The idea of time travel has dazzled sci-fi enthusiasts for years. Science tells us that traveling to the future is technically feasible, at least if you’re willing to go near the speed of light, but going back in time is a no-go. But what if scientists could leverage the advantages of quantum physics to uncover data about complex systems that happened in the past?
New research indicates that this premise may not be that far-fetched. In a paper published June 27, 2024, in Physical Review Letters, Kater Murch, the Charles M. Hohenberg Professor of Physics and Director of the Center for Quantum Leaps at Washington University in St. Louis, and colleagues Nicole Yunger Halpern at NIST and David Arvidsson-Shukur at the University of Cambridge demonstrate a new type of quantum sensor that leverages quantum entanglement to make time-traveling detectors.
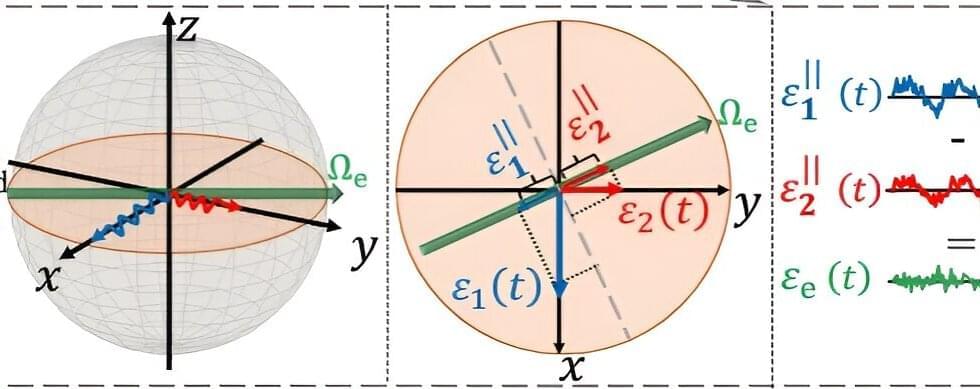
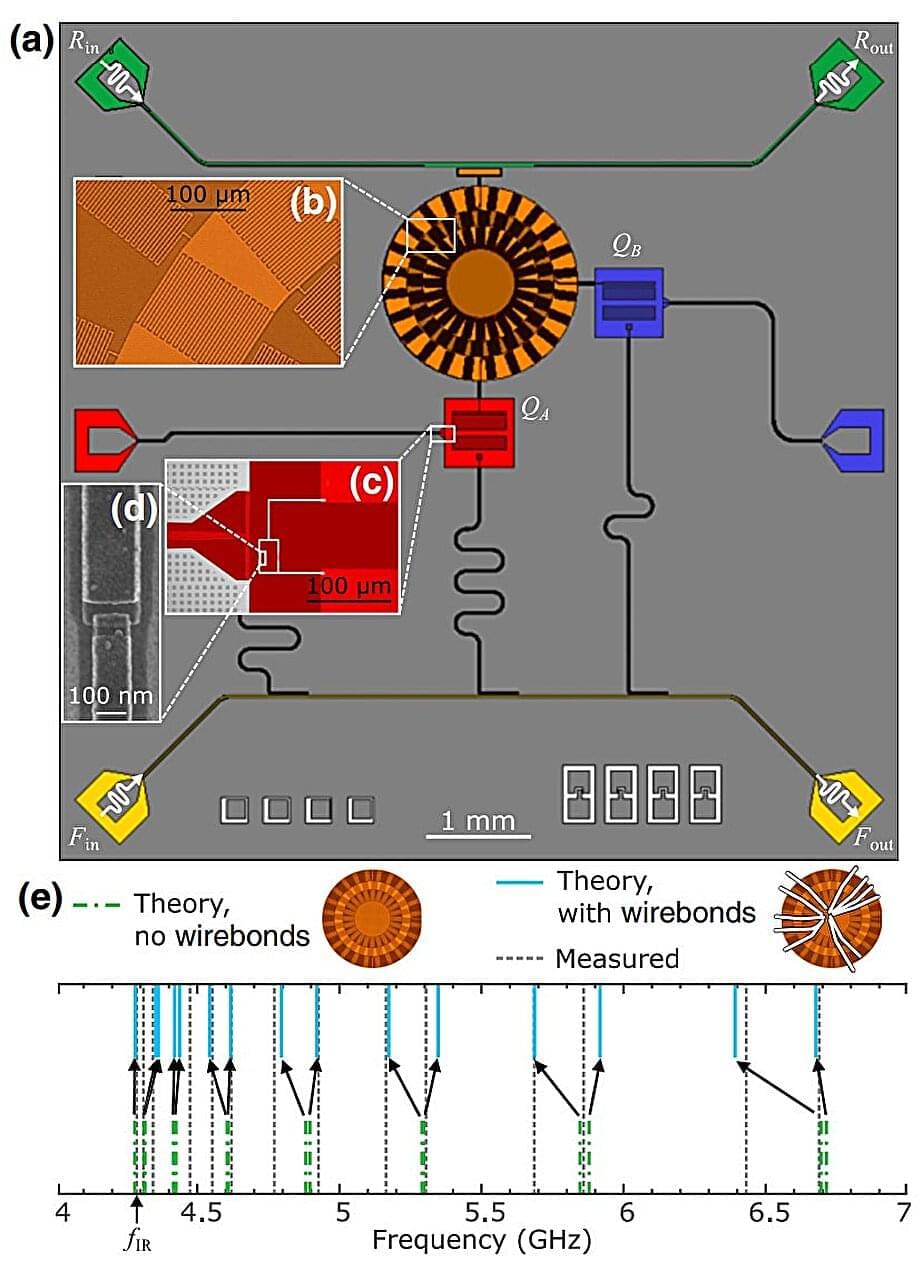
Murch describes this concept as analogous to being able to send a telescope back in time to capture a shooting star that you saw out of the corner of your eye. In the everyday world, this idea is a non-starter. But in the mysterious and enigmatic land of quantum physics, there may be a way to circumvent the rules. This is thanks to a property of entangled quantum sensors that Murch refers to as “hindsight.”