Cold smoked capelin from North Fish USA is potentially contaminated, the FDA says. Botulism attacks nerves in the body and can be fatal.


Aging is the major risk factor for the development of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, and dementia. Therefore, drugs that slow the aging process may help extend both lifespan and healthspan (the length of time that people are healthy).
In a study published online on February 29 in Medical Research Archives, Albert Einstein College of Medicine researchers evaluated U.S. Food and Drug Administration-approved drugs for their anti-aging potential. In ranking those drugs, they gave equal weight to preclinical studies (i.e., effect on rodent lifespan and healthspan) and clinical studies (i.e., reduced mortality from diseases the drugs were not intended to treat). The four therapeutics judged most promising for targeting aging were SGLT2 inhibitors, metformin, bisphosphonates, and GLP-1 receptor agonists. Since these drugs have been approved for safety and used extensively, the researchers recommend they be evaluated for their anti-aging potential in large-scale clinical trials.
The study’s corresponding author was Nir Barzilai, M.D., director of Einstein’s Institute for Aging Research, professor of medicine and of genetics and the Ingeborg and Ira Leon Rennert Chair in Aging Research at Einstein, and a member of the National Cancer Institute–designated Montefiore Einstein Comprehensive Cancer Center. The lead author was Michael Leone, a medical student at Einstein.
Ever wondered how intelligent AI could become by 2034? As we dive into this thought-provoking topic, we’ll explore the potential…
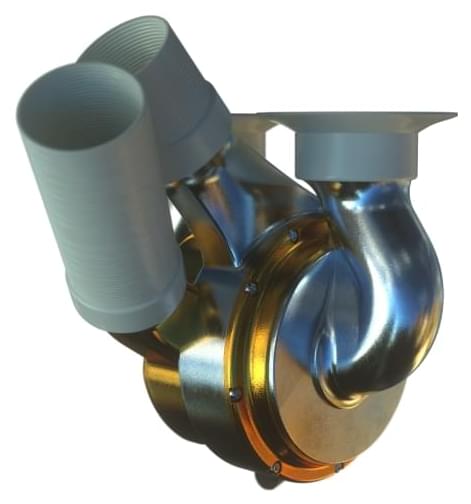

This new titanium heart has a mag lev inside to spin continuously and pump at the same rate as a normal heart.
Heart failure is a global epidemic affecting at least 26 million people worldwide, 6.2 million adults in the U.S., and is increasing in prevalence. Heart transplantations are reserved for those with severe heart failure and are limited to fewer than 6,000 procedures per year globally.
Consequently, the U.S. National Institutes of Health estimated that up to 100,000 patients could immediately benefit from mechanical circulatory support (MCS), and the European market is similarly sized. Without intervention, patients with severe HF have a bleak outlook. For these patients, drug therapy is a limited, relatively ineffective option. Although a heart transplant would meet their needs, only 6,000 donor hearts are available globally each year.
Implantation of a Total Artificial Heart (TAH) is a treatment option for patients with end-stage biventricular HF who need support while on a heart transplant waiting list. Removal of the native ventricles allows the device to completely replace the function of the native heart.
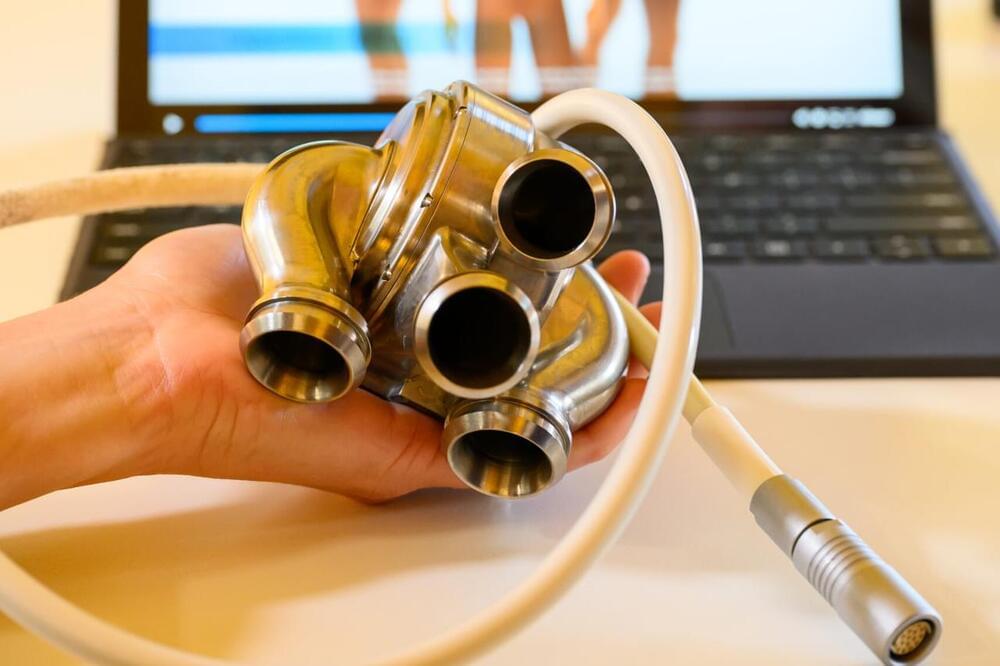

For the first time, the fully mechanical heart made by BiVACOR, which uses the same technology as high-speed rail lines, has been implanted inside a human being. The feat marks a major step in keeping people alive as they wait for heart transplants.
The total artificial heart (TAH) was implanted as part of an early feasibility study overseen by the US Food and Drug Administration. According to a statement from the Texas Heart Institute where the implantation surgery was carried out, the heart “is a titanium-constructed biventricular rotary blood pump with a single moving part that utilizes a magnetically levitated rotor that pumps the blood and replaces both ventricles of a failing heart.”
BiVACOR, which has been working on the device since 2013, says that the advantage of using a magnetically levitated rotor to drive the device’s blood-circulating function is that there is no friction, which can be such a damaging force to machinery that scientists are looking at ways to reduce its effects. The device is by no means the first artificial heart to be used – the first successful implant took place in 1969 – but it is the first to employ this novel use of maglev technology.


Researchers wish to probe whether consciousness has a basis in quantum mechanical phenomena.
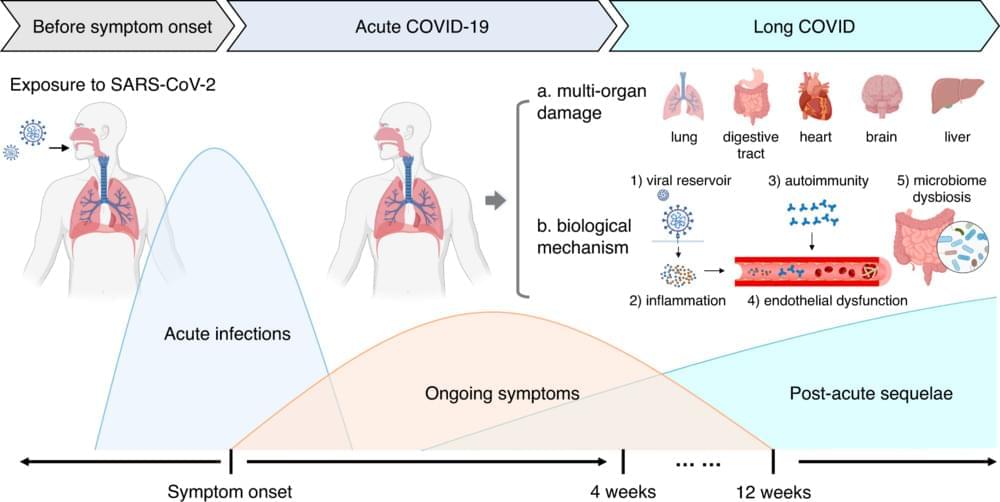
Since 2020, the condition known as long COVID-19 has become a widespread disability affecting the health and quality of life of millions of people across the globe and costing economies billions of dollars in reduced productivity of employees and an overall drop in the work force.
The intense scientific effort that long COVID sparked has resulted in more than 24,000 scientific publications, making it the most researched health condition in any four years of recorded human history.
Long COVID is a term that describes the constellation of long-term health effects caused by infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus. These range from persistent respiratory symptoms, such as shortness of breath, to debilitating fatigue or brain fog that limits people’s ability to work, and conditions such as heart failure and diabetes, which are known to last a lifetime.
In a recent study published in Science Advances, researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, used the nematode model Caenorhabditis elegans to determine whether the olfactory nervous system could non-autonomously control the mitochondrial unfolded protein response in response to cellular stress.
A critical part of maintaining a state of cellular homeostasis is coordinating responses to environmental stress across tissues. Substantial evidence now supports the fact that the central nervous system regulates stress across all tissues. Furthermore, cell non-autonomous induction of stress responses occurs in peripheral tissues when unfolded protein responses (UPR) in the mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum are activated in the neurons.
Stressed cells undergo misfolding or unfolding of proteins, and UPR transmits protein folding status information to the nucleus to enable cellular stress responses or induce apoptotic cell death. The non-autonomous control of cellular stress responses is believed to be essential for the organism to survive toxic environmental conditions.