achieve mass scale and only then invest in proprietary chips to create differentiation, improve operations, and optimize margins.
In the modern satellite communications (SATCOM) ecosystem, this script has been flipped. For the industry’s frontrunners, custom silicon is the starting line where the bets are high, and the rewards are even higher, not a late-stage luxury. Building custom silicon is just a small piece of the big project when it comes to launching a satellite constellation and the fact there are very limited off the shelf options.
The shift toward custom silicon is no longer a theoretical debate; it is a proven competitive requirement. To monetize the massive capital expenditure of a constellation, market leaders are already driving aggressive custom silicon programs for beamformers and modems from the very beginning. The consensus is clear: while commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) and field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) served as useful stopgaps, they have become a strategic liability that compromises price and power efficiency. If the industry is to scale to the mass market, operators must commit to bespoke silicon programs now — or risk being permanently priced out of the sky by competitors who have already optimized their hardware for the unit economics of space.